5.2.1 Image Capture
USB camera
Introduction
In order to achieve environmental perception capability, robot products usually carry cameras to obtain image information. USB cameras are easy to obtain, easy to use, and have good versatility. TogetheROS.Bot supports USB cameras and supports ROS2 standard image messages.
Code repository: (https://github.com/D-Robotics/hobot_usb_cam.git)
Supported Platforms
| Platform | Operating Mode |
|---|---|
| RDK X3, RDK X3 Module | Ubuntu 20.04 (Foxy), Ubuntu 22.04 (Humble) |
| RDK X5, RDK X5 Module | Ubuntu 22.04 (Humble) |
| RDK S100, RDK S100P | Ubuntu 22.04 (Humble) |
| RDK X5, RDK X5 Module | Ubuntu 22.04 (Humble) |
| RDK S100, RDK S100P | Ubuntu 22.04 (Humble) |
| RDK Ultra | Ubuntu 20.04 (Foxy) |
| X86 | Ubuntu 20.04 (Foxy) |
Preparation
RDK
-
Confirm that the USB camera is working properly and connect it to the USB slot of the RDK.
-
RDK has burned the Ubuntu 20.04/22.04 system image provided by D-Robotics.
-
RDK has successfully installed tros.b.
-
Confirm that the PC can access the RDK via the network.
How to Use (default usb_pixel_format is mjpeg)
Taking RDK as an example:
-
Log in to the RDK via SSH and confirm the device name of the USB camera. Here, let's take
/dev/video8as an example. -
Start the USB camera using the following command:
- Foxy
- Humble
# Configure the tros.b environment
source /opt/tros/setup.bash# Configure the tros.b environment
source /opt/tros/humble/setup.bash# Start the launch file
ros2 launch hobot_usb_cam hobot_usb_cam.launch.py usb_video_device:=/dev/video8 -
If the program outputs the following information, it means the node has been successfully launched.
[INFO] [launch]: All log files can be found below /root/.ros/log/2024-01-18-19-44-39-419588-ubuntu-3951
[INFO] [launch]: Default logging verbosity is set to INFO
[INFO] [hobot_usb_cam-1]: process started with pid [3953]
[hobot_usb_cam-1] [WARN] [1705578280.808870437] [hobot_usb_cam]: framerate: 30
[hobot_usb_cam-1] [WARN] [1705578280.809851560] [hobot_usb_cam]: pixel_format_name: mjpeg
[hobot_usb_cam-1] [WARN] [1705578280.936383062] [hobot_usb_cam]: Camera calibration file: [/opt/tros/lib/hobot_usb_cam/config/usb_camera_calibration.yaml] does not exist!
[hobot_usb_cam-1] If you need calibration msg, please make sure the calibration file path is correct and the calibration file exists!
[hobot_usb_cam-1] [WARN] [1705578280.936697507] [hobot_usb_cam]: This devices supproted formats:
[hobot_usb_cam-1] [WARN] [1705578280.936858791] [hobot_usb_cam]: Motion-JPEG: 640 x 480 (30 Hz)
[hobot_usb_cam-1] [WARN] [1705578280.936912830] [hobot_usb_cam]: Motion-JPEG: 1920 x 1080 (30 Hz)
[hobot_usb_cam-1] [WARN] [1705578280.936960328] [hobot_usb_cam]: Motion-JPEG: 320 x 240 (30 Hz)
[hobot_usb_cam-1] [WARN] [1705578280.937007285] [hobot_usb_cam]: Motion-JPEG: 800 x 600 (30 Hz)
[hobot_usb_cam-1] [WARN] [1705578280.937053241] [hobot_usb_cam]: Motion-JPEG: 1280 x 720 (30 Hz)
[hobot_usb_cam-1] [WARN] [1705578280.937098906] [hobot_usb_cam]: Motion-JPEG: 1024 x 576 (30 Hz)
[hobot_usb_cam-1] [WARN] [1705578280.937144528] [hobot_usb_cam]: YUYV 4:2:2: 640 x 480 (30 Hz)
[hobot_usb_cam-1] [WARN] [1705578280.937190068] [hobot_usb_cam]: YUYV 4:2:2: 1920 x 1080 (5 Hz)
[hobot_usb_cam-1] [WARN] [1705578280.937235858] [hobot_usb_cam]: YUYV 4:2:2: 320 x 240 (30 Hz)
[hobot_usb_cam-1] [WARN] [1705578280.937282064] [hobot_usb_cam]: YUYV 4:2:2: 800 x 600 (20 Hz)
[hobot_usb_cam-1] [WARN] [1705578280.937328020] [hobot_usb_cam]: YUYV 4:2:2: 1280 x 720 (10 Hz)
[hobot_usb_cam-1] [WARN] [1705578280.937373518] [hobot_usb_cam]: YUYV 4:2:2: 1024 x 576 (15 Hz) -
Open another terminal to view the USB camera image on the web page:
- Foxy
- Humble
# Configure the tros.b environment
source /opt/tros/setup.bash# Configure the tros.b environment
source /opt/tros/humble/setup.bashros2 launch websocket websocket.launch.py websocket_image_topic:=/image websocket_only_show_image:=true -
Open a web browser (Chrome/Firefox/Edge) on your PC and enter
http://IP:8000(where IP is the RDK IP address). Click on the upper left corner to view the real-time image from the USB camera.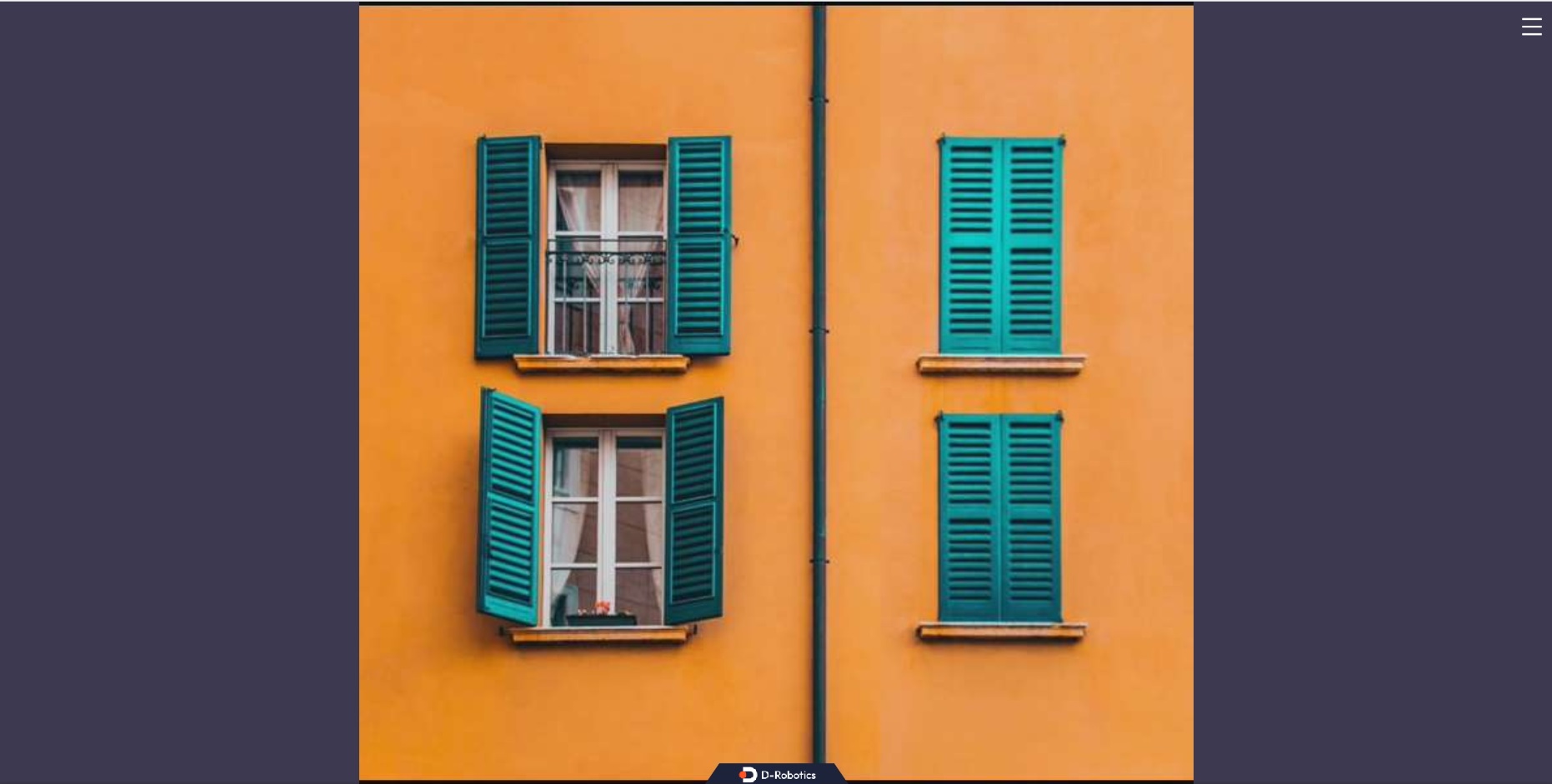
Usage Method 2 (usb_pixel_format is yuyv2rgb)
Here is an example using the RDK platform:
-
SSH into the RDK and confirm the USB camera device name, for example
/dev/video8. -
Start the USB camera using the following command:
- Foxy
- Humble
# Configure the tros.b environment
source /opt/tros/setup.bash# Configure the tros.b environment
source /opt/tros/humble/setup.bashros2 launch hobot_usb_cam hobot_usb_cam.launch.py usb_video_device:=/dev/video8 usb_pixel_format:=yuyv2rgb usb_image_width:=640 usb_image_height:=480 -
If the following information is outputted by the program, it indicates that the node has been successfully launched
[INFO] [launch]: All log files can be found below /root/.ros/log/2024-01-18-19-44-39-419588-ubuntu-3951
[INFO] [launch]: Default logging verbosity is set to INFO
[INFO] [hobot_usb_cam-1]: process started with pid [3953]
[hobot_usb_cam-1] [WARN] [1705578280.808870437] [hobot_usb_cam]: framerate: 30
[hobot_usb_cam-1] [WARN] [1705578280.809851560] [hobot_usb_cam]: pixel_format_name: yuyv2rgb
[hobot_usb_cam-1] [WARN] [1705578280.936383062] [hobot_usb_cam]: Camera calibration file: [/opt/tros/lib/hobot_usb_cam/config/usb_camera_calibration.yaml] does not exist!
[hobot_usb_cam-1] If you need calibration msg, please make sure the calibration file path is correct and the calibration file exists!
[hobot_usb_cam-1] [WARN] [1705578280.936697507] [hobot_usb_cam]: This devices supproted formats:
[hobot_usb_cam-1] [WARN] [1705578280.936858791] [hobot_usb_cam]: Motion-JPEG: 640 x 480 (30 Hz)
[hobot_usb_cam-1] [WARN] [1705578280.936912830] [hobot_usb_cam]: Motion-JPEG: 1920 x 1080 (30 Hz)
[hobot_usb_cam-1] [WARN] [1705578280.936960328] [hobot_usb_cam]: Motion-JPEG: 320 x 240 (30 Hz)
[hobot_usb_cam-1] [WARN] [1705578280.937007285] [hobot_usb_cam]: Motion-JPEG: 800 x 600 (30 Hz)
[hobot_usb_cam-1] [WARN] [1705578280.937053241] [hobot_usb_cam]: Motion-JPEG: 1280 x 720 (30 Hz)
[hobot_usb_cam-1] [WARN] [1705578280.9379806] [hobot_usb_cam]: Motion-JPEG: 1024 x 576 (30 Hz)
[hobot_usb_cam-1] [WARN] [1705578280.937144528] [hobot_usb_cam]: YUYV 4:2:2: 640 x 480 (30 Hz)
[hobot_usb_cam-1] [WARN] [1705578280.937190068] [hobot_usb_cam]: YUYV 4:2:2: 1920 x 1080 (5 Hz)
[hobot_usb_cam-1] [WARN] [1705578280.937235858] [hobot_usb_cam]: YUYV 4:2:2: 320 x 240 (30 Hz)
[hobot_usb_cam-1] [WARN] [1705578280.937282064] [hobot_usb_cam]: YUYV 4:2:2: 800 x 600 (20 Hz)
[hobot_usb_cam-1] [WARN] [1705578280.937328020] [hobot_usb_cam]: YUYV 4:2:2: 1280 x 720 (10 Hz)
[hobot_usb_cam-1] [WARN] [1705578280.937373518] [hobot_usb_cam]: YUYV 4:2:2: 1024 x 576 (15 Hz) -
Encode to mjpeg with hobot codec
- Foxy
- Humble
# Configure the tros.b environment
source /opt/tros/setup.bash# Configure the tros.b environment
source /opt/tros/humble/setup.bash# Start the launch file
ros2 launch hobot_codec hobot_codec_encode.launch.py codec_in_mode:=ros codec_in_format:=rgb8 codec_out_mode:=ros codec_sub_topic:=/image codec_pub_topic:=/image_mjpeg -
View the USB camera image on the web side, open a new terminal:
- Foxy
- Humble
# Configure the tros.b environment
source /opt/tros/setup.bash# Configure the tros.b environment
source /opt/tros/humble/setup.bashros2 launch websocket websocket.launch.py websocket_image_topic:=/image_mjpeg websocket_only_show_image:=true -
Open a browser on your PC (chrome/firefox/edge) and enter
http://IP:8000(IP is the RDK IP address), click on the top left to display the web side to view the real-time image from the USB camera
Notes
-
USB cameras need to be calibrated and the camera calibration file path needs to be set in order to publish camera parameters. However, this does not affect other functionalities.
-
To set the camera calibration file path, follow the steps below:
- Foxy
- Humble
# Configure the tros.b environment
source /opt/tros/setup.bash# Configure the tros.b environment
source /opt/tros/humble/setup.bash# Start with launch command
ros2 launch hobot_usb_cam hobot_usb_cam.launch.py usb_camera_calibration_file_path:=(actual calibration file absolute path) -
Changes to the pixel_format configuration:
hobot_usb_cam supports the following configurations: "mjpeg","mjpeg2rgb","rgb8","yuyv","yuyv2rgb","uyvy","uyvy2rgb","m4202rgb","mono8","mono16","y102mono8"
Start usb camera with the default parameters of the first type to query the formats supported by the device hardware, as shown in the log below:
[hobot_usb_cam-1] [WARN] [1705548544.174669672] [hobot_usb_cam]: This devices supproted formats:
[hobot_usb_cam-1] [WARN] [1705548544.174844917] [hobot_usb_cam]: Motion-JPEG: 640 x 480 (30 Hz)
[hobot_usb_cam-1] [WARN] [1705548544.174903166] [hobot_usb_cam]: Motion-JPEG: 1920 x 1080 (30 Hz)
[hobot_usb_cam-1] [WARN] [1705548544.174950581] [hobot_usb_cam]: Motion-JPEG: 320 x 240 (30 Hz)
[hobot_usb_cam-1] [WARN] [1705548544.174996788] [hobot_usb_cam]: Motion-JPEG: 800 x 600 (30 Hz)
[hobot_usb_cam-1] [WARN] [1705548544.175043412] [hobot_usb_cam]: Motion-JPEG: 1280 x 720 (30 Hz)
[hobot_usb_cam-1] [WARN] [1705548544.175089161] [hobot_usb_cam]: Motion-JPEG: 1024 x 576 (30 Hz)
[hobot_usb_cam-1] [WARN] [1705548544.175135035] [hobot_usb_cam]: YUYV 4:2:2: 640 x 480 (30 Hz)
[hobot_usb_cam-1] [WARN] [1705548544.175180325] [hobot_usb_cam]: YUYV 4:2:2: 1920 x 1080 (5 Hz)
[hobot_usb_cam-1] [WARN] [1705548544.175226449] [hobot_usb_cam]: YUYV 4:2:2: 320 x 240 (30 Hz)
[hobot_usb_cam-1] [WARN] [1705548544.175272365] [hobot_usb_cam]: YUYV 4:2:2: 800 x 600 (20 Hz)
[hobot_usb_cam-1] [WARN] [1705548544.175318697] [hobot_usb_cam]: YUYV 4:2:2: 1280 x 720 (10 Hz)
[hobot_usb_cam-1] [WARN] [1705548544.175365195] [hobot_usb_cam]: YUYV 4:2:2: 1024 x 576 (15 Hz)a. Query the image formats supported by the usb camera, as shown in the log above. The log shows support for mjpeg and YUYV.
b. Only "mjpeg", "mjpeg2rgb", "yuyv", and "yuyv2rgb" can be set; otherwise, the hobot_usb_cam program will exit.
MIPI camera
Introduction
To achieve environmental perception capabilities, robots often carry cameras, ToF, and other types of sensors. In order to reduce the cost of sensor adaptation and usage for users, TogetheROS.Bot wraps multiple commonly used sensors into the hobot_sensor module and abstracts them into ROS standard image messages. When the configured sensor parameters do not match the connected camera, the program will automatically adapt to the correct sensor type. The currently supported MIPI sensor types are as follows:
| Index | Name | Representational Image | Parameters | support platform | Reference Link |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | F37 | 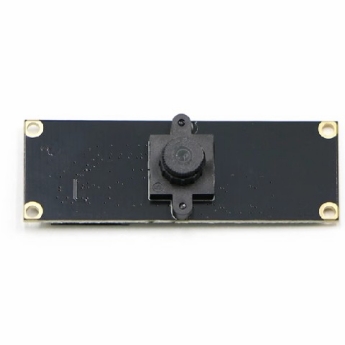 | 200W Pixel | RDK X3, RDK X3 Module | F37 |
| 2 | GC4663 |  | 400W Pixel | RDK X3, RDK X3 Module | GC4663 |
| 3 | IMX219 |  | 800W Pixel | RDK X3, RDK X3 Module, RDK Ultra, RDK X5 | IMX219 |
| 4 | IMX477 |  | 200W Pixel | RDK X3, RDK X3 Module | IMX477 |
| 5 | OV5647 |  | 200W Pixel | RDK X3, RDK X3 Module, RDK X5 | OV5647 |
| 6 | IMX415 |  | 200W Pixel | RDK X5 | IMX415 |
Code repository: (https://github.com/D-Robotics/hobot_mipi_cam.git)
Supported Platforms
| Platform | System | Function |
|---|---|---|
| RDK X3, RDK X3 Module, RDK X5 | Ubuntu 20.04 (Foxy), Ubuntu 22.04 (Humble) | Start MIPI camera and display images through Web |
Preparation
RDK
-
Confirm that the camera is correctly connected to RDK.
For example F37 connection RDK X3:
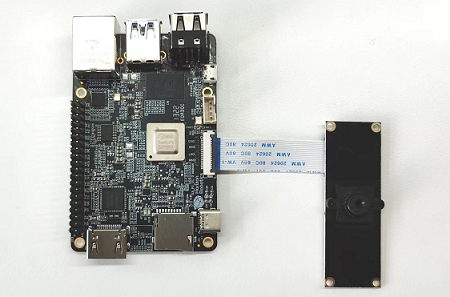
For example imx219 connection RDK S100:

-
RDK is flashed with the Ubuntu 20.04/22.04 system image provided by D-Robotics
-
RDK has successfully installed tros.b
-
Confirm that the PC can access RDK through the network
Usage
RDK Platform
Introduce the method of acquiring and previewing images:
-
SSH into RDK.
-
Start the
hobot_sensornode with the following command:- Foxy
- Humble
# Configure the tros.b environment
source /opt/tros/setup.bash# Configure the tros.b environment
source /opt/tros/humble/setup.bash# Start the launch file
ros2 launch mipi_cam mipi_cam.launch.py -
If the following information is outputted, it means that the node has been successfully started:
[INFO] [launch]: All log files can be found below /root/.ros/log/2022-06-11-15-16-13-641715-ubuntu-8852
[INFO] [launch]: Default logging verbosity is set to INFO
[INFO] [mipi_cam-1]: process started with pid [8854]
... -
To view the camera image on the web, as raw data needs to be encoded into JPEG images, two terminals need to be launched separately: one for subscribing to MIPI data and encoding it into JPEG, and one for publishing with a webservice.
- Foxy
- Humble
# Configure the tros.b environment
source /opt/tros/setup.bash# Configure the tros.b environment
source /opt/tros/humble/setup.bash# Start encoding
ros2 launch hobot_codec hobot_codec_encode.launch.py
# Launch another terminal,and configure the tros.b environment
# Start websocket
ros2 launch websocket websocket.launch.py websocket_image_topic:=/image_jpeg websocket_only_show_image:=true -
Open a web browser on the PC (Chrome/Firefox/Edge) and enter
http://IP:8000(IP address of the RDK) to see the real-time display of the camera's output.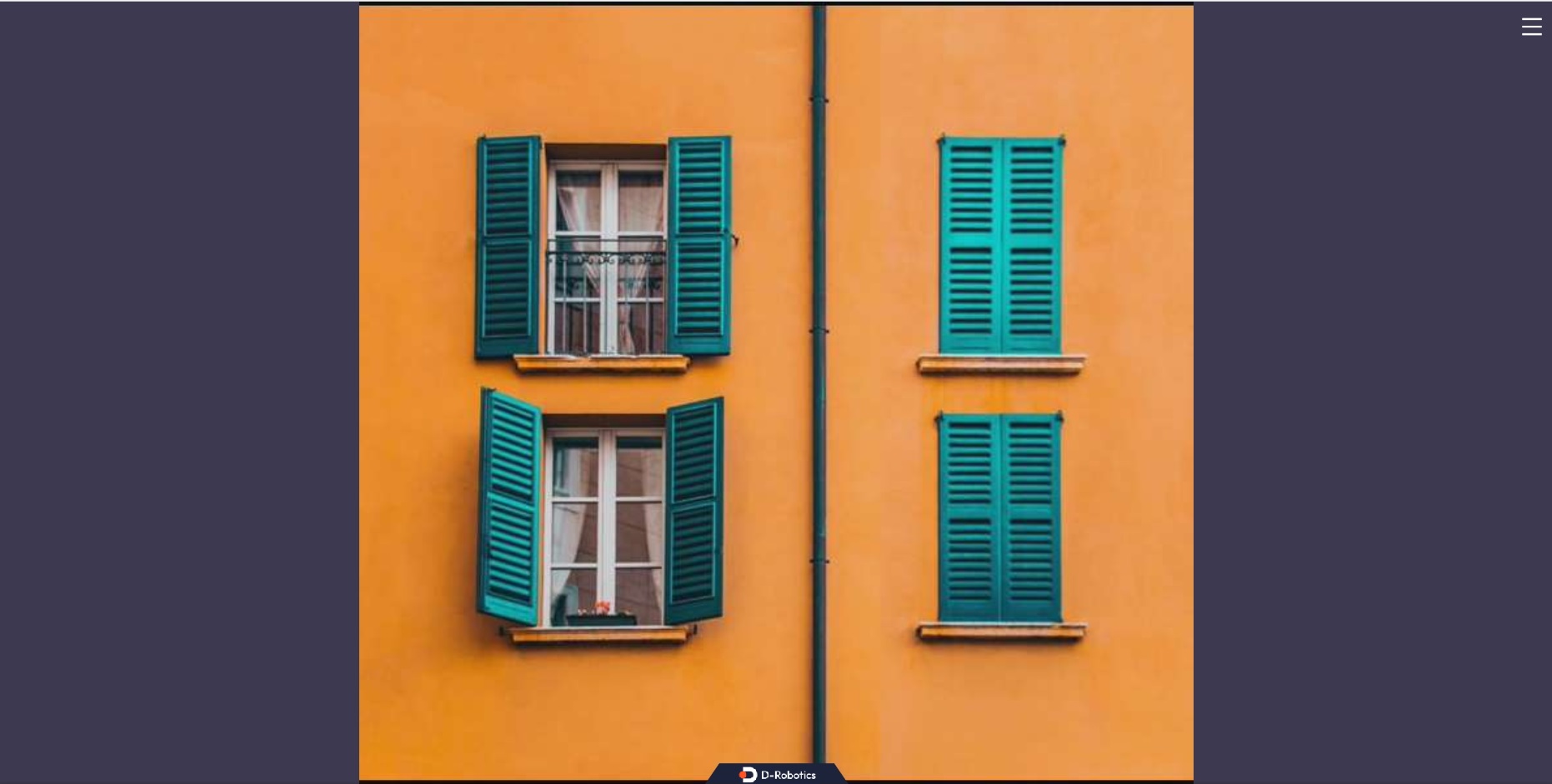
-
To query the camera's intrinsic parameters on the PC (the specific data may vary depending on the calibrated camera file), use the following command and view the results:
- Foxy
- Humble
root@ubuntu:~# source /opt/ros/foxy/setup.bashroot@ubuntu:~# source /opt/ros/humble/setup.bashroot@ubuntu:~# ros2 topic echo /camera_info
header:
stamp:
sec: 1662013622
nanosec: 672922214
frame_id: default_cam
height: 1080
width: 1920
distortion_model: plumb_bob
d:
- 0.169978
- -0.697303
- -0.002944
- -0.004961
- 0.0
k:
- 1726.597634
- 0.0
- 904.979671
- 0.0
- 1737.359551
- 529.123375
- 0.0
- 0.0
- 1.0
r:
- 1.0
- 0.0- 0.0
- 0.0
- 1.0
- 0.0
- 0.0
- 0.0
- 1.0
p:
- 1685.497559
- 0.0
- 881.6396
- 0.0
- 0.0
- 1756.460205
- 526.781147
- 0.0
- 0.0
- 0.0
- 1.0
- 0.0
binning_x: 0
binning_y: 0
roi:
x_offset: 0
y_offset: 0
height: 0
width: 0
do_rectify: false
Caution
-
mipi_cam provides the calibration files for two types of cameras, F37 and GC4663. By default, it reads the calibration file for F37,
F37_calibration.yaml. If you want to use GC4663, please change the path to the camera calibration file accordingly, as below:- Foxy
- Humble
# Configure the tros.b environment
source /opt/tros/setup.bash# Configure the tros.b environment
source /opt/tros/humble/setup.bash# Start the launch file
ros2 launch mipi_cam mipi_cam.launch.py mipi_video_device:=GC4663 mipi_camera_calibration_file_path:=/opt/tros/${TROS_DISTRO}/lib/mipi_cam/config/GC4663_calibration.yaml -
Caution when plugging/unplugging the camera:
NEVER plug or unplug the camera module without powering off the development board first. Otherwise, it may result in damaging the camera module.
-
If you encounter any issues with the startup of the hobot_sensor node, you can troubleshoot the problems by following these steps:
- Check the hardware connections.
- Make sure you have set up the tros.b environment.
- Verify the parameters are correct, for more details refer to the Hobot_Sensors README.md file.
-
Due to image conflicts caused by two image streams sending images to the same topic simultaneously, the topic needs to be remapped when starting the second image stream, and an instruction to start the second camera (only for X5 and S100):
- Foxy
- Humble
# Configure the tros.b environment
source /opt/tros/setup.bash# Configure the tros.b environment
source /opt/tros/humble/setup.bash# run mode
ros2 run mipi_cam mipi_cam --ros-args --remap /image_raw:=/image_raw_alias
# launch mode
ros2 launch mipi_cam mipi_cam_topic_remap.launch.py
Dual MIPI camera
Introduction
To achieve environmental perception capabilities, robots often carry stereo cameras, ToF, and other types of sensors. In order to reduce the cost of sensor adaptation and usage for users, TogetheROS.Bot wraps multiple commonly used sensors into the hobot_sensor module and abstracts them into ROS standard image messages. When the configured sensor parameters do not match the connected camera, the program will automatically adapt to the correct sensor type. The currently supported MIPI sensor types are as follows:
| Type | Model | Specifications | Supported Platforms |
|---|---|---|---|
| Camera | SC230ai | 200W | RDK X5 |
Code repository: (https://github.com/D-Robotics/hobot_mipi_cam.git)
Supported Platforms
| Platform | System | Function |
|---|---|---|
| RDK X5 | Ubuntu 22.04 (Humble) | Start MIPI camera and display images through Web |
Preparation
RDK
-
Confirm that the camera is correctly connected to RDK.
For example, the connection between the dual camera and RDK X5 is shown in the following figure:
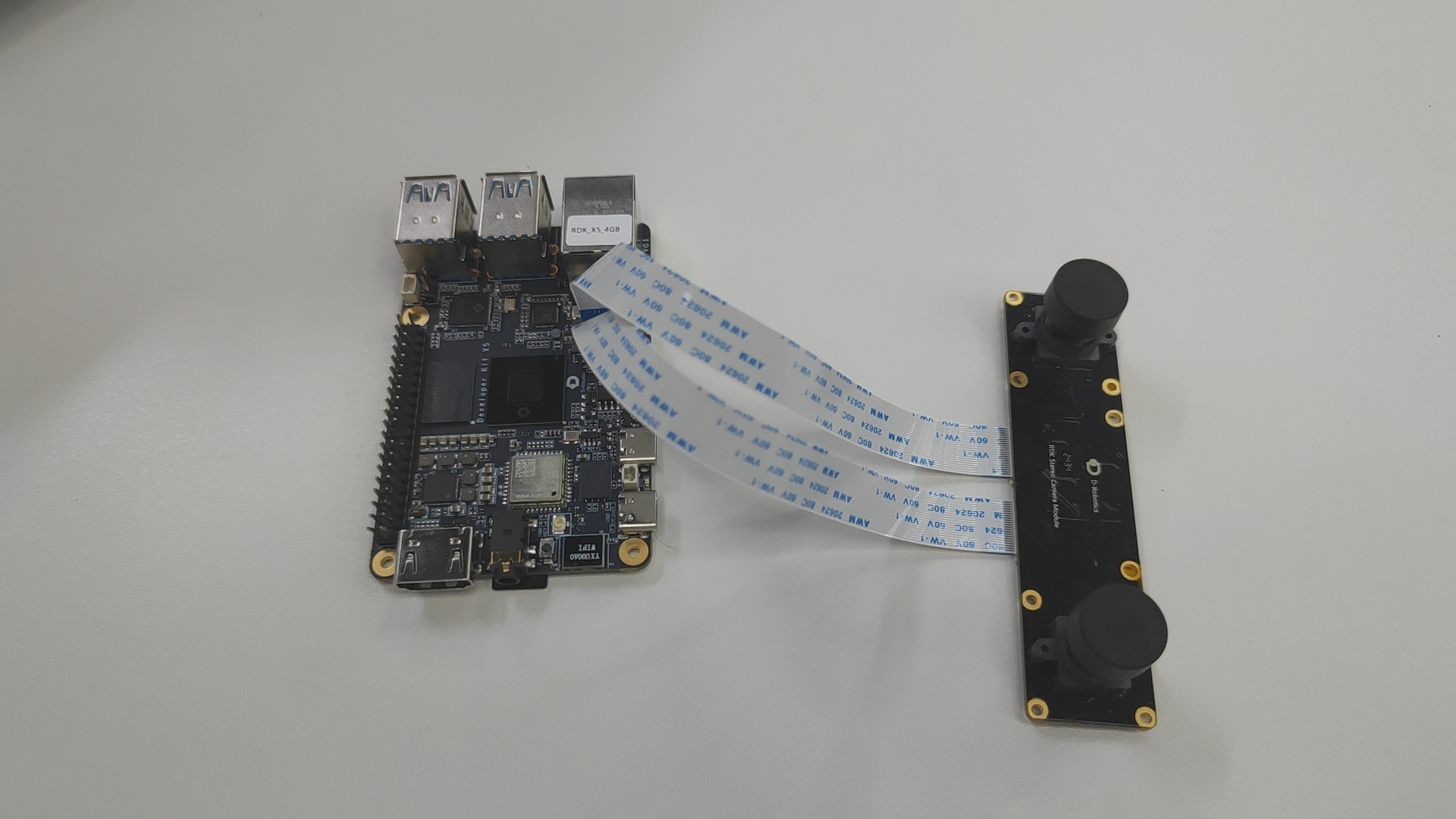
For example, the sc230ai connection between the dual camera and RDK S100 is shown in the following figure:
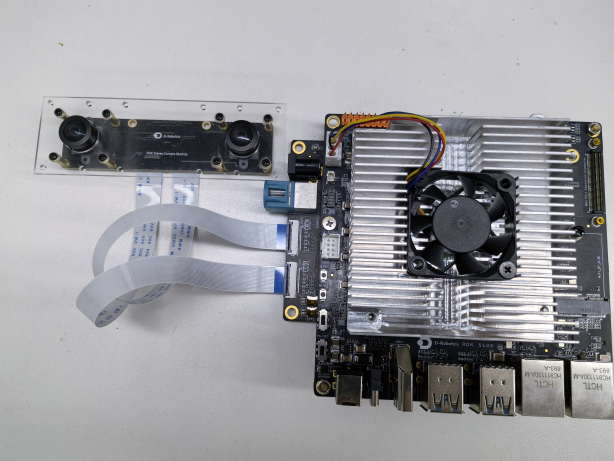
-
RDK is flashed with the Ubuntu 22.04 system image provided by D-Robotics
-
RDK has successfully installed tros.b
-
Confirm that the PC can access RDK through the network
Usage
RDK Platform
Take the SC230ai as an example to introduce the method of acquiring and previewing images:
-
SSH into RDK and determine the camera model, take
SC230aias an example. -
Start the
hobot_sensornode with the following command:- Humble
# Configure the tros.b environment
source /opt/tros/humble/setup.bash# Start the launch file
ros2 launch mipi_cam mipi_cam_dual_channel.launch.py -
If the following information is outputted, it means that the node has been successfully started:
[INFO] [launch]: All log files can be found below /root/.ros/log/2024-09-18-19-15-26-160110-ubuntu-3931
[INFO] [launch]: Default logging verbosity is set to INFO
config_file_path is /opt/tros/humble/lib/mipi_cam/config/
Hobot shm pkg enables zero-copy with fastrtps profiles file: /opt/tros/humble/lib/hobot_shm/config/shm_fastdds.xml
Hobot shm pkg sets RMW_FASTRTPS_USE_QOS_FROM_XML: 1
env of RMW_FASTRTPS_USE_QOS_FROM_XML is 1 , ignore env setting
[INFO] [mipi_cam-1]: process started with pid [3932]
[mipi_cam-1] [WARN] [1726658126.449994704] [mipi_node]: frame_ts_type value: sensor
[mipi_cam-1] [ERROR] [1726658126.455022356] [mipi_factory]: This is't support device type(), start defaule capture.
[mipi_cam-1]
[mipi_cam-1] [WARN] [1726658126.456074125] [mipi_cam]: this board support mipi:
[mipi_cam-1] [WARN] [1726658126.456274529] [mipi_cam]: host 0
[mipi_cam-1] [WARN] [1726658126.456333567] [mipi_cam]: host 2
[mipi_cam-1] [WARN] [1726658128.722451045] [mipi_cam]: [init]->cap default init success.
[mipi_cam-1]
... -
To view the dual camera image on the web, as raw data needs to be encoded into JPEG images, need to be coded Jpeg image node, and one for publishing with a webservice node.
- Humble
# Configure the tros.b environment
source /opt/tros/humble/setup.bash# Start the launch file
ros2 launch mipi_cam mipi_cam_dual_channel_websocket.launch.py -
Open a web browser on the PC (Chrome/Firefox/Edge) and enter
http://IP:8000(IP address of the RDK) to see the real-time display of the dual camera's output.
Caution
-
Caution when plugging/unplugging the camera:
NEVER plug or unplug the camera module without powering off the development board first. Otherwise, it may result in damaging the camera module.
-
If you encounter any issues with the startup of the hobot_sensor node, you can troubleshoot the problems by following these steps:
- Check the hardware connections.
- Make sure you have set up the tros.b environment.
- Verify the parameters are correct, for more details refer to the Hobot_Sensors README.md file.
RGBD camera
Introduction
In order to achieve environmental perception capability, robot products usually carry cameras, ToF and other types of sensors. To reduce the cost of sensor adaptation and usage for users, TogetheROS.Bot encapsulates and abstracts multiple commonly used sensors into the hobot_sensor module, which supports ROS standard image messages, custom image message output, and camera calibration data publishing. Currently supported types of RGBD sensors are as follows:
| Type | Model | Specification | Supported Platforms |
|---|---|---|---|
| Camera | CP3AM | 200W | RDK X3 |
Code Repository: (https://github.com/D-Robotics/hobot_rgbd_cam.git)
Supported Platforms
| Platform | System | Function |
|---|---|---|
| RDK X3 | Ubuntu 20.04 (Foxy), Ubuntu 22.04 (Humble) | Start RGBD camera and preview RGB and depth images on PC using rviz2 |
Note: Only supports RDK X3, RDK X3 Module is not supported yet.
Preparations
RDK Platform
-
Make sure the camera is correctly connected to the RDK. The connection for RGBD module to RDK X3 is shown as below:
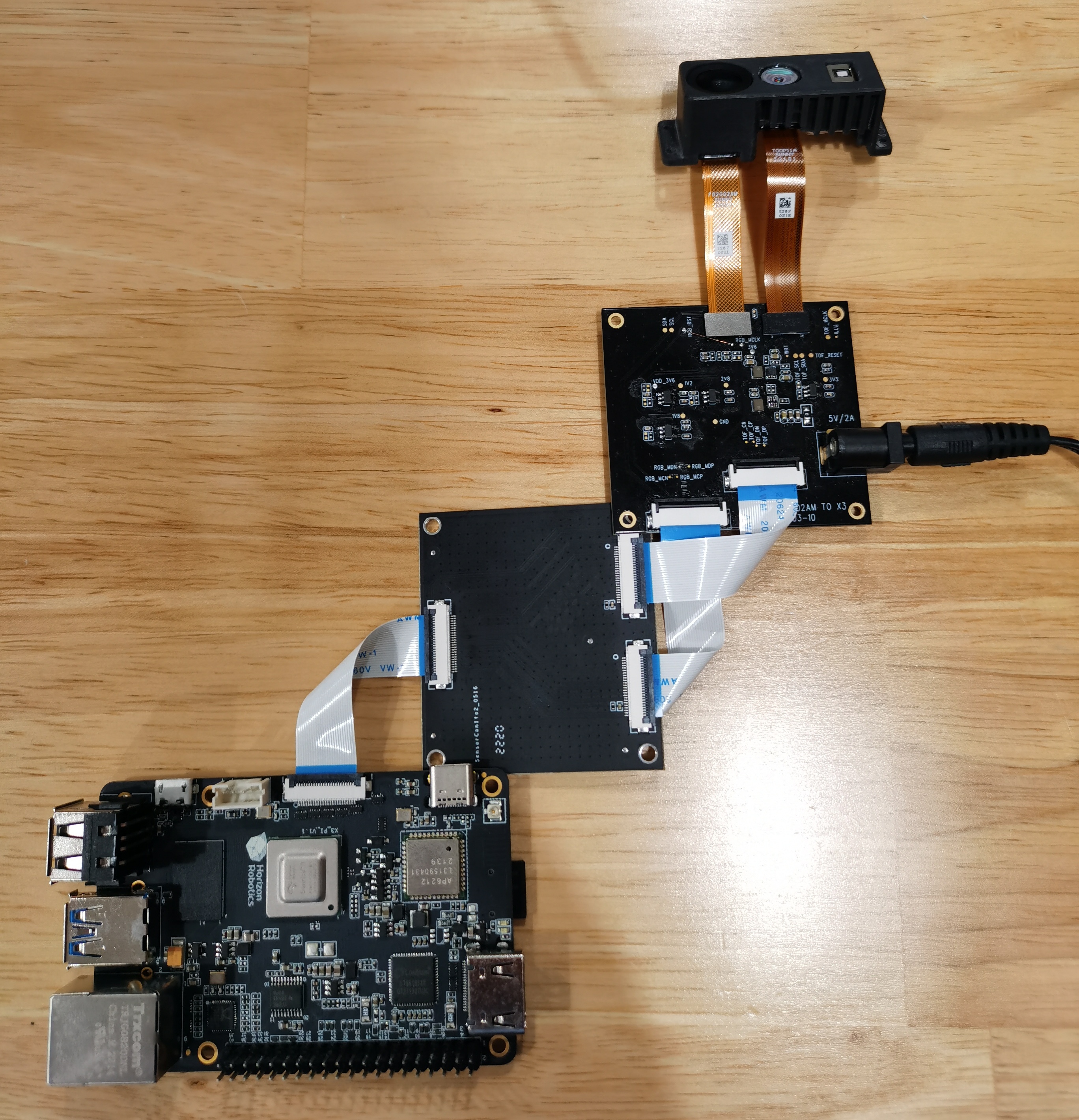
Note: The RGBD module needs an additional adapter board to connect to RDK X3.
-
RDK has been flashed with the Ubuntu 20.04/22.04 system image provided by D-Robotics.
-
RDK has successfully installed tros.b.
-
Make sure the PC can access the RDK through the network.
-
Install ros2 foxy version and rviz2 on the PC, using the following command:
sudo apt install ros-foxy-rviz-common ros-foxy-rviz-default-plugins ros-foxy-rviz2
Usage
RDK
Taking CP3AM as an example, the method of acquiring and previewing camera data is introduced below:
-
SSH into the RDK and start the hobot_sensor node with the following command:
- Foxy
- Humble
# Configure the tros.b environment
source /opt/tros/setup.bash# Configure the tros.b environment
source /opt/tros/humble/setup.bashcp -r /opt/tros/lib/rgbd_sensor/parameter .
# Launch the node
ros2 launch rgbd_sensor rgbd_sensor.launch.py -
If the program outputs the following information, it indicates that the node has been successfully launched:
[WARN] [1654573498.706920307] [example]: [wuwl]->This is rgbd!
sh: 1: echo: echo: I/O error
pipeId[1], mipiIdx[1], vin_vps_mode[3]
[ERROR]["LOG"][irs2381c_utility.c:192] 2381 enter sensor_init_setting
[ERROR]["LOG"][irs2381c_utility.c:200] start write 2381c reg
camera read reg: 0xa001 val:0x7
...
[ERROR]["LOG"][irs2381c_utility.c:207] end write 2381c reg
HB_MIPI_InitSensor end
HB_MIPI_SetDevAttr end
pstHbVideoDev->vin_fd = 29
sensorID: 634-2362-2676-68d0
find local calib_file
find local calib_file
SDK Version: V4.4.35 build 20220525 09:27:53.
read file(./calib-0634-2362-2676-68d0.bin), ok, file_len=132096, read_len=132096.......
module config file(user custom) is: ./parameter/T00P11A-17.ini.
parse calib data, data len:132096...
sunny_degzip2 decode_len=155575.
calib data with crc.
parse calib data, ok.
max roi (firstly): (0, 224, 0, 128).
cur roi (firstly): (0, 224, 0, 128).
HB_MIPI_InitSensor end
HB_MIPI_SetDevAttr end
pstHbVideoDev->vin_fd = 55
vencChnAttr.stRcAttr.enRcMode=11
mmzAlloc paddr = 0x1a6e6000, vaddr = 0x917e1000
camera read reg: 0x9400 val:0x1
...
[wuwl-StartCamera]->camT=3, ret=0.
camera read reg: 0x3e val:0x40
[ERROR]["vio_devop"][utils/dev_ioctl.c:121] [499334.399304]dev_node_dqbuf_ispoll[121]: failed to ioctl: dq (14 - Bad address)
[ERROR]["vio_devop"][utils/dev_ioctl.c:189] [499334.399355]entity_node_dqbuf_ispoll[189]: dev type(9) dq failed
[ERROR]["vio_core"][commom_grp/binding_main.c:1034] [499334.399371]comm_dq_no_data[1034]: G1 MIPI_SIF_MODULE module chn0 dq failed! maybe framedrop error_detail -14
```[wuwl-StartCamera]->camT=1, ret=0.
[INFO] [1654573500.226606117] [rclcpp]: [childStart]-> ret=0 !
[INFO] [1654573500.226831567] [rclcpp]: [StartStream]->pthread create sucess
[INFO] [1654573500.226963854] [rclcpp]: <========>[doCapStreamLoop]->Start.
[WARN] [1654573500.226998103] [rgbd_node]: [RgbdNode]->mipinode init sucess.
[WARN] [1654573500.227352507] [example]: [wuwl]->rgbd init!
[WARN] [1654573500.228502174] [example]: [wuwl]->rgbd add_node!
[INFO] [1662723985.860666547] [rgbd_node]: publish camera info.
[INFO] [1662723985.866077156] [rgbd_node]: [pub_ori_pcl]->pub pcl w:h=24192:1,nIdx-24192:sz=24192.
[INFO] [1662723985.876428980] [rgbd_node]: [timer_ros_pub]->pub dep w:h=224:129,sz=982464, infra w:h=224:108, sz=24192.
[INFO] [1662723985.946767230] [rgbd_node]: publish camera info.
[INFO] [1662723985.951415418] [rgbd_node]: [pub_ori_pcl]->pub pcl w:h=24192:1,nIdx-24192:sz=24192.
[INFO] [1662723985.960161280] [rgbd_node]: [timer_ros_pub]->pub dep w:h=224:129,sz=982464, infra w:h=224:108, sz=24192.
...
- Query the current topic on the PC, and the command are as follows:
- Foxy
- Humble
source /opt/ros/foxy/setup.bash
source /opt/ros/humble/setup.bash
ros2 topic list
The result are as follows:
/rgbd_CP3AM/depth/image_rect_raw
/rgbd_CP3AM/depth/color/points
/rgbd_CP3AM/color/camera_info
/rgbd_CP3AM/aligned_depth_to_color/color/points
/rgbd_CP3AM/infra/image_rect_raw
/rgbd_CP3AM/color/image_rect_raw
/parameter_events
/rosout
- Subscribe to topics and preview camera data on a PC.
- Foxy
- Humble
source /opt/ros/foxy/setup.bash
source /opt/ros/humble/setup.bash
ros2 run rviz2 rviz2
Click the "add" button in the rviz2 interface to add topics published by rgbd_sensor (refer to the rgbd_CP3AM related topics indicated in section 3). To subscribe to point cloud data, modify the "Fixed Frame" option in the Global Options of rviz2 configuration to "depth". Then you can view real-time point cloud information. In the point topic configuration, select "points" as the point type.
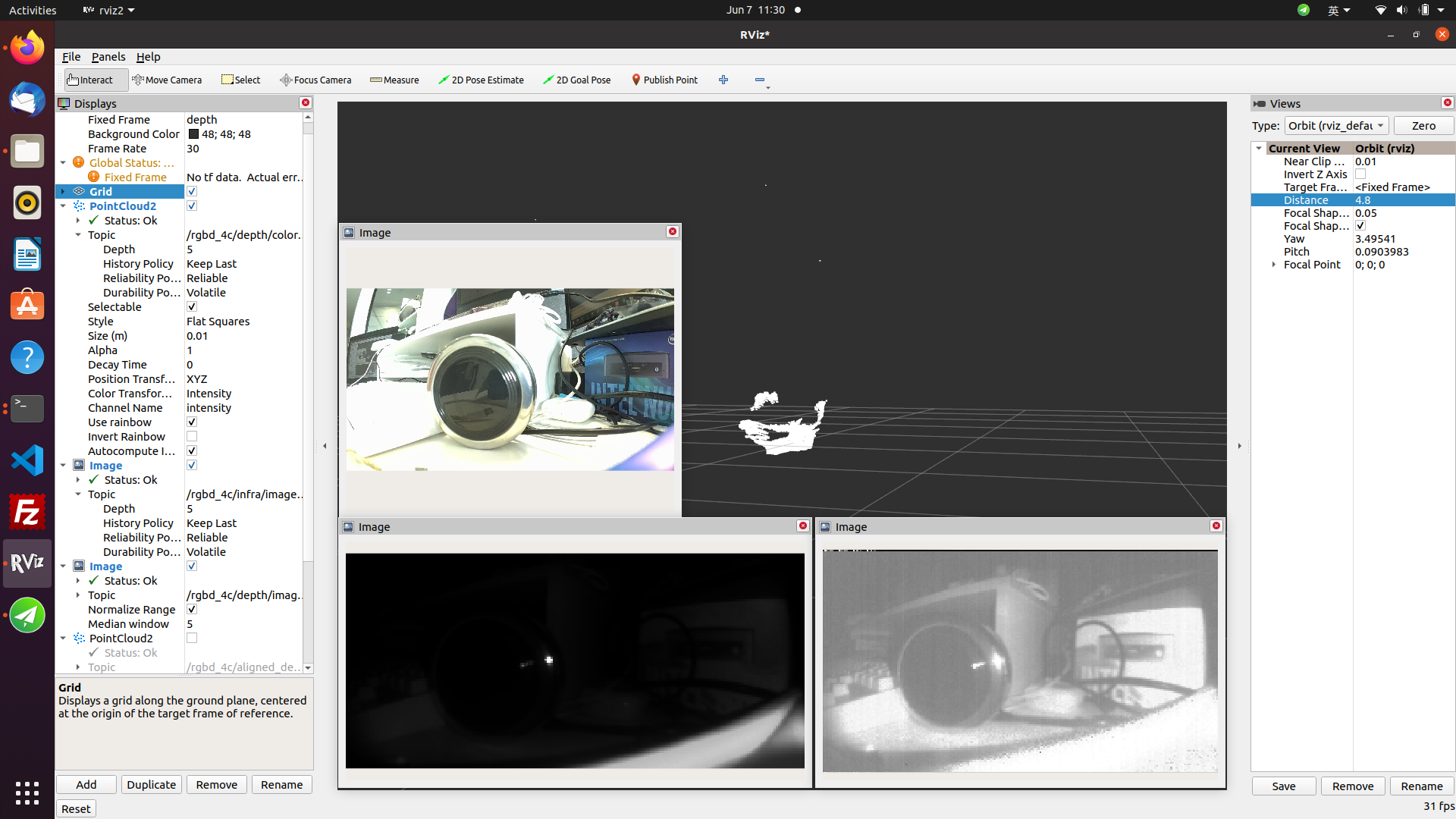
- Query camera intrinsics on a PC.
- Foxy
- Humble
source /opt/ros/foxy/setup.bash
source /opt/ros/humble/setup.bash
ros2 topic echo /rgbd_CP3AM/color/camera_info
The output result is as follows:
header:
stamp:
sec: 119811
nanosec: 831645108
frame_id: color
height: 1080
width: 1920
distortion_model: plumb_bob
d:
- -0.32267
- 0.083221
- 0.000164
- -0.002134
- 0.0
k:
- 1066.158339
- 0.0
- 981.393777
- 0.0
- 1068.659998
- 545.569587
- 0.0
- 0.0
- 1.0
r:
- 1.0
- 0.0
- 0.0```
- 0.0
- 1.0
- 0.0
- 0.0
- 0.0
- 1.0
p:
- 741.315308
- 0.0
- 968.865379
- 0.0
- 0.0
- 969.43042
- 546.524343
- 0.0
- 0.0
- 0.0
- 1.0
- 0.0
binning_x: 0
binning_y: 0
roi:
x_offset: 0
y_offset: 0
height: 0
width: 0
do_rectify: false
Instructions
If there is an abnormality in the startup of the hobot_sensor node, you can troubleshoot the problem using the following steps:
- Check hardware connections.
- Check if the tros.b environment is set.
- Check if the parameters are correct. For specific details, please refer to the Hobot_Sensors README.md file.
RealSense Image Capture
Feature Overview
Stereo cameras are commonly used sensors in robotics, often serving as the "eyes" of the robot. They have diverse applications, including navigation and obstacle avoidance, object recognition, 3D reconstruction, and human-robot interaction. The RDK platform supports popular stereo camera models such as RealSense and Orbbec.
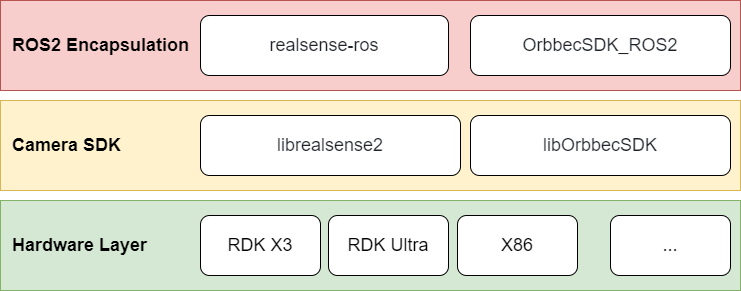
Currently, the usage of RealSense and Orbbec stereo cameras on ROS follows the architecture shown below. It requires platform-specific SDK library files. These SDKs provide APIs for camera initialization and configuration. On top of these SDKs, ROS wrappers are implemented, enabling the integration of stereo cameras into ROS.
The general installation process for stereo camera ROS packages involves:
- Installing the camera's SDK library files.
- Installing the ROS wrapper for the camera.
This section explains how to use a RealSense camera on the RDK platform.
Supported Platforms
| Platform | Operating System |
|---|---|
| RDK X3, RDK X3 Module | Ubuntu 20.04 (Foxy), Ubuntu 22.04 (Humble) |
| RDK X5 | Ubuntu 22.04 (Humble) |
| RDK Ultra | Ubuntu 20.04 (Foxy) |
Preparation
RDK Platform
- Ensure your RealSense camera is functioning properly and connect it to the RDK's USB port using the provided USB cable.
- Verify that the RDK is flashed with the Ubuntu 20.04/Ubuntu 22.04 system image.
- Confirm that tros.b is successfully installed on the RDK.
- Ensure that your PC can access the RDK over the network.
Usage Instructions
To use the RealSense series cameras on the RDK platform, install RealSense SDK 2.0 and the RealSense ROS wrapper using the apt command.
Below are the GitHub repositories for RealSense SDK 2.0 and the RealSense ROS wrapper. This guide references these repositories, which also contain more detailed instructions for advanced use cases:
- RealSense SDK 2.0: GitHub Repository
- RealSense ROS wrapper: GitHub Repository
1. Log in to the RDK via Serial Port or SSH and Verify the ROS Version
- Foxy
- Humble
# Configure the tros.b environment
source /opt/tros/setup.bash
# Print the ROS version environment variable
echo $ROS_DISTRO
# Configure the tros.b environment
source /opt/tros/humble/setup.bash
# Print the ROS version environment variable
echo $ROS_DISTRO
2. Install RealSense SDK 2.0 and RealSense ROS2 Wrapper
# Install RealSense SDK 2.0
sudo apt-get install ros-$ROS_DISTRO-librealsense2* -y
# Install RealSense ROS2 wrapper
sudo apt-get install ros-$ROS_DISTRO-realsense2-* -y
3. Start the RealSense Camera
After installation, you can start the RealSense camera using the following ROS command:
ros2 launch realsense2_camera rs_launch.py
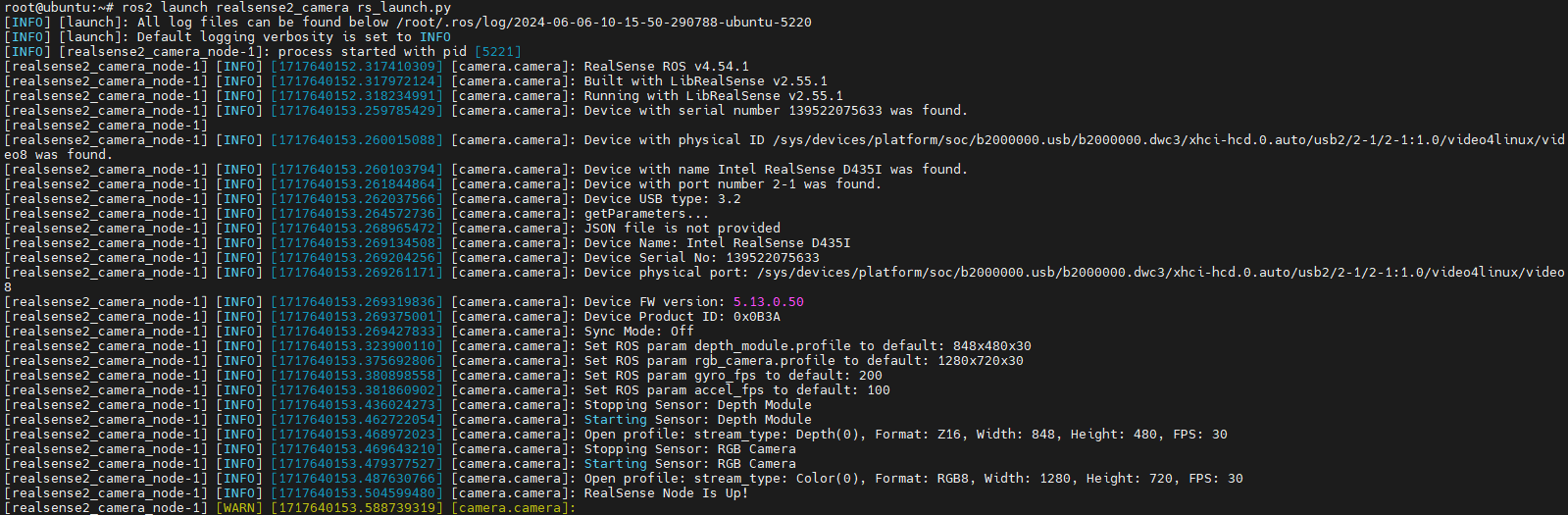
You can use the ros2 topic list command to view the topics published by the RealSense camera. When started with default parameters, the RealSense camera will only enable the depth and RGB data streams.
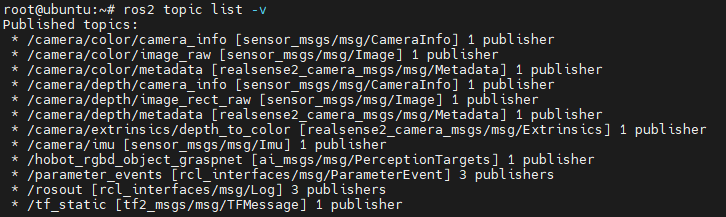
The RealSense ROS wrapper provides numerous configurable parameters. For example:
- Setting
enable_infra1:=trueenables the camera's left IR data stream. - Setting
pointcloud.enable:=trueenables the point cloud data stream.
ros2 launch realsense2_camera rs_launch.py enable_infra1:=true pointcloud.enable:=true
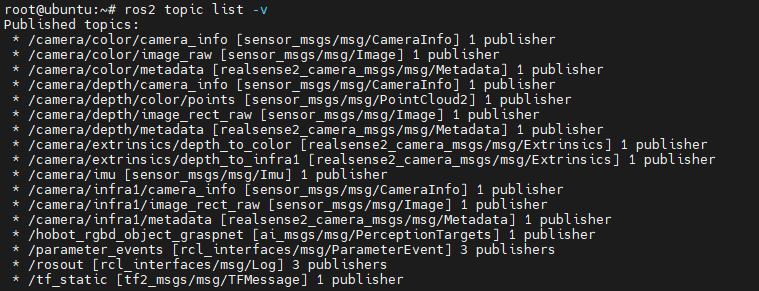

Additionally, RealSense provides several services that can be viewed using the ros2 service list command. For example, you can use these services to query the camera's serial number, firmware version, and other information.
ros2 service call /camera/device_info realsense2_camera_msgs/srv/DeviceInfo
For more details on topics and service configurations, refer to the RealSense ROS wrapper's GitHub repository.
4. Depth and RGB Alignment
In practical applications, it's often necessary to align the depth map with the color image. RealSense provides corresponding launch methods to achieve this.
ros2 launch realsense2_camera rs_launch.py enable_rgbd:=true enable_sync:=true align_depth.enable:=true enable_color:=true enable_depth:=true
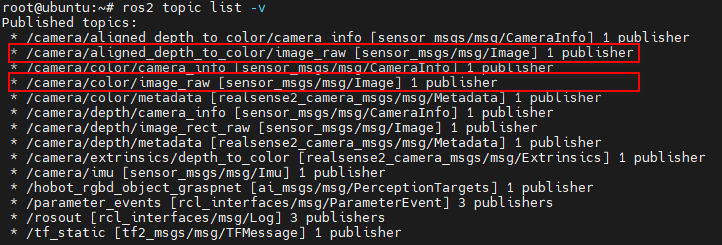

5. Displaying Images and Point Clouds
There are multiple ways to display images and point clouds from the RealSense camera. Refer to 2.2 Data Visualization for details.
For example, you can use rviz2 on a PC to display the data. Ensure that the PC can access the RDK over the network. Note that since data is transmitted over the network, this method may cause significant load and result in lag or stuttering.
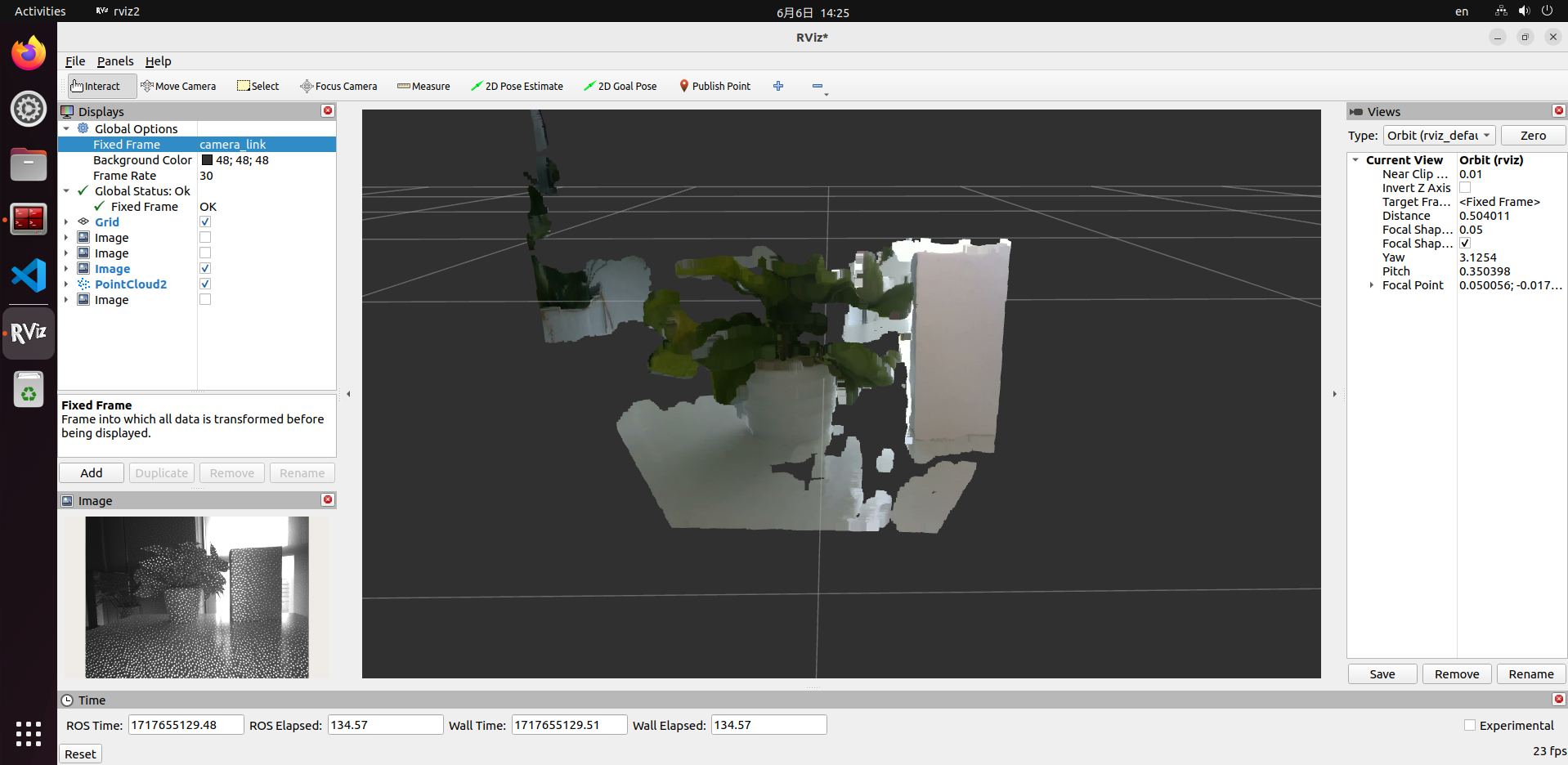
It is recommended to directly read data on the RDK to verify if the output stream is functioning correctly. You can use ros2 topic echo topic_name to print the data or write code to subscribe to the relevant topics.
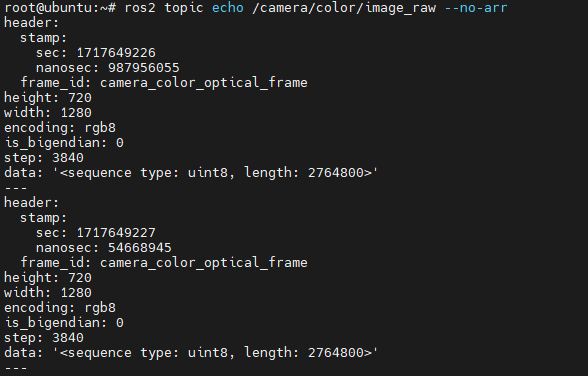
Orbbec camera
Introduction
Stereo cameras are commonly used sensors in robot development, often serving as the "eyes" of robots. Applications of stereo cameras in robots cover various aspects, such as navigation and obstacle avoidance, target recognition, 3D reconstruction, and human-robot interaction. The RDK platform supports popular stereo cameras on the market, including the RealSense, Orbbec, ZED, and other series.
Currently, the use of RealSense and Orbbec stereo cameras on ROS follows the architecture described below. Firstly, SDK library files compiled for different hardware platforms are required. The camera SDK provides APIs for camera startup and settings. Based on this, ROS wrapping is performed to enable ROS to call the camera.
Therefore, the general installation process for the stereo camera ROS package is: first install the camera's SDK library files, then install the camera's ROS wrapper package.

This section introduces the usage of Orbbec cameras on the RDK platform.
Supported Platforms
| Platform | Operating Mode |
|---|---|
| RDK X3, RDK X3 Module | Ubuntu 20.04 (Foxy), Ubuntu 22.04 (Humble) |
| RDK X5 | Ubuntu 22.04 (Humble) |
Preparations
RDK Platform
- Ensure that the Orbbec camera is functioning properly and connect the USB cable to the USB3.0 slot of the RDK (currently, USB2.0 may have issues with startup).
- The RDK has Ubuntu 20.04/Ubuntu 22.04 system images burned onto it.
- The RDK has successfully installed tros.b.
- Confirm that the PC can access the RDK via the network.
Usage
Currently, Orbbec cameras do not support direct installation of SDK library files and ROS wrapper packages using apt commands. Instead, source code must be downloaded and compiled before they can be run on the RDK platform.
Here are the GitHub repositories for the Orbbec SDK and Orbbec ROS2 wrapper. This tutorial is also based on these repositories, and users can refer to the more detailed tutorials in these repositories.
- Orbbec SDK: https://github.com/orbbec/OrbbecSDK
- Orbbec ROS2 wrapper: https://github.com/orbbec/OrbbecSDK_ROS2
1. Log in to the RDK via serial port or SSH and confirm the ROS version.
- Foxy
- Humble
# Configure the tros.b environment
source /opt/tros/setup.bash
# Print the ROS version environment variable
echo $ROS_DISTRO
# Configure the tros.b environment
source /opt/tros/humble/setup.bash
# Print the ROS version environment variable
echo $ROS_DISTRO
2. Download the Orbbec ROS2 wrapper source code for compilation.
# First, create a ros workspace
mkdir -p tros_ws/src
cd tros_ws/src
# Download the Orbbec ROS2 wrapper source code to the tros_ws/src directory
git clone https://github.com/orbbec/OrbbecSDK_ROS2.git
Note that the OrbbecSDK_ROS2 repository already contains the SDK library files for the Orbbec camera, located in the OrbbecSDK_ROS2/orbbec_camera/SDK directory. The arm64 version is required for compilation on the RDK platform.
After downloading the source code, the next step is to compile it. However, compiling this program requires at least 4GB of memory, and the RDK platform may encounter memory insufficiency issues, leading to compilation failures.
There are two solutions:
- Set up swap space to serve as temporary memory.
- Use cross-compilation, compiling on a PC and running on the RDK.
The advantage of Solution 1 is simplicity and direct compilation on the RDK platform, but the disadvantage is slower compilation speed due to limited RDK platform performance. For example, compilation on the RDK X3 platform takes about 30 minutes. The advantage of Solution 2 is faster compilation speed, but the disadvantage is the complexity of setting up the cross-compilation environment. This tutorial introduces the implementation of Solution 1, and Solution 2 can be referenced in the tutorial: Cross-compilation Environment Deployment.
Below is how to set up swap space:
# Create a 4GB swap file in the /swapfile directory
sudo dd if=/dev/zero of=/swapfile bs=1M count=4096
# For security reasons, set the permissions of the swap file to allow only the root user to read and write
sudo chmod 600 /swapfile
# Use the mkswap command to format the file as swap space
sudo mkswap /swapfile
# Use the swapon command to enable the swap file
sudo swapon /swapfile
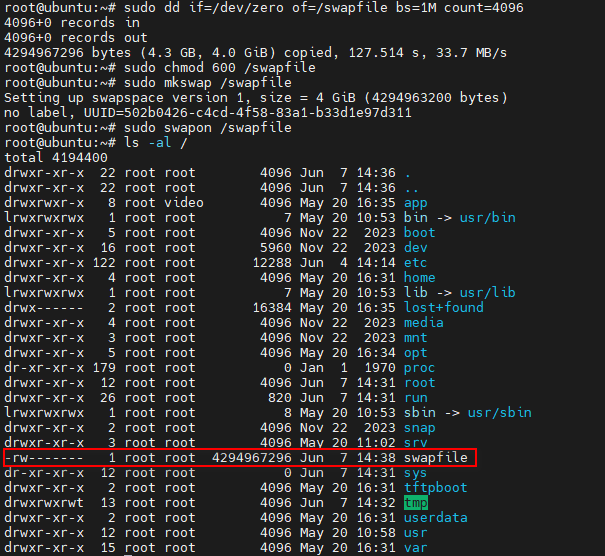
After setting up the swap space, you can use swapon --show, free -h, or htop commands to check the current swap usage. For example, using the htop command:
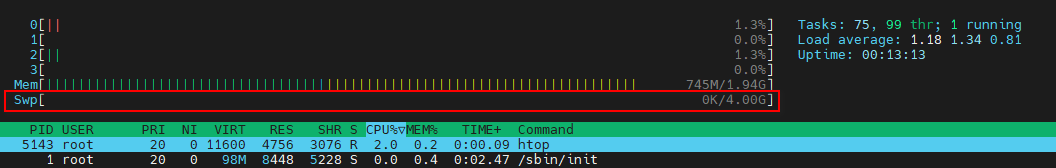
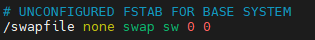
This setting is only temporary and will be lost after a power cycle. If you want the swap space to be used after a system reboot, you can either re-execute sudo swapon /swapfile or add it to the /etc/fstab file.
# Open /etc/fstab using vim
sudo vim /etc/fstab
# Add the following line, save and exit
/swapfile none swap sw 0 0
# Execute sync to flush the cache and ensure all data is correctly written to disk
sync
To delete the swap space, you can execute the following commands.
# Use the swapoff command to disable the swap file
sudo swapoff /swapfile
# Delete the swap file
sudo rm -rf /swapfile
# If the swap file entry was added in /etc/fstab, remove it
sudo vim /etc/fstab
# Delete the following line
/swapfile none swap sw 0 0
After setting up the swap space, you can proceed with the compilation.
# Return to the ros workspace
cd tros_ws
# Execute colcon to build, which may take a while, please be patient
colcon build
Compilation results on the RDK X3 platform:
3. Start the Orbbec camera.
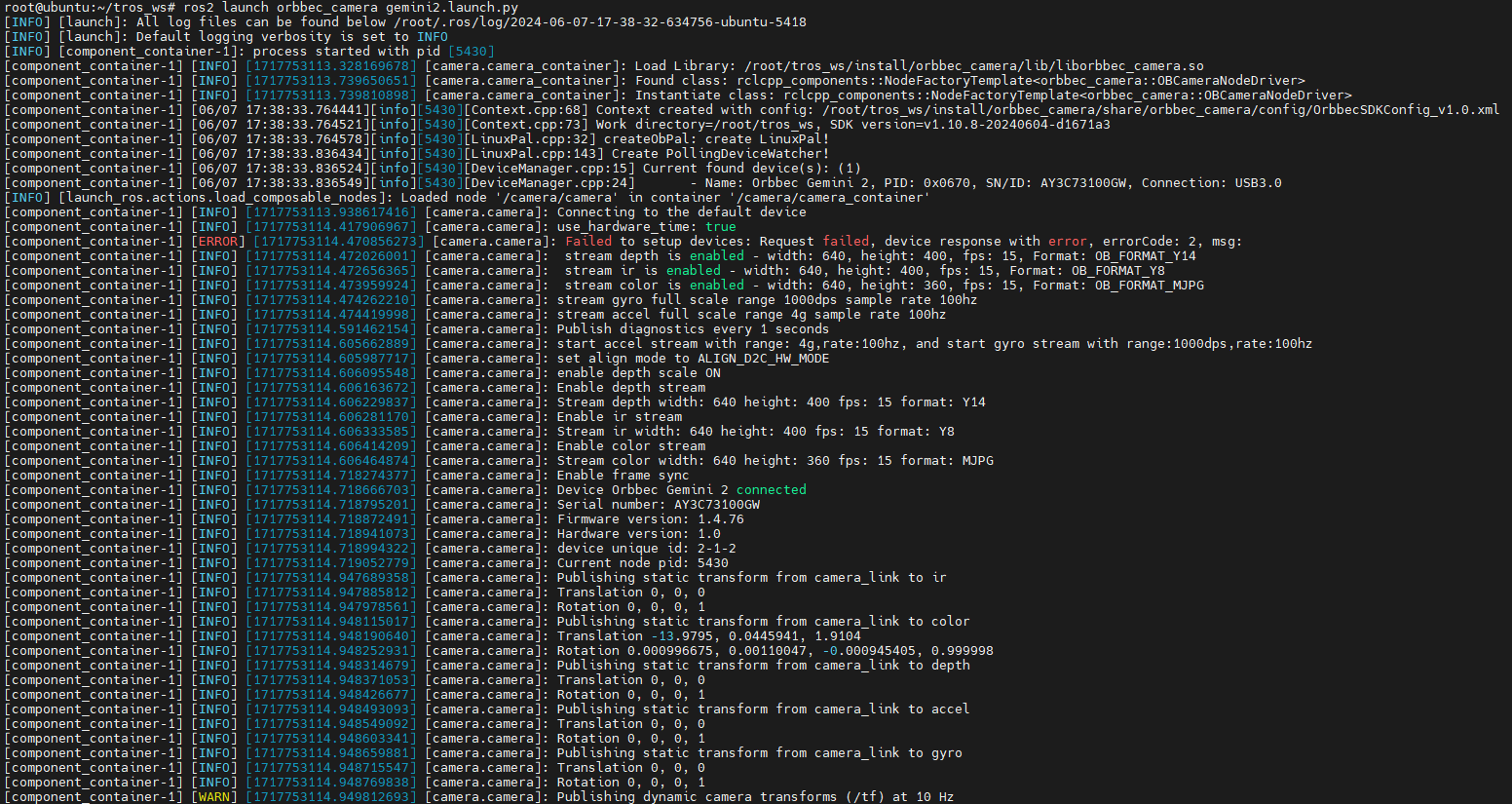
After compilation, the Orbbec camera can be started through ROS commands. OrbbecSDK_ROS2 has launch files for all Orbbec cameras, including the Astra series, Dabai series, and Gemini series. Simply use the corresponding launch file to start. This tutorial takes the Gemini2 camera as an example.
cd tros_ws
source ./install/setup.bash
ros2 launch orbbec_camera gemini2.launch.py
You can use ros2 topic list to view the topics published by Gemini2. With default parameters, starting the Gemini2 camera will enable the camera's depth data stream, RGB data stream, IR data stream, and point cloud data stream.
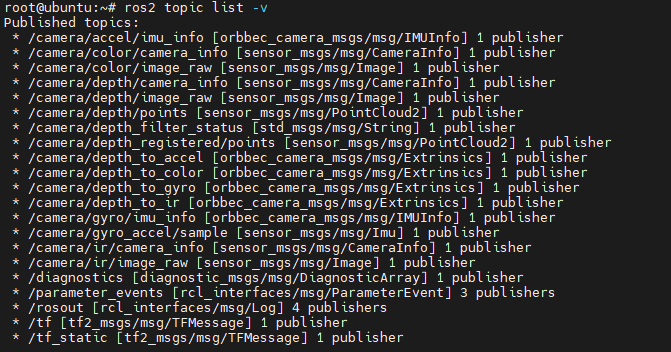
The Orbbec ROS2 wrapper offers numerous configurable parameters. For instance, setting enable_point_cloud:=false and enable_colored_point_cloud:=false will disable the camera's point cloud data streams.
Moreover, the Orbbec camera activates several services, which can be viewed using ros2 service list. These services allow for querying the camera's SDK version, adjusting or querying exposure time and gain, enabling or disabling the laser, among other functionalities. For example:
# Query SDK Version
ros2 service call /camera/get_sdk_version orbbec_camera_msgs/srv/GetString '{}'
# Disable Color Camera Auto Exposure
ros2 service call /camera/set_color_auto_exposure std_srvs/srv/SetBool '{data: false}'
# Enable Laser
ros2 service call /camera/set_laser_enable std_srvs/srv/SetBool '{data: true}'
For more detailed settings regarding topics and services, please refer to the Orbbec ROS2 wrapper's GitHub repository.
4. Depth and RGB Alignment
In practical applications, it is often necessary to align the depth map of a stereo camera with its color image. Orbbec provides a corresponding launch configuration for this purpose.
cd tros_ws
source ./install/setup.bash
ros2 launch orbbec_camera gemini2.launch.py depth_registration:=true

5. Displaying Images and Point Clouds
There are multiple methods to display Orbbec's images and point clouds. For reference, see 2.2 Data Visualization. For instance, you can use rviz2 on a PC to display the data, but note that this requires the PC to access the RDK via the network, which can be demanding and may lead to lag.
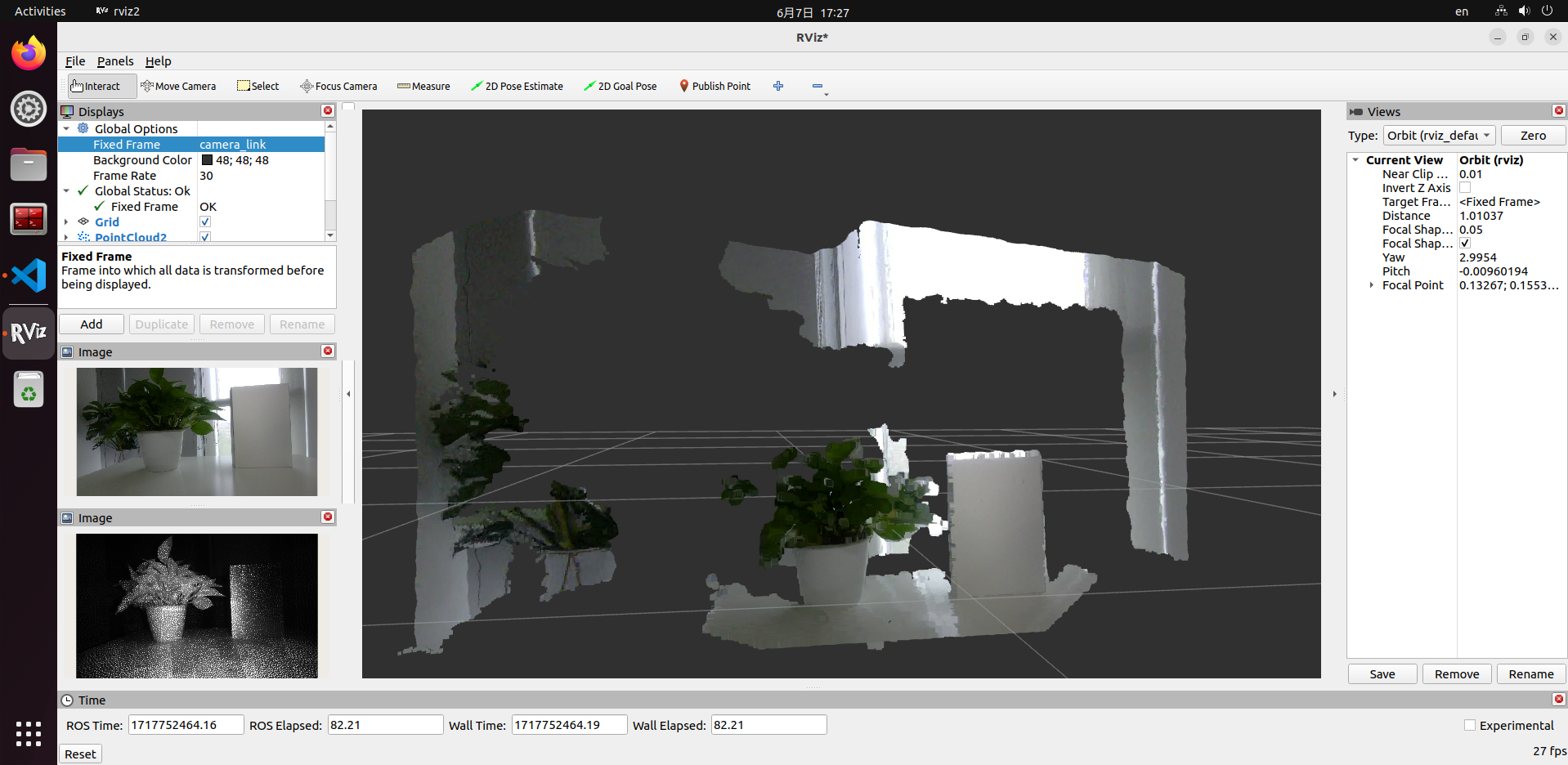
It is recommended to read the data directly on the RDK to verify the data flow. You can use ros2 topic echo topic_name to print data or write code to subscribe to the corresponding topics.
ZED camera
Introduction
Stereo cameras are commonly used sensors in robot development, often serving as the "eyes" of robots. Their applications in robotics span various aspects, including navigation and obstacle avoidance, object recognition, 3D reconstruction, and human-robot interaction. The RDK platform supports popular stereo cameras on the market, such as RealSense, Orbbec, and ZED series cameras.
Code Repository: https://github.com/D-Robotics/hobot_zed_cam
This section introduces how to use the ZED camera on the RDK platform.
Supported Platforms
| Platform | Operating System |
|---|---|
| RDK X5 | Ubuntu 22.04 (Humble) |
Preparation
RDK Platform
- Ensure that the ZED camera is functioning properly and connect it to the RDK via a USB cable.
- The RDK should have Ubuntu 22.04 system image flashed onto it.
- The RDK should have
tros.binstalled successfully. - Ensure that the PC can access the RDK via the network.
Usage
- Log in to the RDK via SSH and start the ZED camera using the following commands:
# Configure the tros.b environment
source /opt/tros/humble/setup.bash
# Launch the ZED camera to publish stereo image data
ros2 launch hobot_zed_cam pub_stereo_imgs.launch.py need_rectify:=true
- If the program outputs information similar to the following, it indicates that the node has been successfully launched:
[anypub_stereo_imgs-1] [INFO] [0946684888.710715101] [pub_stereo_imgs_nv12_node]: => connected to camera sn: 38085162[/dev/video0]
[anypub_stereo_imgs-1] [INFO] [0946684888.779280740] [pub_stereo_imgs_nv12_node]: => calibration file found. Loading...
[anypub_stereo_imgs-1] [INFO] [0946684888.831008271] [pub_stereo_imgs_nv12_node]: => camera Matrix L:
[anypub_stereo_imgs-1] [514.5878861678406, 0, 665.3764572143555, 0;
[anypub_stereo_imgs-1] 0, 514.5878861678406, 320.3872646755642, 0;
[anypub_stereo_imgs-1] 0, 0, 1, 0]
[anypub_stereo_imgs-1] [INFO] [0946684888.831235937] [pub_stereo_imgs_nv12_node]: => camera Matrix R:
[anypub_stereo_imgs-1] [514.5878861678406, 0, 665.3764572143555, 61695.48427422668;
[anypub_stereo_imgs-1] 0, 514.5878861678406, 320.3872646755642, 0;
[anypub_stereo_imgs-1] 0, 0, 1, 0]
[anypub_stereo_imgs-1] [INFO] [0946684888.831287187] [pub_stereo_imgs_nv12_node]: => rectified fx: 514.587886, fy: 514.587886, cx: 665.376457, cy: 320.387265, base_line: 0.119893
[anypub_stereo_imgs-1] [INFO] [0946684888.831357562] [pub_stereo_imgs_nv12_node]: => camera_fx:=514.587886 camera_fy:=514.587886 camera_cx:=665.376457 camera_cy:=320.387265 base_line:=0.119893
[anypub_stereo_imgs-1] [INFO] [0946684888.851400416] [pub_stereo_imgs_nv12_node]: => raw img size: [1280, 720]
[anypub_stereo_imgs-1] [INFO] [0946684888.883419384] [pub_stereo_imgs_nv12_node]: => rectify img size: [1280, 640]
- Open a web browser on the PC (
Chrome/Firefox/Edge), enterIP:8000(where IP is the IP address of the RDK), and click on the web display in the top left corner to view the real-time ZED camera feed.
