Intelligent Voice
Introduction
The D-Robotics intelligent voice algorithm adopts a local offline mode, subscribes to audio data and sends it to BPU for processing, and then publishes messages such as wake-up, command word recognition, DOA(Direction of Arrival), and ASR(Automatic Speech Recognition). The implementation of intelligent voice function corresponds to the hobot_audio package of TogetheROS.Bot, which is suitable for the circular and linear four-microphone arrays supported by RDK.
Code repository: (https://github.com/D-Robotics/hobot_audio.git)
Application scenarios: The intelligent voice algorithm can recognize wake-up words and custom command words in audio, interpret speech content as corresponding instructions or convert it into text, and can achieve functions such as voice control and speech translation. It is mainly used in areas such as smart home, intelligent cockpit, and smart wearables.
Example of voice-controlled car movement: Voice-controlled car movement
Supported Platforms
| Platform | System | Function |
|---|---|---|
| RDK X3, RDK X5 | Ubuntu 20.04 (Foxy), Ubuntu 22.04 (Humble) | Start the audio module algorithm and display the results in the terminal |
Note: Only supports RDK X3.
Preparation
-
The RDK has been burned with the Ubuntu 20.04/22.04 system image provided by D-Robotics.
-
The TogetheROS.Bot has been successfully installed on the RDK.
-
The intelligent voice algorithm package has been successfully installed on the RDK, installation command:
- Foxy
- Humble
sudo apt update
sudo apt install tros-hobot-audiosudo apt update
sudo apt install tros-humble-hobot-audio -
Connect the circular or linear four-microphone audio board to the RDK according to the following method.
Connect the audio board
Interface connection
Circular microphone array
The circular microphone board is an integrated design, as shown in the following image:
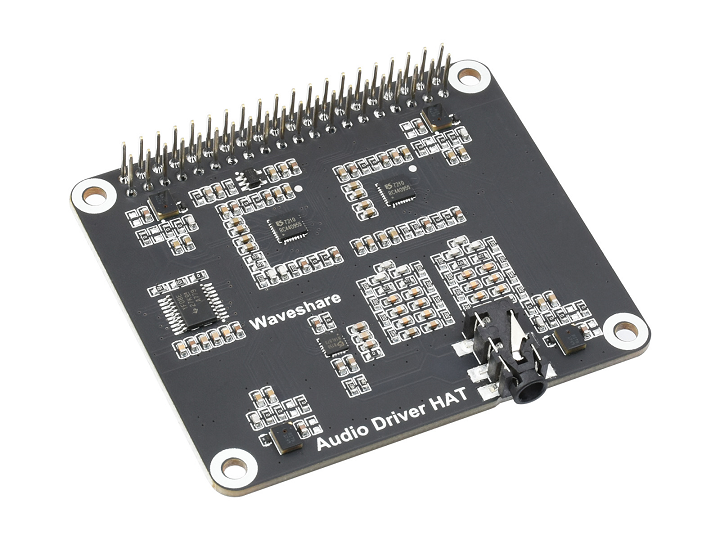
Purchase link:
(https://www.waveshare.net/shop/Audio-Driver-HAT.htm)
Connection steps:
-
Connect the microphone board to the RDK X3 40-pin GPIO GPIO interface. After the connection, it looks like the following image:
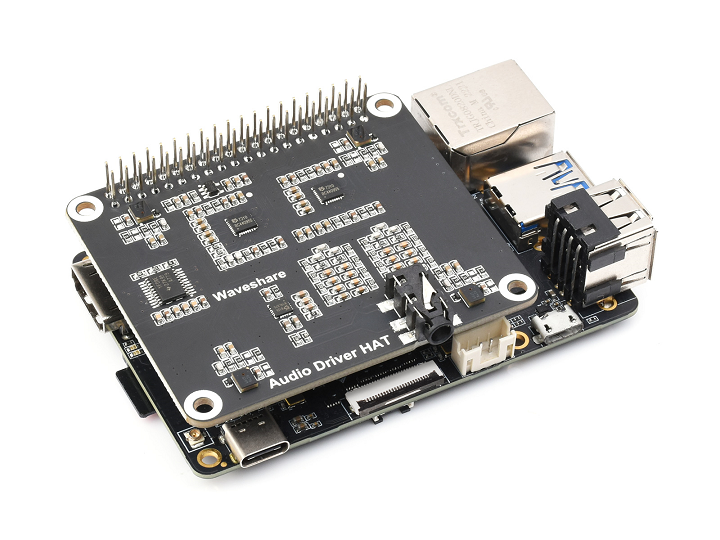
-
Connect the power supply, network cable, etc.
Linear Microphone Array
The linear microphone array consists of an audio adapter board and a linear microphone board. The physical diagram and connection instructions are as follows:
Audio adapter board:

Linear microphone board:
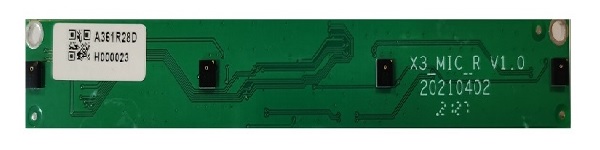
-
First, connect the RDK X3 to the audio adapter board, aligning the pins of both devices. The connection is shown in the following figure:
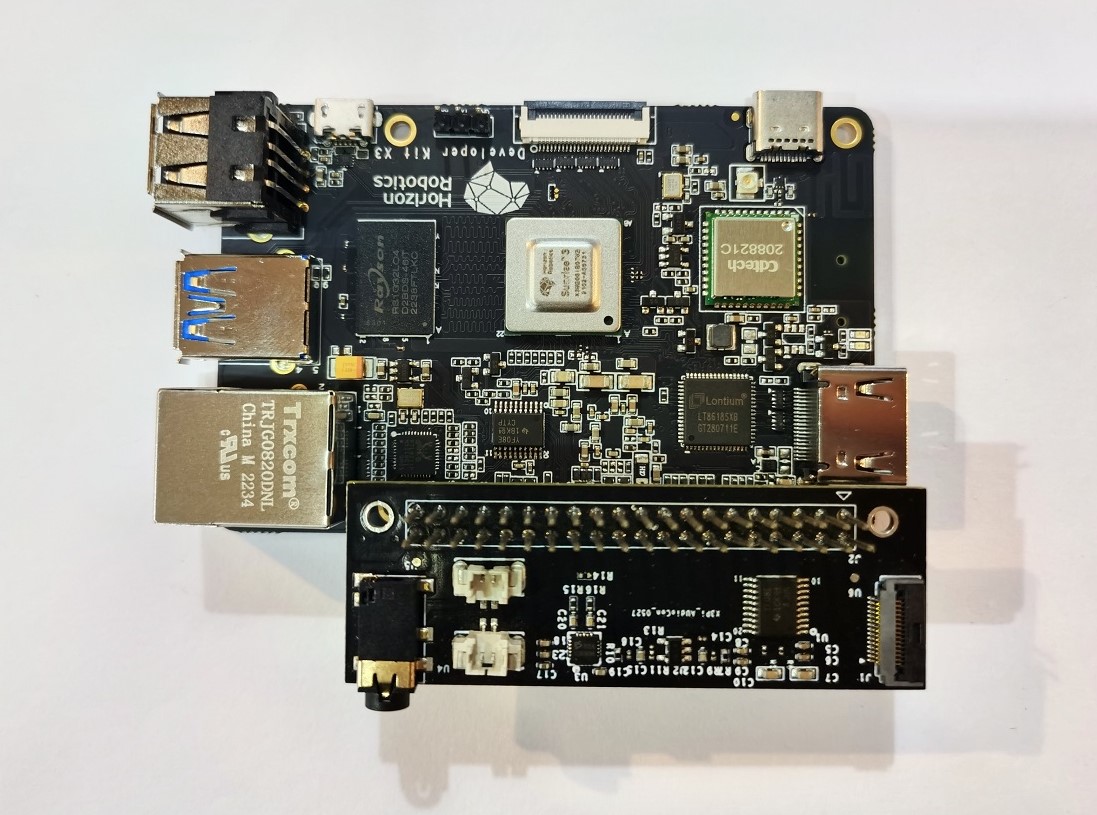

-
Next, connect the RDK X3 to the microphone array board. The adapter board FPC interface is connected to the microphone array board with a 15-pin FFC cable.The connection is shown in the following figure:
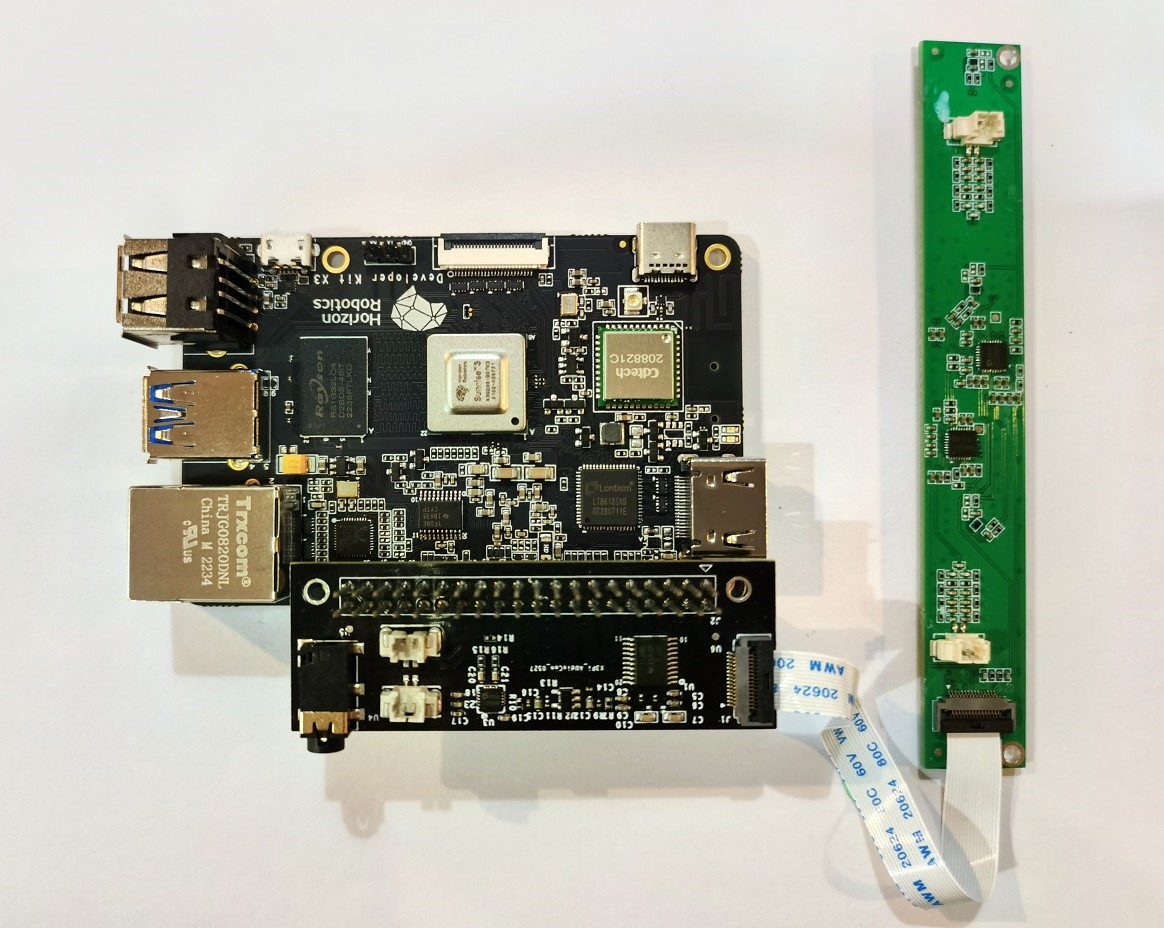

-
Connect the AEC line.
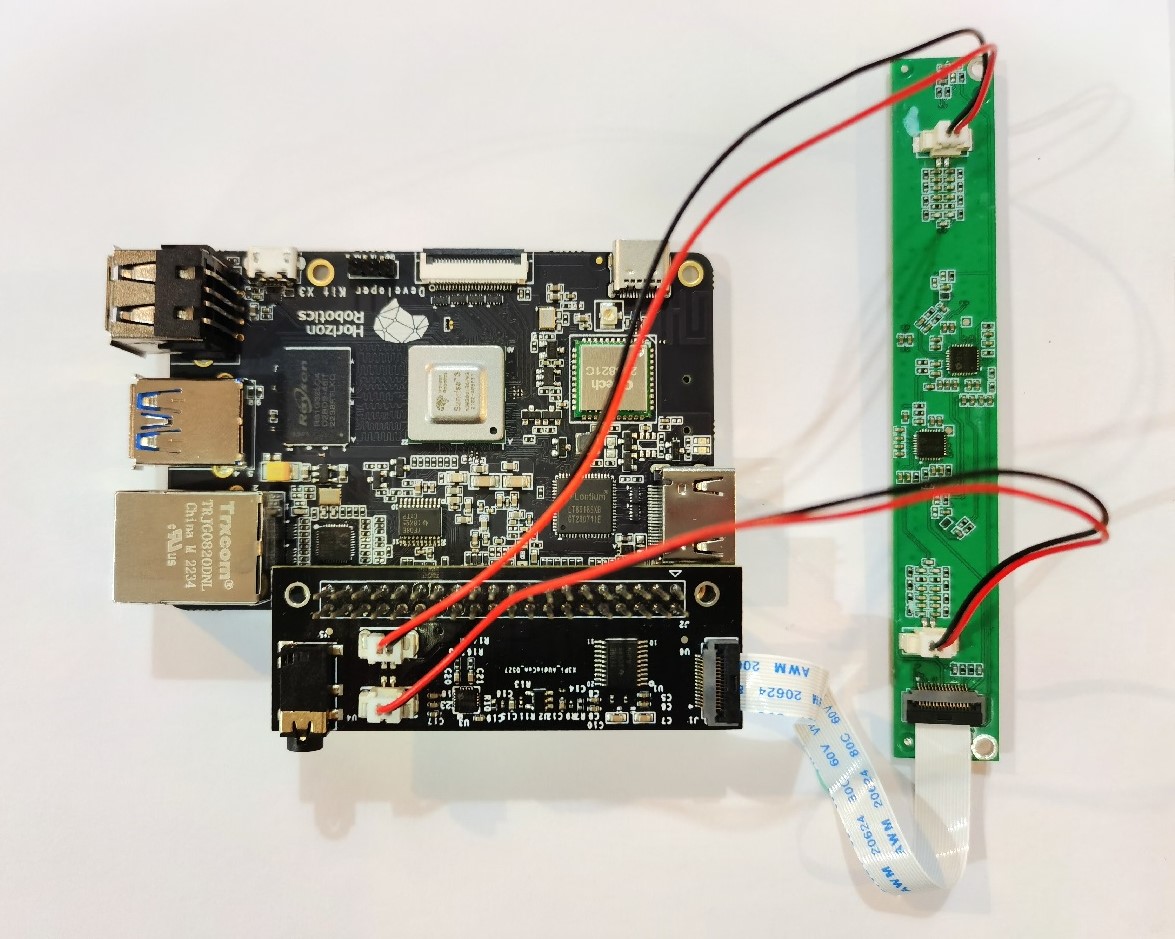
-
Connect the power supply, network cable, etc.
Power Check
After connecting the RDK to the microphone array, power it on. Use the command i2cdetect -r -y 0 to check the device connection. If the connection is successful, three addresses should be read on the I2C bus. See the following figure:
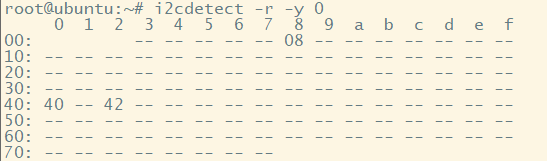
If no devices are detected, please check the device connection again.
Configure the Audio Board
For the first-time use of the audio board, use srpi-config to configure it. Refer to the RDK user manual's Audio Adapter Board section for configuration instructions.
Usage
After the smart voice hobot_audio package starts running, it will capture audio from the microphone array and send the captured audio data to the smart voice algorithm SDK module for intelligent processing. It will output wake-up events, command words, ASR results, and other smart information. Wake-up events and command words are published as audio_msg::msg::SmartAudioData type messages, while ASR results are published as std_msgs::msg::String type messages.
The specific process is shown in the following diagram:
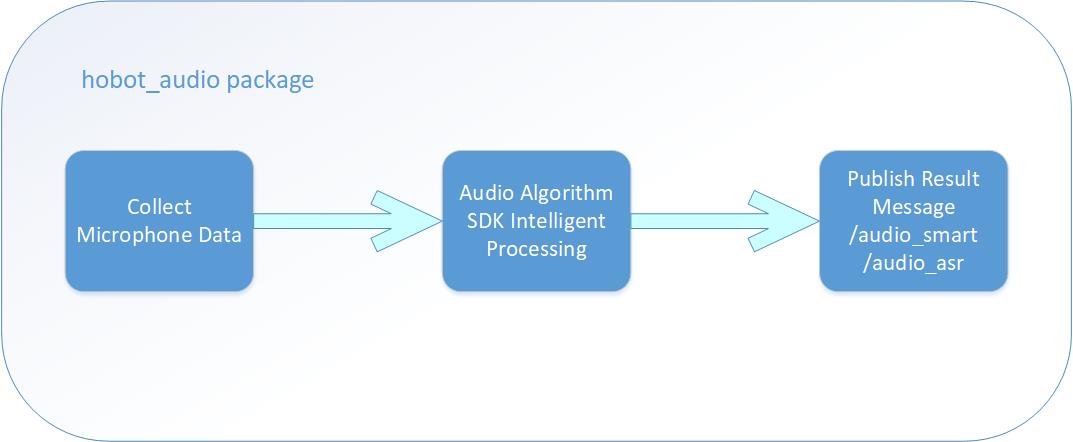
The smart voice function supports ASR recognition after denoising the raw audio. The default wake word and command words are defined in the config/hrsc/cmd_word.json file under the root directory of the smart voice function module, which are set in chinese as:
{
"cmd_word": [
"地瓜你好",
"向前走",
"向后退",
"向左转",
"向右转",
"停止运动"
]
}
The wake-up word and command words can be configured according to your needs. Changing the wake-up word may affect the default wake-up word and command word effects. It is recommended to use Chinese wake-up words and command words, preferably phrases that are easy to pronounce, with a length of 3 to 5 characters.
In addition, the smart voice function supports outputting the DOA (Direction of Arrival) of the sound source, measured in degrees. For a circular microphone array, the DOA angle range is 0 degrees to 360 degrees, and for a linear microphone array, the DOA angle range is 0 degrees to 180 degrees.
The relative position relationship of the angles is closely related to the installation position of the microphones. Here are the DOA angle diagrams for a circular microphone array and a linear microphone array:
DOA angle diagram for circular microphone array:
![]()
DOA angle diagram for linear microphone array:
![]()
To run the hobot_audio package on the RDK:
- Copy the configuration file
- Foxy
- Humble
# Configure the tros.b environment
source /opt/tros/setup.bash
# Configure the tros.b environment
source /opt/tros/humble/setup.bash
# Copy the configuration file required for running the example from the installation path of tros.b.
cp -r /opt/tros/${TROS_DISTRO}/lib/hobot_audio/config/ .
-
Confirm the configuration file
The default configuration of the configuration file config/audio_config.json is as follows:
{
"micphone_enable": 1,
"micphone_name": "hw:0,0",
"micphone_rate": 16000,
"micphone_chn": 8,
"micphone_buffer_time": 0,
"micphone_nperiods": 4,
"micphone_period_size": 512,
"voip_mode": 0,
"mic_type": 0,
"asr_mode": 0,
```"asr_channel": 3,
"save_audio": 0
}The configuration that needs to be confirmed includes: microphone device number, microphone array type, and whether ASR results need to be published.
- The microphone device number is set through the
micphone_namefield, with the default value being "hw:0,0", which represents audio device Card0 Device0. The device number can be checked using the commandls /dev/snd, such as: "pcmC0D1c"; the last letter "c" represents capture device, C0 represents Card0, D1 represents Device1, and this parameter can be modified to "hw:0,1". - The microphone array type is set through the
mic_typefield, with the default value being0, which represents the circular microphone array. If a linear microphone array is used, this field should be modified to1. - ASR output is set through the
asr_modefield, with the default value being0, which means no ASR results will be outputted. To enable ASR output, this field needs to be changed to1or2, where1means performing ASR recognition and publishing results once after wake-up, and2means continuously performing ASR recognition and publishing results.
- The microphone device number is set through the
-
Configure the tros.b environment and launch the application
- Foxy
- Humble
# Configure the tros.b environment
source /opt/tros/setup.bash
# Disable debug print information
export GLOG_minloglevel=3
# Start the launch file
ros2 launch hobot_audio hobot_audio.launch.py
# Configure the tros.b environment
source /opt/tros/humble/setup.bash
# Disable debug print information
export GLOG_minloglevel=3
# Start the launch file
ros2 launch hobot_audio hobot_audio.launch.py
Result Analysis
The following information is outputted on the terminal:
alsa_device_init, snd_pcm_open. handle((nil)), name(hw:0,0), direct(1), mode(0)
snd_pcm_open succeed. name(hw:0,0), handle(0x557d6e4d00)
Rate set to 16000Hz (requested 16000Hz)
Buffer size range from 16 to 20480
Period size range from 16 to 10240
Requested period size 512 frames
Periods = 4
was set period_size = 512
was set buffer_size = 2048
alsa_device_init. hwparams(0x557d6e4fa0), swparams(0x557d6e5210)
The above log shows that the audio device initialization is successful, and the audio device is opened for audio collection.
When a person speaks the Chinese command words "地瓜你好", "向前走", "向左转", "向右转", "向后退" one by one next to the microphone, the speech algorithm SDK outputs the recognition results after intelligent processing, and the log shows the following:
recv hrsc sdk event wakeup success, wkp count is 1
[WARN] [1657869437.600230208] [hobot_audio]: recv event:0
recv hrsc sdk doa data: 100
recv hrsc sdk command data: Go forward
[WARN] [1657869443.870029101] [hobot_audio]: recv cmd word: Walk forward
recv hrsc sdk doa data: 110
recv hrsc sdk command data: Turn left
[WARN] [1657869447.623147766] [hobot_audio]: recv cmd word: Turn left
recv hrsc sdk doa data: 100
recv hrsc sdk command data: Turn right
[WARN] [1657869449.865822772] [hobot_audio]: recv cmd word: Turn right
recv hrsc sdk doa data: 110
recv hrsc sdk command data: Move backward
[WARN] [1657869452.313969277] [hobot_audio]: recv cmd word: Move backward
log shows that the voice commands "向前走", "向左转", "向右转"and "向后退" are recognized, and the DOA angle information is output, e.g. "recv hrsc sdk doa data: 110" indicates that the DOA angle is 110 degrees.
The default topic name for the smart audio messages published by hobot_audio is: /audio_smart. In another terminal, you can use the command ros2 topic list to query the information of this topic:
$ ros2 topic list
/audio_smart
If ASR output is enabled, the message topic published is: /audio_asr, and the ros2 topic list result is:
$ ros2 topic list
/audio_smart
/audio_asr