3.3.5 YOLOv5x Model Example Introduction
Example Overview
The YOLOv5X object detection example is a Python interface development code sample located in /app/pydev_demo/09_yolov5x_sample/, demonstrating how to use the YOLOv5X model for high-precision object detection tasks. YOLOv5X is the largest and most accurate model variant in the YOLOv5 series, offering higher detection accuracy compared to YOLOv5s, making it suitable for applications requiring higher detection precision.
Result Demonstration
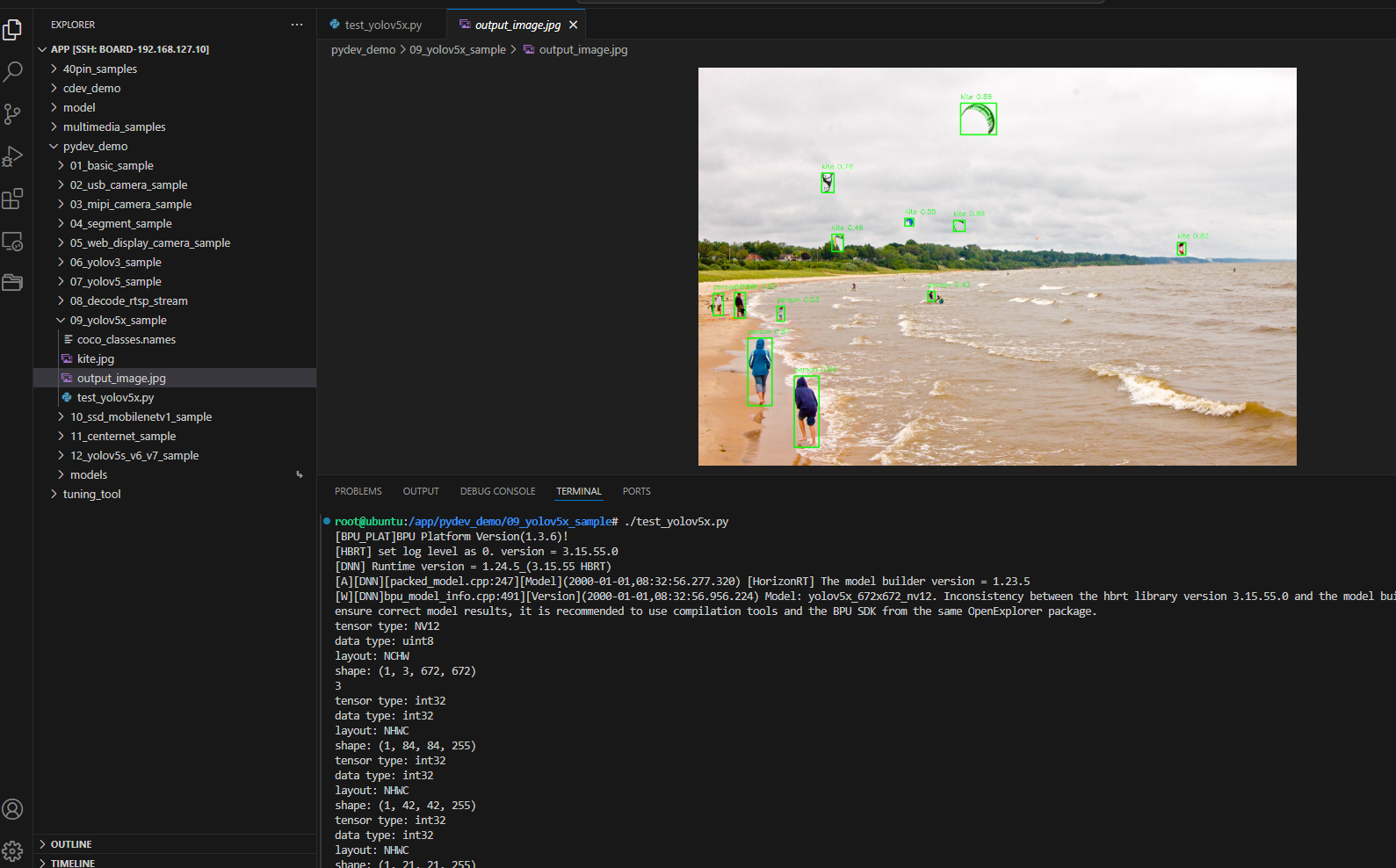
Hardware Preparation
Hardware Connection
This example only requires the RDK development board itself, with no additional peripherals needed. Ensure the development board is properly powered and the system is booted.

Quick Start
Code and Board Location
Navigate to /app/pydev_demo/09_yolov5x_sample/ to see the YOLOv5X example containing the following files:
root@ubuntu:/app/pydev_demo/09_yolov5x_sample# tree
.
├── coco_classes.names
├── kite.jpg
└── test_yolov5x.py
Compilation and Execution
The Python example does not require compilation and can be run directly:
python3 test_yolov5x.py
Execution Result
After running, the program will load the pre-trained YOLOv5X model, perform object detection on the kite.jpg image, and generate a result image with detection boxes named output_image.jpg.
root@ubuntu:/app/pydev_demo/09_yolov5x_sample# ./test_yolov5x.py
[BPU_PLAT]BPU Platform Version(1.3.6)!
[HBRT] set log level as 0. version = 3.15.55.0
[DNN] Runtime version = 1.24.5_(3.15.55 HBRT)
[A][DNN][packed_model.cpp:247][Model](2000-01-01,08:32:56.277.320) [HorizonRT] The model builder version = 1.23.5
[W][DNN]bpu_model_info.cpp:491][Version](2000-01-01,08:32:56.956.224) Model: yolov5x_672x672_nv12. Inconsistency between the hbrt library version 3.15.55.0 and the model build version 3.15.47.0 detected, in order to ensure correct model results, it is recommended to use compilation tools and the BPU SDK from the same OpenExplorer package.
tensor type: NV12
data type: uint8
layout: NCHW
shape: (1, 3, 672, 672)
3
tensor type: int32
data type: int32
layout: NHWC
shape: (1, 84, 84, 255)
tensor type: int32
data type: int32
layout: NHWC
shape: (1, 42, 42, 255)
tensor type: int32
data type: int32
layout: NHWC
shape: (1, 21, 21, 255)
inferece time is : 0.10300564765930176
postprocess time is : 0.060691237449645996
draw result time is : 0.048194289207458496
Detailed Introduction
Example Program Parameter Options
The YOLOv5X object detection example does not require command-line parameters and can be run directly. The program will automatically load the kite.jpg image in the same directory for detection processing.
Software Architecture Description
The software architecture of the YOLOv5X object detection example includes the following core components:
-
Model Loading: Use the pyeasy_dnn module to load the pre-trained YOLOv5X model
-
Image Preprocessing: Convert the input image to the NV12 format and specified size (672x672) required by the model
-
Model Inference: Call the model for forward computation to generate feature maps
-
Post-processing: Use the libpostprocess library to parse the model output and generate detection results
-
Result Visualization: Draw detection boxes and category information on the original image
-
Result Saving: Save the visualized result as an image file

API Process Description
Model Loading: models = dnn.load('../models/yolov5x_672x672_nv12.bin')
Image Preprocessing: Adjust image size and convert to NV12 format
Model Inference: outputs = models[0].forward(nv12_data)
Post-processing Configuration: Set post-processing parameters (size, threshold, etc.)
Result Parsing: Call the post-processing library to parse output tensors
Result Visualization: Draw detection boxes and label information on the original image
Result Saving: Save the result as an image file

FAQ
Q: What is the difference between YOLOv5X and YOLOv5s?
A: YOLOv5X is the largest and most accurate model variant in the YOLOv5 series, with approximately 4 times the parameters of YOLOv5s, offering higher detection accuracy but slower inference speed.
Q: What should I do if I encounter a "No module named 'hobot_dnn'" error when running the example?
A: Please ensure that the RDK Python environment is correctly installed, including the hobot_dnn module and other official dedicated inference libraries.
Q: How can I change the test image?
A: Place the new image file in the example directory and modify img_file = cv2.imread('your_image_path') in the code.
Q: What should I do if the detection results are inaccurate?
A: The YOLOv5X model is trained on the COCO dataset. For specific scenarios, fine-tuning or using a more suitable model may be necessary.
Q: How can I adjust the detection threshold?
A: Modify the value of yolov5_postprocess_info.score_threshold in the code. For example, changing it to 0.5 can increase detection sensitivity.
Q: Can real-time video stream processing be implemented?
A: The current example is designed for single images, but the code can be modified to achieve real-time object detection for video streams. Due to the large size of the YOLOv5X model, real-time processing may require reducing the frame rate or resolution.
Q: How to choose the appropriate YOLOv5 model variant?
A: Select based on application requirements: choose YOLOv5X for the highest accuracy; YOLOv5s or YOLOv5m for balanced accuracy and speed; YOLOv5n for resource-constrained environments.
Q: How to handle input images of different sizes?
A: The YOLOv5X model requires fixed-size input (672x672). The program will automatically resize the input image to this dimension.
Q: How to further improve detection accuracy?
A: Try using larger input sizes (if the model supports it) or fine-tuning the model for specific scenarios.