3.3.11 RTSP Stream Decoding Example Introduction
Example Overview
The RTSP stream decoding example is a Python interface development code sample located in /app/pydev_demo/08_decode_rtsp_stream/. It demonstrates how to obtain H.264/H.265 streams from an RTSP video stream and implement real-time video decoding and object detection functions through hardware decoding, video processing, and AI inference. This example showcases a complete video processing pipeline, including RTSP stream reception, hardware decoding, video processing, AI inference, and result display.
Result Display
Hardware Preparation
Hardware Connection
- Prepare an RDK development board
- Connect the development board to a display via an HDMI cable
- Connect an Ethernet cable to the development board
- Connect the power cable

Quick Start
Code and Board Location
Navigate to the /app/pydev_demo/08_decode_rtsp_stream/ directory. The RTSP stream decoding example includes the following files:
root@ubuntu:/app/pydev_demo/08_decode_rtsp_stream# tree
.
��├── 1080P_test.h264
├── decode_rtsp_stream.py
└── live555MediaServer
Compilation and Execution
First, perform the preparatory steps. If displaying via HDMI, use the systemctl stop lightdm command to stop the graphical interface service for optimal display performance.
The example includes a default 1080P_test.h264 file. If you want to try an H.265 format file, you can copy it from elsewhere on the board, such as from the /opt/tros/humble/lib/hobot_codec/config/1920x1080.h265 directory.
First, start the RTSP streaming media server, then run the Python script:
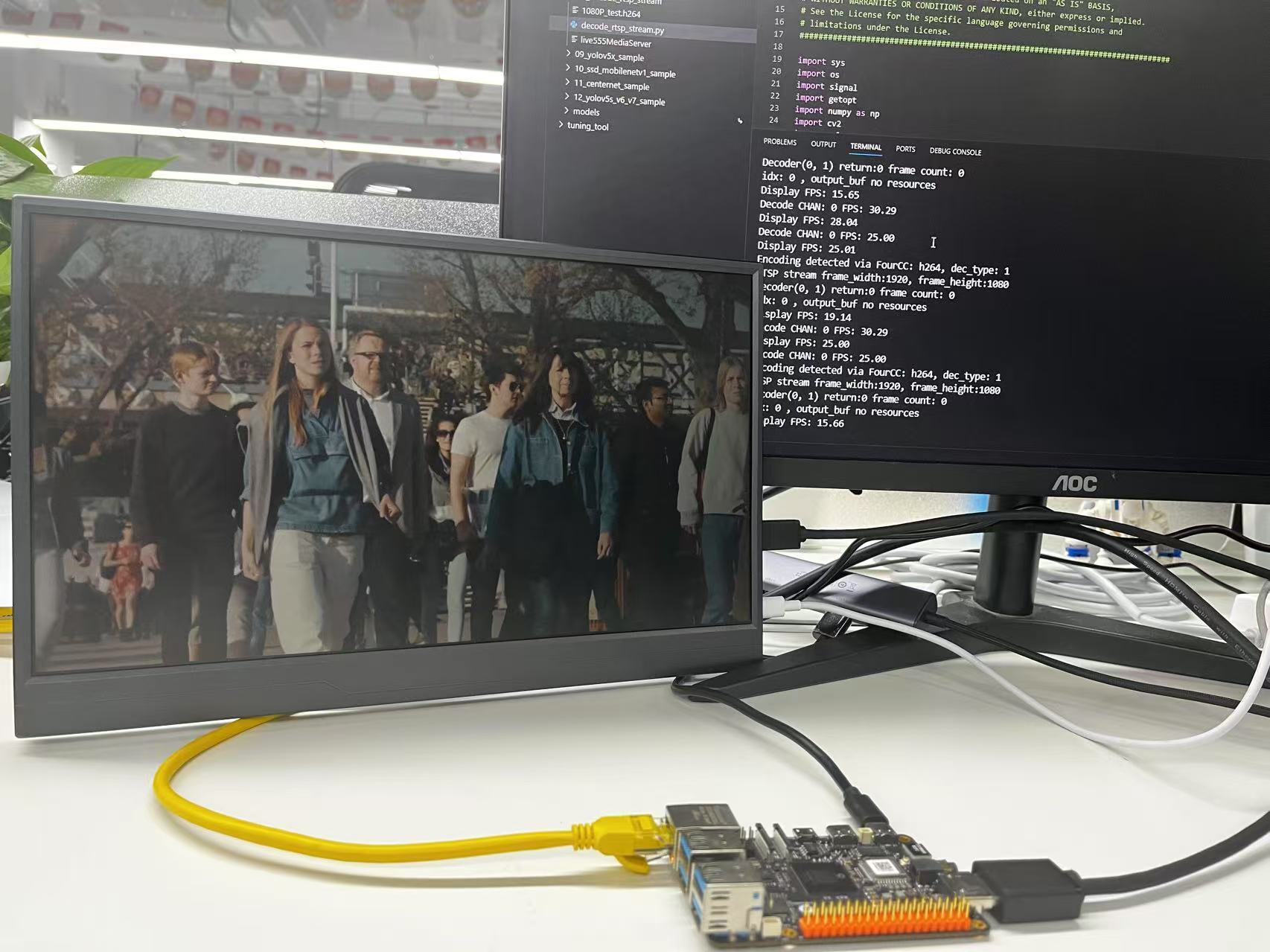
Execution Result
# Stop the graphical interface service for optimal display performance
systemctl stop lightdm
# Start the RTSP streaming media server
./live555MediaServer &
# Run the RTSP stream decoding example (h264)
python3 decode_rtsp_stream.py -u rtsp://127.0.0.1/1080P_test.h264 -d 1 -a 1
After running, the program will connect to the RTSP streaming media server, decode the video stream, perform object detection, and display the results via HDMI:
root@ubuntu:/app/pydev_demo/08_decode_rtsp_stream#./live555MediaServer &
version 1.01 (LIVE555 Streaming Media library version 2020.07.09).
Play streams from this server using the URL
rtsp://192.168.127.10/<filename>
where <filename> is a file present in the current directory.
Each file's type is inferred from its name suffix:
".264" => a H.264 Video Elementary Stream file
".265" => a H.265 Video Elementary Stream file
".aac" => an AAC Audio (ADTS format) file
".ac3" => an AC-3 Audio file
".amr" => an AMR Audio file
".dv" => a DV Video file
".m4e" => a MPEG-4 Video Elementary Stream file
".mkv" => a Matroska audio+video+(optional)subtitles file
".mp3" => a MPEG-1 or 2 Audio file
".mpg" => a MPEG-1 or 2 Program Stream (audio+video) file
".ogg" or ".ogv" or ".opus" => an Ogg audio and/or video file
".ts" => a MPEG Transport Stream file
(a ".tsx" index file - if present - provides server 'trick play' support)
".vob" => a VOB (MPEG-2 video with AC-3 audio) file
".wav" => a WAV Audio file
".webm" => a WebM audio(Vorbis)+video(VP8) file
See http://www.live555.com/mediaServer/ for additional documentation.
(We use port 80 for optional RTSP-over-HTTP tunneling, or for HTTP live streaming (for indexed Transport Stream files only).)
root@ubuntu:/app/pydev_demo/08_decode_rtsp_stream# ./decode_rtsp_stream.py
['rtsp://127.0.0.1/1080P_test.h264']
Encoding detected via FourCC: h264, dec_type: 1
RTSP stream frame_width:1920, frame_height:1080
Decoder(0, 1) return:0 frame count: 0
Opened DRM device: /dev/dri/card0
.............
.............
.............
To try decoding an H.265 file, refer to the following commands:
# Stop the graphical interface service for optimal display performance
systemctl stop lightdm
# Copy the H.265 file to the example directory.
cp /opt/tros/humble/lib/hobot_codec/config/1920x1080.h265 /app/pydev_demo/08_decode_rtsp_stream/
# Run the RTSP stream decoding example (h265)
python3 decode_rtsp_stream.py -u rtsp://127.0.0.1/1920x1080.h265 -d 1
root@ubuntu:/app/pydev_demo/08_decode_rtsp_stream# systemctl stop lightdm
root@ubuntu:/app/pydev_demo/08_decode_rtsp_stream# ./live555MediaServer &
[1] 4030
LIVE555 Media Server
version 1.01 (LIVE555 Streaming Media library version 2020.07.09).
root@ubuntu:/app/pydev_demo/08_decode_rtsp_stream# Play streams from this server using the URL
rtsp://10.0.0.32/<filename>
where <filename> is a file present in the current directory.
Each file's type is inferred from its name suffix:
".264" => a H.264 Video Elementary Stream file
".265" => a H.265 Video Elementary Stream file
".aac" => an AAC Audio (ADTS format) file
".ac3" => an AC-3 Audio file
".amr" => an AMR Audio file
".dv" => a DV Video file
".m4e" => a MPEG-4 Video Elementary Stream file
".mkv" => a Matroska audio+video+(optional)subtitles file
".mp3" => a MPEG-1 or 2 Audio file
".mpg" => a MPEG-1 or 2 Program Stream (audio+video) file
".ogg" or ".ogv" or ".opus" => an Ogg audio and/or video file
".ts" => a MPEG Transport Stream file
(a ".tsx" index file - if present - provides server 'trick play' support)
".vob" => a VOB (MPEG-2 video with AC-3 audio) file
".wav" => a WAV Audio file
".webm" => a WebM audio(Vorbis)+video(VP8) file
See http://www.live555.com/mediaServer/ for additional documentation.
(We use port 80 for optional RTSP-over-HTTP tunneling, or for HTTP live streaming (for indexed Transport Stream files only).)
root@ubuntu:/app/pydev_demo/08_decode_rtsp_stream#
root@ubuntu:/app/pydev_demo/08_decode_rtsp_stream#
root@ubuntu:/app/pydev_demo/08_decode_rtsp_stream# python3 decode_rtsp_stream.py -u rtsp://127.0.0.1/1920x1080.h265 -d 1
['rtsp://127.0.0.1/1920x1080.h265']
Encoding detected via FourCC: hevc, dec_type: 2
RTSP stream frame_width:1920, frame_height:1080
Decoder(0, 2) return:0 frame count: 0
Opened DRM device: /dev/dri/card0
1920x1080
1280x800
1280x720
720x576
720x480
640x480
Resolution 1920x1080 exists in the list.
Opened DRM device: /dev/dri/card0
DRM is available, using libdrm for rendering.
------------------------------------------------------
Plane 0:
Plane ID: 41
Src W: 1920
Src H: 1080
......
......
......
Detailed Introduction
Example Program Parameter Options
The RTSP stream decoding example supports the following command-line parameters:
# Basic usage
python3 decode_rtsp_stream.py [-u <rtsp_url>] [-d] [-a]
# Multi-stream example
python3 decode_rtsp_stream.py [-u <rtsp_url1;rtsp_url2>] [-d] [-a]
Parameter description:
-u, --rtsp_url: Specify the RTSP stream URL. Supports multiple stream URLs separated by semicolons.
-d: Enable display function (0 - disable, 1 - enable)
-a: Enable AI inference function (display function is automatically enabled when this is enabled)
Software Architecture Description
The RTSP stream decoding example is slightly complex as it requires coordination with an RTSP server and uses a multi-threaded architecture internally. Therefore, a component-level architecture diagram is provided for explanation.
It includes three core threads:
-
RTSP Stream Decoding Thread (DecodeRtspStream):
Connect to the RTSP streaming media server
Automatically detect stream encoding format (H.264/H.265/MJPEG)
Use hardware decoder to decode the video stream
Manage decoded frame queue -
Video Display Thread (VideoDisplay):
Initialize HDMI display
Use VPS for video processing (scaling, format conversion)
Send processed video frames to the display queue -
AI Inference Thread (AiInference):
Load object detection model (FCOS)
Perform inference on video frames
Post-process and draw detection results

API Flow Description

FAQ
Q: What should I do if the example prompts "fail to open rtsp" when running?
A: Ensure the RTSP streaming media server is started correctly and the network connection is normal. You can use netstat -tlnp to check the server port status.
Q: How to view supported encoding formats?
A: The program automatically detects the stream encoding format and outputs the detection result in the console,
e.g., "Encoding detected via FourCC: h264, dec_type: 1".
Q: What to do if the video stream has high latency?
A: Try reducing the resolution or frame rate of the video stream, or use a lighter object detection model.
Q: How to process multiple RTSP streams simultaneously?
A: Use semicolons to separate multiple RTSP addresses, e.g., -u rtsp://url1;rtsp://url2. Each stream will use a different decoding channel.
Q: How to modify the object detection model?
A: Modify the model loading path in the code, e.g., models = dnn.load('../models/your_model.bin').
Q: What to do if the display is abnormal or has no output?
A:
(1) Check the HDMI connection and ensure the display service is stopped (e.g., using systemctl stop lightdm).
(2) Check if the display resolution matches the output video resolution. If not, find a suitable source file.
Q: How to save the processed video stream?
A: You can add video saving logic in the code, for example, using OpenCV's VideoWriter class to save the video file.
Q: How to adjust the detection threshold?
A: Modify the value of fcos_postprocess_info.score_threshold in the code. For example, changing it to 0.5 can increase detection sensitivity.
Q: Which RTSP transport protocols are supported?
A: TCP and UDP transport protocols are supported, depending on the RTSP server configuration.