YOLO
Introduction
YOLO detection algorithm example uses images as input, performs algorithm inference using BPU, and publishes algorithm messages containing object categories and detection boxes. Currently, it supports four versions: YOLOv2、YOLOv3、Ultralytics YOLOv5、YOLOv5x、Ultralytics YOLOv8、YOLOv10、Ultralytics YOLO11、YOLO12.
Since all YOLOs after YOLOv8 are based on the Ultralytics algorithm framework, the Parser of YOLOv8 can be used. The relevant bin model can be found on GitHub⭐️ : Get it RDK_Model_Zoo.
The model is trained using the COCO dataset, and the supported object detection types include humans, animals, fruits, and vehicles, totaling 80 types.
You can also use the Ultralytics software package to train on custom datasets. (https://docs.ultralytics.com/zh/modes/train)
Code repository: (https://github.com/D-Robotics/hobot_dnn)
Use cases: As a representative algorithm in single-stage object detection, the YOLO series has the advantages of fast speed and good generalization, and can be used for garbage recognition, vehicle detection, and other functions, mainly applied in autonomous driving, smart home, and other fields.
Car Detection Example: (https://github.com/JunshengFu/vehicle-detection)
Fall Down Detection Example: (https://github.com/xiaobin1231/Fall-Detection-By-YOLOV3-and-LiteFlowNet)
Supported Platforms
| Platform | System | Supported Algorithms | Function |
|---|---|---|---|
| RDK X3, RDK X3 Module | Ubuntu 20.04 (Foxy), Ubuntu 22.04 (Humble) | yolov2/yolov3/yolov5 | · Start MIPI/USB cameras and display results through web · Use local data offline, and save results |
| RDK X5, RDK X5 Module | Ubuntu 22.04 (Humble) | yolov2/yolov3/yolov5/yolov8/yolov10/yolov11/yolov12 | · Start MIPI/USB cameras and display results through web · Use local data offline, and save results |
| RDK S100, RDK S100P | Ubuntu 22.04 (Humble) | yolov2/yolov3/yolov5/yolov8/yolov10/yolov11/yolov12 | · Start MIPI/USB cameras and display results through web · Use local data offline, and save results |
Algorithm Information
| Model Type | Platform | Input Size | Frequency (fps) |
|---|---|---|---|
| yolov2 | X3 | 1x608x608x3 | 12.60 |
| yolov3 | X3 | 1x416x416x3 | 11.71 |
| yolov5 | X3 | 1x512x512x3 | 32.62 |
| yolov2 | X5 | 1x608x608x3 | 38.33 |
| yolov3 | X5 | 1x416x416x3 | 31.28 |
| yolov5 | X5 | 1x512x512x3 | 10.37 |
| yolov8n | X5 | 1x3x640x640 | 140.46 |
| yolov10n | X5 | 1x3x640x640 | 36.47 |
| yolov11m | X5 | 1x3x640x640 | 28.95 |
| yolov12m | X5 | 1x3x640x640 | 74 |
| yolov2 | S100 | 1x3x608x608 | 226.19 |
| yolov3 | S100 | 1x3x416x416 | 212.55 |
| yolov5 | S100 | 1x3x672x672 | 62.24 |
| yolov8n | S100 | 1x3x640x640 | 506.57 |
| yolov10n | S100 | 1x3x640x640 | 494.10 |
| yolov11m | S100 | 1x3x640x640 | 162.46 |
| yolo12n | S100 | 1x3x640x640 | 42.66 |
Preparations
RDK
-
RDK has been burned with the Ubuntu 20.04/22.04 system image provided by D-Robotics.
-
RDK has successfully installed TogetheROS.Bot.
-
RDK has installed MIPI or USB cameras. If there is no camera available, the algorithm can be experienced offline by local JPEG/PNG images or MP4, H.264, and H.265 videos.
-
Confirm that the PC can access the RDK through the network.
Usage
RDK
Use MIPI Cameras to Publish Images
YOLOv2 object detection algorithm example subscribes to images published by a MIPI camera and publish algorithm msg after inference. It displays published images and corresponding results on PC browsers through the websocket package.
- Foxy
- Humble
# Configure the tros.b environment
source /opt/tros/setup.bash
# Configure the tros.b environment
source /opt/tros/humble/setup.bash
# Configuring MIPI camera
export CAM_TYPE=mipi
# Start the launch file
ros2 launch dnn_node_example dnn_node_example.launch.py dnn_example_config_file:=config/yolov2workconfig.json dnn_example_image_width:=1920 dnn_example_image_height:=1080
Use USB Camera to Publish Images
YOLOv2 object detection algorithm example subscribes to images published by a USB camera, publishes algorithm msg after inference, and displays published images and corresponding results on PC browsers through the websocket package.
- Foxy
- Humble
# Configure the tros.b environment
source /opt/tros/setup.bash
# Configure the tros.b environment
source /opt/tros/humble/setup.bash
# Configuring USB camera
export CAM_TYPE=usb
# Start the launch file
ros2 launch dnn_node_example dnn_node_example.launch.py dnn_example_config_file:=config/yolov2workconfig.json dnn_example_image_width:=1920 dnn_example_image_height:=1080
Use Local Data Offline
YOLOv2 object detection algorithm uses local JPEG/PNG images offline. After inference, the rendered images of the results are stored in the local path.
- Foxy
- Humble
# Configure the tros.b environment
source /opt/tros/setup.bash
# Configure the tros.b environment
source /opt/tros/humble/setup.bash
# Start the launch file
ros2 launch dnn_node_example dnn_node_example_feedback.launch.py dnn_example_config_file:=config/yolov2workconfig.json dnn_example_image:=config/target.jpg
In addition to the YOLOv2, YOLO series are also supported. The algorithm can be switched using the config_file parameter in the startup command. For example, to use the YOLOv3, the startup configuration should be dnn_example_config_file:="config/yolov3workconfig.json", and for the YOLOv5 algorithm, the startup configuration should be dnn_example_config_file:="config/yolov5workconfig.json", and for the YOLOv8 algorithm, the startup configuration should be dnn_example_config_file:="config/yolov8workconfig.json", and for the YOLOv10 algorithm, the startup configuration should be dnn_example_config_file:="config/yolov10workconfig.json", and for the YOLOv11 algorithm, the startup configuration should be dnn_example_config_file:="config/yolov11workconfig.json", and for the YOLOv12 algorithm, the startup configuration should be dnn_example_config_file:="config/yolov12workconfig.json".
Result Analysis
Use a Camera to Publish Images
The terminal output during execution shows the following information:
[example-3] [WARN] [1655095347.608475236] [example]: Create ai msg publisher with topic_name: hobot_dnn_detection
[example-3] [WARN] [1655095347.608640353] [example]: Create img hbmem_subscription with topic_name: /hbmem_img
[example-3] [WARN] [1655095348.709411619] [img_sub]: Sub img fps 12.95
[example-3] [WARN] [1655095348.887570945] [example]: Smart fps 12.10
[example-3] [WARN] [1655095349.772225728] [img_sub]: Sub img fps 11.30
[example-3] [WARN] [1655095349.948913662] [example]: Smart fps 11.31
[example-3] [WARN] [1655095350.834951431] [img_sub]: Sub img fps 11.30
[example-3] [WARN] [1655095351.011915729] [example]: Smart fps 11.30
The log shows that the topic for publishing the inference results is hobot_dnn_detection, and the topic for subscribing to images is /hbmem_img.
You can view the image and algorithm rendering effects by entering http://IP:8000 in the browser on the PC (where IP is the IP address of the RDK):

Use Local Data Offline
The terminal output during execution shows the following information:
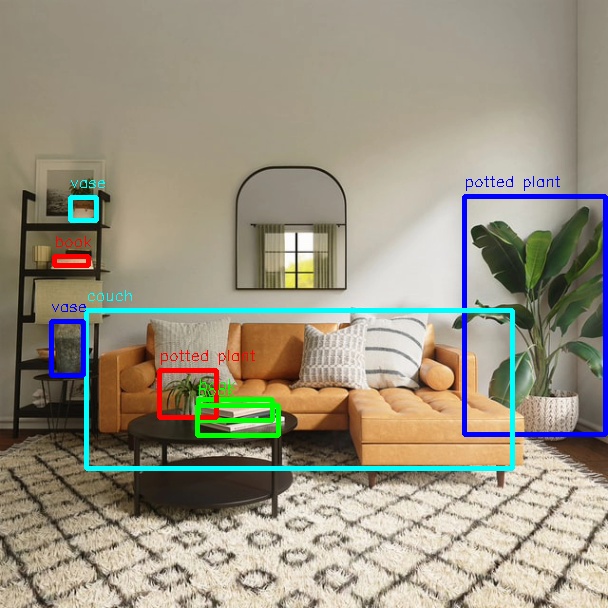
[example-1] [INFO] [1654925067.952159234] [PostProcessBase]: out box size: 8
[example-1] [INFO] [1654925067.952227232] [PostProcessBase]: det rect: 464.03 196.145 605.525 434.865, det type: potted plant, score:0.813219
[example-1] [INFO] [1654925067.952319229] [PostProcessBase]: det rect: 86.5421 310.158 512.542 468.201, det type: couch, score:0.669208
[example-1] [INFO] [1654925067.952392268] [PostProcessBase]: det rect: 198.968 399.91 273.841 421.767, det type: book, score:0.539755
[example-1] [INFO] [1654925067.952465182] [PostProcessBase]: det rect: 159.861 370.656 217.685 417.746, det type: potted plant, score:0.480698
[example-1] [INFO] [1654925067.952533221] [PostProcessBase]: det rect: 51.2147 321.047 84.0969 375.842, det type: vase, score:0.433644
[example-1] [INFO] [1654925067.952607802] [PostProcessBase]: det rect: 70.0548 197.381 96.1826 221.062, det type: vase, score:0.399885
[example-1] [INFO] [1654925067.952675924] [PostProcessBase]: det rect: 197.706 405.271 278.929 435.743, det type: book, score:0.384268
[example-1] [INFO] [1654925067.952743463] [PostProcessBase]: det rect: 54.0955 256.68 88.6269 266.159, det type: book, score:0.307426
The log shows that the algorithm infers 8 targets from the input image and outputs the coordinates of the object detection boxes (the order of the coordinates is the top-left x and y coordinates and the bottom-right x and y coordinates of the bounding box) and the object categories. The rendered image file is saved as render_feedback_0_0.jpeg, and the rendering effect is shown below: