5.2.2 Display
Web
Introduction
Web is used to preview camera images (JPEG format) and algorithm results. The images and algorithm results are transmitted to the PC browser through the network and rendered for display. The display interface also supports displaying only the video without rendering the intelligent results.
Code Repository: (https://github.com/D-Robotics/hobot_websocket)
Supported Platforms
| Platform | Operating System | Example Functionality |
|---|---|---|
| RDK X3, RDK X3 Module | Ubuntu 20.04 (Foxy), Ubuntu 22.04 (Humble) | Start MIPI cameras and display images via Web |
| RDK X5 | Ubuntu 22.04 (Humble) | Start MIPI cameras and display images via Web |
| RDK S100 | Ubuntu 22.04 (Humble) | Start MIPI cameras and display images via Web |
Preparation
RDK
-
Confirm that the camera F37 is correctly connected to the RDK.
-
Confirm that the PC can access the RDK through the network.
-
Confirm that TogetheROS.Bot has been successfully installed.
Usage
RDK
-
Log in to the RDK through SSH and start the programs on the board.
a. Launch mipi_cam
- Foxy
- Humble
# Configure the tros.b environment
source /opt/tros/setup.bash# Configure the tros.b environment
source /opt/tros/humble/setup.bashros2 launch mipi_cam mipi_cam.launch.py mipi_video_device:=F37b. Launch encoding
- Foxy
- Humble
# Configure the tros.b environment
source /opt/tros/setup.bash# Configure the tros.b environment
source /opt/tros/humble/setup.bashros2 launch hobot_codec hobot_codec_encode.launch.pyc. Launch WebSocket
- Foxy
- Humble
# Configure the tros.b environment
source /opt/tros/setup.bash# Configure the tros.b environment
source /opt/tros/humble/setup.bashros2 launch websocket websocket.launch.py websocket_image_topic:=/image_jpeg websocket_only_show_image:=true -
Open a PC browser (Chrome/Firefox/Edge) and enter
http://IP:8000to view the image and algorithm effects. IP refers to the RDK IP address.
Notes
-
WebSocket uses port 8000. If the port is already in use, the launch will fail. Here are some solutions:
-
Use the command
lsof -i:8000to check the processes that are occupying port 8000, and usekill <PID>to close the process, and then relaunch WebSocket. -
If the user does not want to stop the service that is currently using port 8000, you can modify the
listenport number in the configuration file/opt/tros/lib/websocket/webservice/conf/nginx.confto a port number that is greater than 1024 and not being used. After modifying the port number, the URL used in the browser also needs to be modified accordingly.
-
HDMI
Introduction
This chapter introduces the use of displaying camera nv12 images through HDMI. RDK can display real-time image effects by connecting to a monitor via HDMI, corresponding to the hobot_hdmi package.
Code Repository: (https://github.com/D-Robotics/hobot_hdmi)
Supported Platforms
| Platform | System | Function |
|---|---|---|
| RDK X3, RDK X3 Module, RDK X5, RDK X5 Module, RDK S100 | Ubuntu 20.04 (Foxy), Ubuntu 22.04 (Humble) | Start MIPI camera and display image through HDMI |
HDMI EOL Description:
- The
RDK X3andRDK X3 Moduleplatforms are supported up to version2.1.0, corresponding to TROS version2.2.0 (2024-04-11). - The
RDK X5andRDK X5 Moduleplatforms are supported up to version2.4.2, corresponding to TROS version2.3.1 (2024-11-20).
Preparation
RDK
-
RDK has been flashed with the Ubuntu 20.04/22.04 system image provided by D-Robotics.
-
TogetheROS.Bot has been successfully installed on the RDK.
-
RDK is connected to a monitor via HDMI.
Instructions
RDK
Log in to the development board via SSH and start the relevant programs on the board:
- Foxy
- Humble
# Configure the tros.b environment
source /opt/tros/setup.bash
# Configure the tros.b environment
source /opt/tros/humble/setup.bash
If use RDK X5, run commod:
# 关闭桌面显示
sudo systemctl stop lightdm
# 复制运行依赖
cp -r /opt/tros/${TROS_DISTRO}/lib/hobot_hdmi/config/ .
ros2 launch hobot_hdmi hobot_hdmi.launch.py device:=F37
Result Analysis
The following information is displayed in the running terminal:
[INFO] [launch]: All log files can be found below /root/.ros/log/2022-07-27-15-27-26-362299-ubuntu-13432
[INFO] [launch]: Default logging verbosity is set to INFO
[INFO] [mipi_cam-1]: process started with pid [13434]
[INFO] [hobot_hdmi-2]: process started with pid [13436]
The monitor displays the image as follows:

RViz2
Introduction
TogetheROS.Bot is compatible with ROS2 Foxy version. To conveniently preview image effects, you can use RViz2 to get images.
Supported Platforms
| Platform | System | Sample Function |
|---|---|---|
| RDK X3, RDK X3 Module, RDK X5, RDK X5 Module, RDK S100 | Ubuntu 20.04 (Foxy), Ubuntu 22.04 (Humble) | Start the MIPI camera to capture images and use RViz2 to preview on PC |
Preparation
RDK
-
RDK has flashed with the Ubuntu 20.04/22.04 system image provided by D-Robotics.
-
RDK has successfully installed tros.b.
-
The PC has Ubuntu 20.04/Ubuntu 22.04 installed, along with the desktop version of ROS 2 Foxy/Humble and the data visualization tool RViz2, and is on the same network segment as the RDK (the first three octets of the IP address are identical).
-
ROS 2 installation reference: Foxy version, Humble version
-
Install RViz2 on the PC:
sudo apt install ros-$ROS_DISTRO-rviz-common ros-$ROS_DISTRO-rviz-default-plugins ros-$ROS_DISTRO-rviz2. Here,$ROS_DISTROrefers to the ROS 2 version, e.g.,foxyorhumble.
-
Usage
RDK
-
SSH into the development board and start the corresponding program on the board
- Foxy
- Humble
# Configure the tros.b environment
source /opt/tros/setup.bash# Configure the tros.b environment
source /opt/tros/humble/setup.bash# Start the F37 camera to publish images in BGR8 format
ros2 launch mipi_cam mipi_cam.launch.py mipi_out_format:=bgr8 mipi_image_width:=480 mipi_image_height:=272 mipi_io_method:=ros mipi_video_device:=F37Note: Do not change the
mipi_out_formatarbitrarily. RViz2 only supports image formats like RGB8, RGBA8, BGR8, BGRA8, etc. -
If the following information is output, it means that the node has been successfully started
[INFO] [launch]: All log files can be found below /root/.ros/log/2022-08-19-03-53-54-778203-ubuntu-2881662
[INFO] [launch]: Default logging verbosity is set to INFO
[INFO] [mipi_cam-1]: process started with pid [2881781] -
A new window is created in the RDK to execute the topic query command and the results are as follows:
- Foxy
- Humble
# Configure the tros.b environment
source /opt/tros/setup.bash# Configure the tros.b environment
source /opt/tros/humble/setup.bash# Query topics
ros2 topic listOutput:
/camera_info
/image_raw
/parameter_events
/rosout -
On the PC, the current topics are queried using the following command and the results are as follows:
- Foxy
- Humble
source /opt/ros/foxy/setup.bash
source /opt/ros/humble/setup.bash
ros2 topic list
Output:
/camera_info
/image_raw
/parameter_events
/rosout
- Subscribing to a topic and previewing camera data on the PC:
- Foxy
- Humble
source /opt/ros/foxy/setup.bash
source /opt/ros/humble/setup.bash
ros2 run rviz2 rviz2
On the RViz2 interface, first click the "add" button, then select the published image based on the topic, which in this example is named /image_raw. Then click "image":
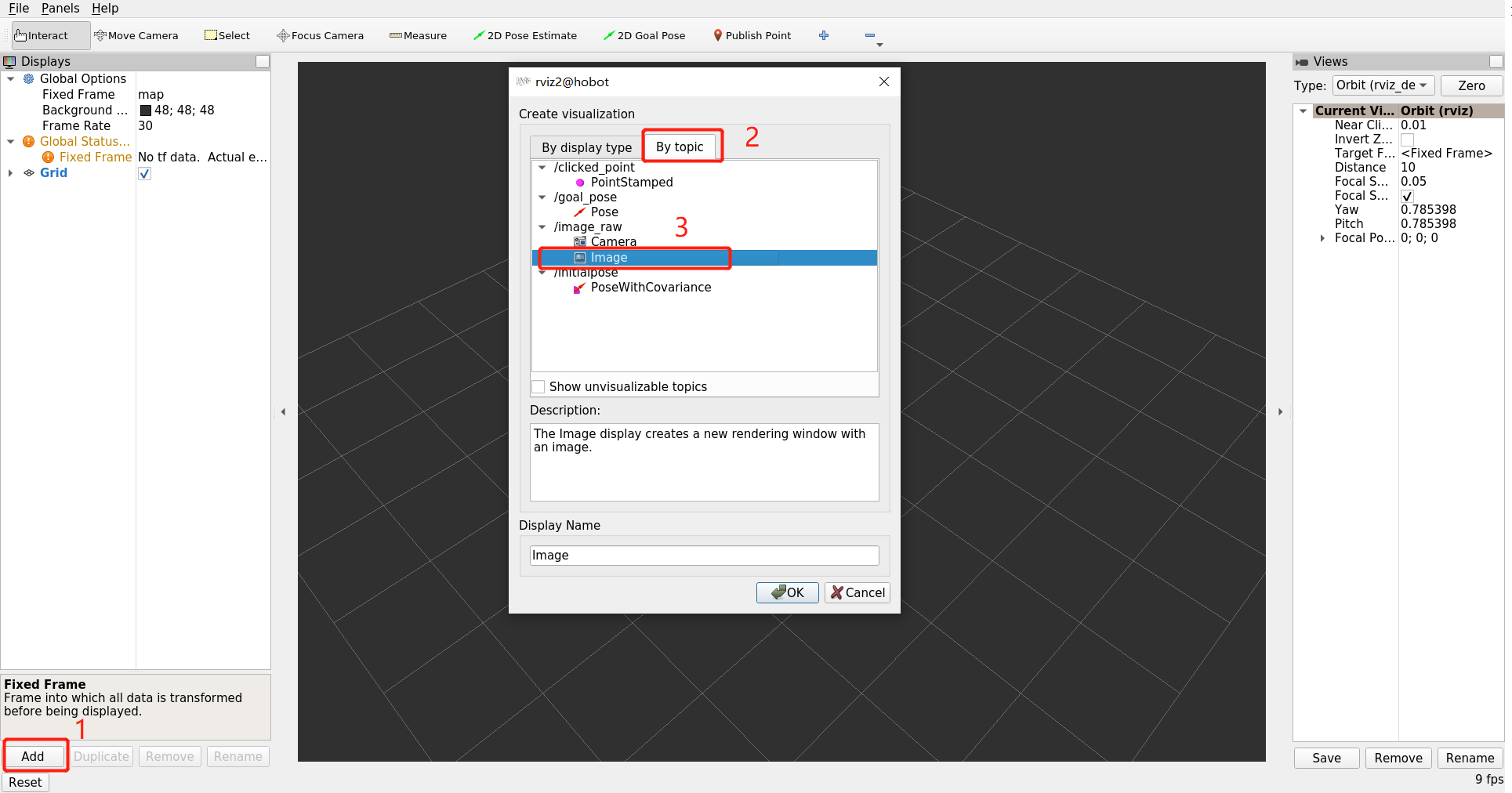
The image result is as follows:
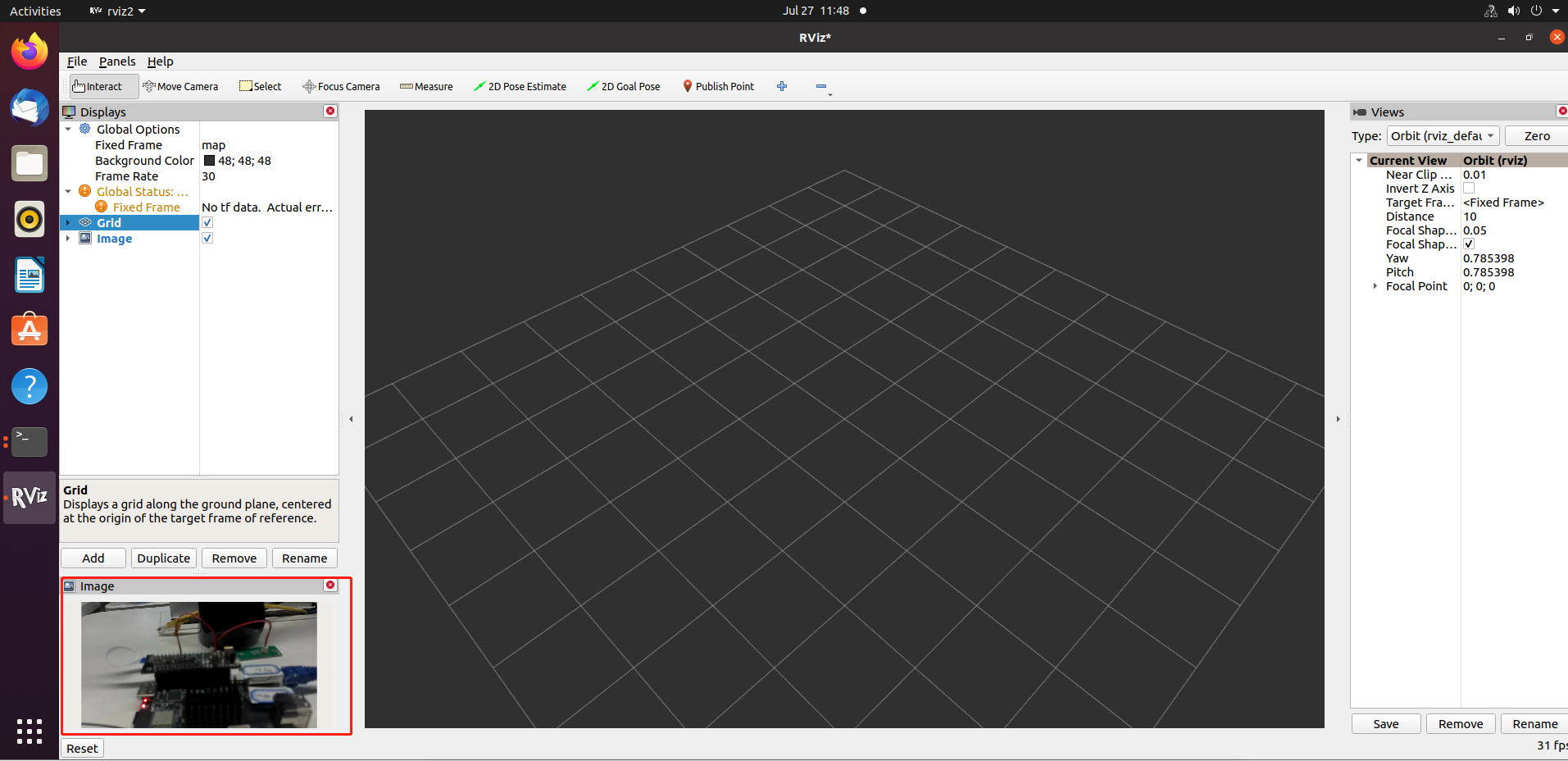
Attention
-
If the PC terminal's
ros2 topic listdoes not recognize the camera topic, please check the following:-
Check if RDK is publishing images properly:
- Foxy
- Humble
# Configure the tros.b environment
source /opt/tros/setup.bash# Configure the tros.b environment
source /opt/tros/humble/setup.bashros2 topic listOutput:
/camera_info
/image_raw
/parameter_events
/rosout -
Check if the PC and RDK networks can ping each other;
-
Check if the IP addresses of the PC and RDK have the same first three digits;
-
RQt
Introduction
TogetheROS.Bot is compatible with ROS2 Foxy and supports previewing compressed format images through RQt, greatly reducing network bandwidth consumption.
Supported Platforms
| Platform | System | Function |
|---|---|---|
| RDK X3, RDK X3 Module, RDK X5, RDK X5 Module, RDK S100 | Ubuntu 20.04 (Foxy), Ubuntu 22.04 (Humble) | Start MIPI camera to capture images and use RQt to preview on PC |
Preparation
RDK
-
RDK has been flashed with the provided Ubuntu 20.04/22.04 system image.
-
RDK has successfully installed tros.b.
-
The PC has Ubuntu 20.04/Ubuntu 22.04 installed, together with the desktop version of ROS 2 Foxy/Humble and the data visualization tool RQt, and it is on the same network segment as the RDK (the first three octets of the IP address are the same).
-
ROS 2 installation reference: Foxy version, Humble version
-
Install rqt-image-view on the PC:
sudo apt install ros-$ROS_DISTRO-rqt-image-view ros-$ROS_DISTRO-rqt. Here,$ROS_DISTROrefers to the ROS 2 version, e.g.,foxyorhumble.
-
Usage
RDK
-
SSH into the development board and start relevant programs on the board:
a. Start F37 camera
- Foxy
- Humble
# Configure the tros.b environment
source /opt/tros/setup.bash# Configure the tros.b environment
source /opt/tros/humble/setup.bashros2 launch mipi_cam mipi_cam.launch.py mipi_image_width:=640 mipi_image_height:=480 mipi_video_device:=F37b. Start hobot_codec and publish compressed format images
- Foxy
- Humble
# Configure the tros.b environment
source /opt/tros/setup.bash# Configure the tros.b environment
source /opt/tros/humble/setup.bashros2 launch hobot_codec hobot_codec_encode.launch.py codec_out_format:=jpeg codec_pub_topic:=/image_raw/compressed -
If the program output shows the following information, it means the nodes have been successfully launched
[INFO] [launch]: All log files can be found below /root/.ros/log/2023-05-15-17-08-02-144621-ubuntu-4755
[INFO] [launch]: Default logging verbosity is set to INFO
[INFO] [mipi_cam-1]: process started with pid [4757]
[mipi_cam-1] This is version for optimizing camera timestamp[INFO] [launch]: All log files can be found below /root/.ros/log/2023-05-15-17-08-17-960398-ubuntu-4842
[INFO] [launch]: Default logging verbosity is set to INFO
[INFO] [hobot_codec_republish-1]: process started with pid [4844] -
Subscribe to the topic on the PC and preview the camera data;
- Foxy
- Humble
source /opt/ros/foxy/setup.bash
source /opt/ros/humble/setup.bash
ros2 run rqt_image_view rqt_image_view
Select the topic /image_raw/compressed, and the image is as follows:
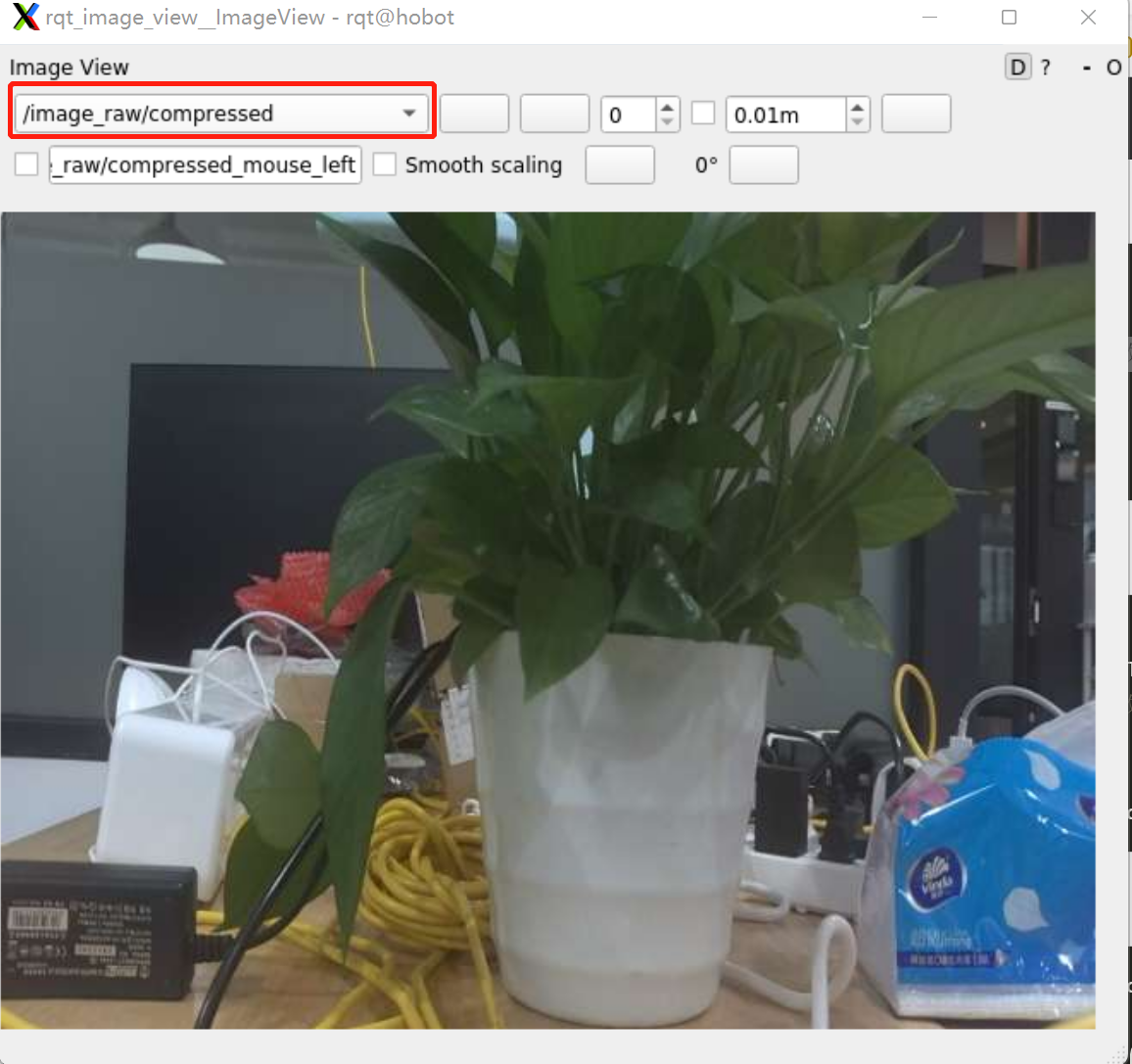
Notes
-
If ros2 topic list does not recognize the camera topic on the PC, perform the following troubleshooting steps:
-
Check if the RDK is publishing images correctly
- Foxy
- Humble
# Configure the tros.b environment
source /opt/tros/setup.bash# Configure the tros.b environment
source /opt/tros/humble/setup.bashros2 topic listOutput:
/camera_info
/hbmem_img000b0c26001301040202012020122406
/image_raw
/image_raw/compressed
/parameter_events
/rosout -
Check if the PC and RDK can ping each other;
-
Check if the PC and RDK have the same first three segments of IP address;
-
Foxglove
Introduction
Foxglove is an open-source toolkit that includes both online and offline versions. It aims to simplify the development and debugging of robotic systems. It provides a range of features for building robot applications.
In this section, we will primarily use the data recording and playback feature of Foxglove: Foxglove allows recording the data of ROS2 topics into files for subsequent playback and analysis. This is very useful for system troubleshooting, performance optimization, and algorithm debugging.
In the demonstration, we will use the hobot_visualization package developed by TogetheROS.Bot to convert intelligent inference results into ROS2 rendered topic information.
Code repository: (https://github.com/D-Robotics/hobot_visualization)
Supported Platforms
| Platform | System | Function |
|---|---|---|
| RDK X3, RDK X3 Module | Ubuntu 20.04 (Foxy), Ubuntu 22.04 (Humble) | Offline object detection, and display images and algorithm effects using Foxglove |
| RDK X5, RDK X5 Module | Ubuntu 22.04 (Humble) | Offline object detection, and display images and algorithm effects using Foxglove |
| RDK S100, RDK S100P | Ubuntu 22.04 (Humble) | Offline object detection, and display images and algorithm effects using Foxglove |
Preparation
RDK
-
Confirm that TogetheROS.Bot has been successfully installed.
-
Confirm that the PC can access the RDK via the network.
Usage
RDK
- Log in to the RDK via SSH and start the relevant programs on the board side:
- Foxy
- Humble
# Configure the tros.b environment
source /opt/tros/setup.bash
# Configure the tros.b environment
source /opt/tros/humble/setup.bash
export CAM_TYPE=fb
cp -r /opt/tros/${TROS_DISTRO}/lib/dnn_node_example/config/ .
ros2 launch hobot_visualization hobot_vis_render.launch.py
At the same time, log in to another terminal using SSH and record topic information on the board side:
- Foxy
- Humble
# Configure the tros.b environment
source /opt/tros/setup.bash
# Configure the tros.b environment
source /opt/tros/humble/setup.bash
# Record rosbag data, which will be generated in the current working directory
ros2 bag record -a
- Play rosbag data on the Foxglove online page
-
In a PC browser (chrome/firefox/edge), enter (https://foxglove.dev/studio) to access the Foxglove website.
PS: Registration is required for first-time use. You can register using a Google account or a third-party email.

-
Enter the visualization function interface.
-
Click to select the local rosbag file.
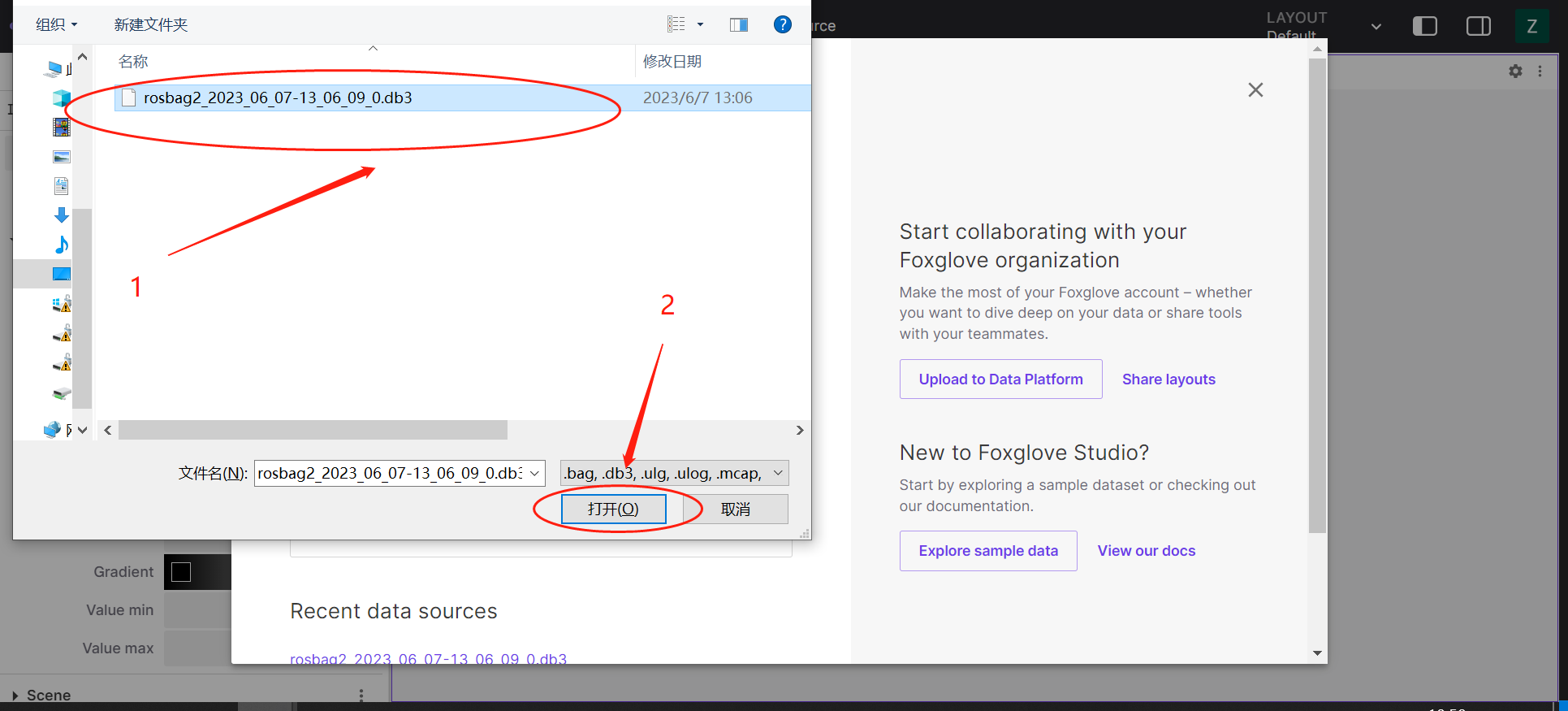
-
Open the layout interface. In the top right corner of the layout interface, click on the settings, select the icon, and open the play marker rendering message function.
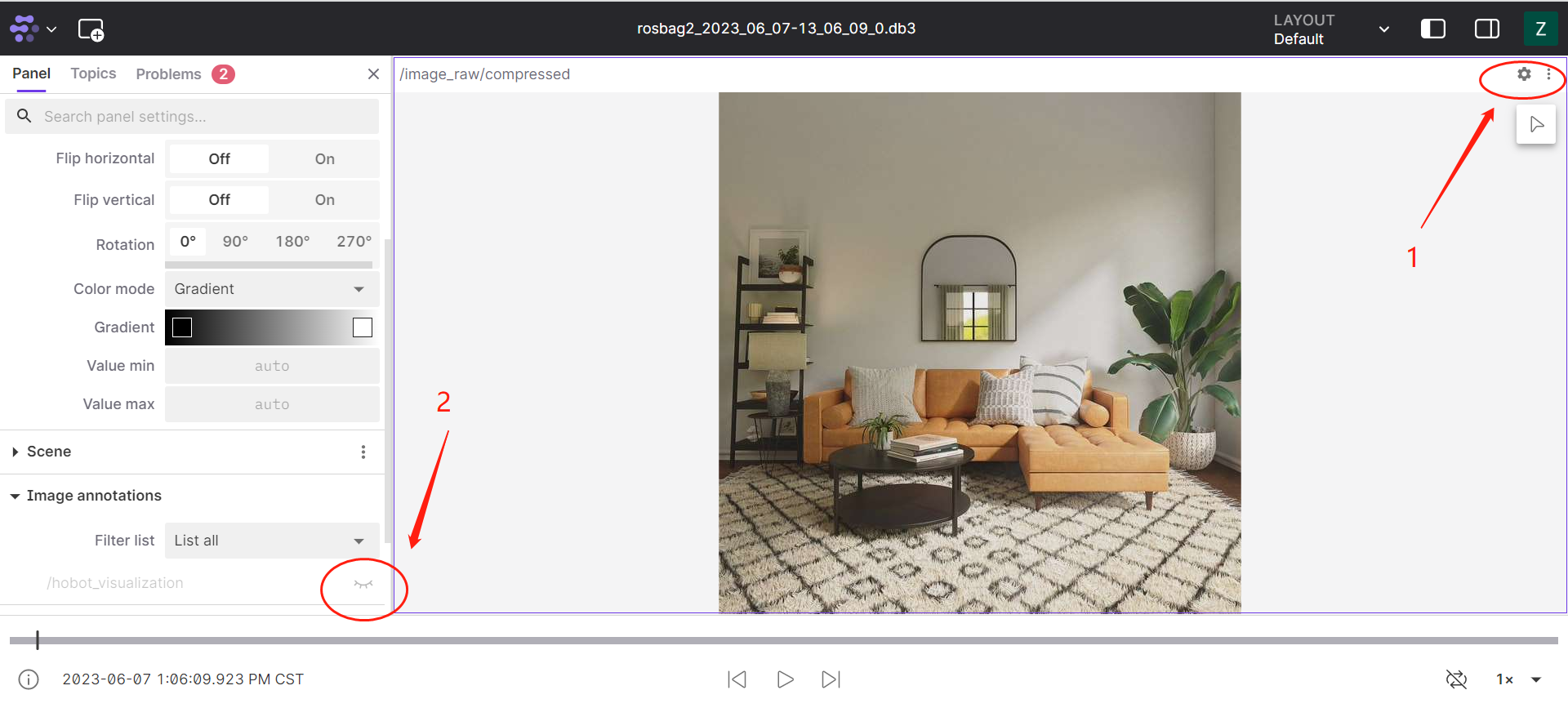
-
Click Play
-
View Data
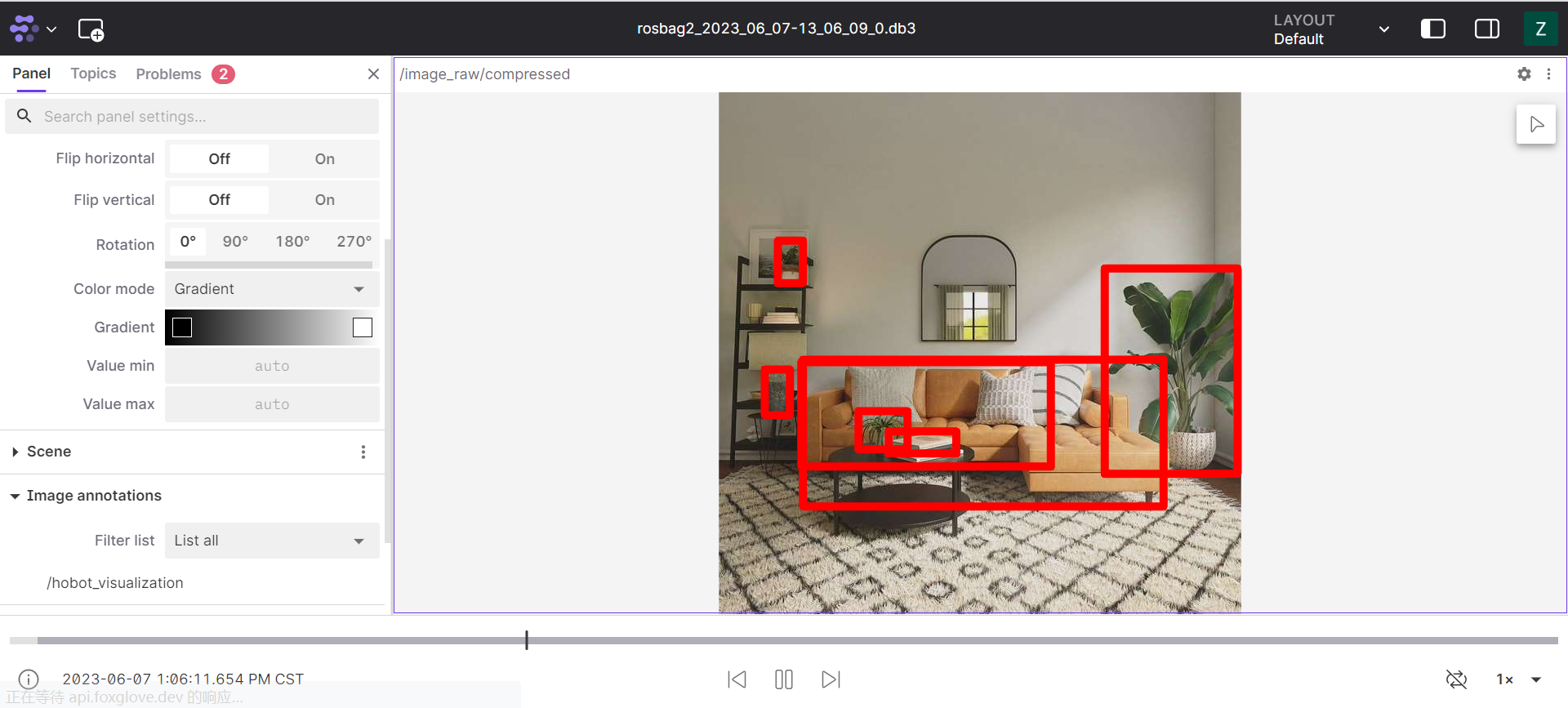
Note
-
Foxglove visualizes image data using the official ROS2 message format and supports image encoding formats. For more details, please refer to (https://foxglove.dev/docs/studio/panels/image).
-
When recording messages with
rosbag, it may record topic information from other devices. To ensure cleanrosbagdata, you can setexport ROS_DOMAIN_ID=xxx, such asexport ROS_DOMAIN_ID=1.