Visual SLAM
Introduction
SLAM stands for Simultaneous Localization and Mapping. ORB-SLAM3 is one of the most researched algorithms in this field. TogetheROS.Bot integrates, improves, and optimizes ORB-SLAM3 to facilitate the development of visual SLAM-based applications.
- Integrated and adapted the SuperPoint feature extraction model to optimize the robustness of image feature extraction in visual SLAM's frontend, and reduce CPU workload. The model is converted to a fixed-point model runnable on the RDK using the D-Robotics floating-point model conversion tool, thus reducing the CPU workload of RDK.
- Wrapped the point cloud and pose information publishing, as well as image and IMU subscribing of ORB-SLAM3 with ROS2.
- Added Track asynchronous interface to separate feature extraction and feature point tracking into different threads, improving processing frame rate and facilitating practical engineering applications.
- Added bag-of-words library creation program to help developers build their own bag-of-words libraries.
In this chapter, ORB-SLAM3 is used as the mapping algorithm, and the EuRoC open dataset and RealSense D435i camera are used as the data sources for testing.
Code repository: (https://github.com/D-Robotics/orb_slam3)
Application scenarios: Visual SLAM algorithm can calculate the three-dimensional structure of the environment while computing its own position and orientation, enabling real-time localization and map construction. It is mainly used in fields such as autonomous driving, smart homes, and 3D reconstruction.
SLAM Mapping Example: SLAM Mapping
Supported Platforms
| Platform | System |
|---|---|
| RDK X3, RDK X3 Module, RDK X5 | Ubuntu 20.04 (Foxy), Ubuntu 22.04 (Humble) |
Note: SuperPoint optimization only supports RDK X3, RDK X3 Module, RDK X5 platforms.
Preparation
-
RDK is flashed with the provided Ubuntu 20.04/22.04 system image.
-
TogetheROS.Bot is successfully installed on RDK.
-
ORB-SLAM3 algorithm package is successfully installed on RDK using the command:
- Foxy
- Humble
sudo apt update
sudo apt install tros-orb-slam3 tros-orb-slam3-example-ros2sudo apt update
sudo apt install tros-humble-orb-slam3 tros-humble-orb-slam3-example-ros2 -
RealSense D435i camera is installed on RDK.
-
EuRoC open dataset.
-
A PC on the same network segment as RDK, with Ubuntu 20.04, ROS2 Foxy Desktop edition, and data visualization tool Rviz2 installed.
Usage
ORB-SLAM3 project itself integrates various types of test programs, such as mono/stereo and mono/stereo+IMU, and also classifies them according to different benchmark datasets and sensors.
Use EuRoC Dataset
Dataset URL: (http://robotics.ethz.ch/~asl-datasets/ijrr_euroc_mav_dataset/vicon_room2/V2_01_easy/V2_01_easy.zip). After downloading the dataset, go to the ORB-SLAM3 project directory. Extract the dataset and the bag-of-words library to your local machine, and run the test program. If you want to achieve a higher frame rate, you can overclock the RDK CPU, but this will also increase power consumption.
Command to run:
- Foxy
- Humble
source /opt/tros/setup.bash
source /opt/tros/humble/setup.bash
# Overclock X3 CPU to 1.5GHz
sudo bash -c 'echo 1 > /sys/devices/system/cpu/cpufreq/boost'
# Enable X3 CPU performance mode
sudo bash -c 'echo performance > /sys/devices/system/cpu/cpufreq/policy0/scaling_governor'
# Go to the ORB_SLAM3 project directory
cd /opt/tros/${TROS_DISTRO}/share/orb_slam3
# Unzip the dataset - V2_01_easy.zip needs to be downloaded separately!
unzip V2_01_easy.zip -d V2_01_easy
# Extract the bag-of-words library
tar -xvf ./Vocabulary/ORBvoc.txt.tar.gz
# Grant execution permission to the program
sudo chmod +x ./Examples/Monocular/mono_euroc
# Run the program - V2_01_easy directory is the directory of the EuRoC open dataset downloaded from the internet, developers need to download it themselves!
./Examples/Monocular/mono_euroc ./ORBvoc_refine.txt ./Examples/Monocular/EuRoC.yaml ./V2_01_easy/ ./Examples/Monocular/EuRoC_TimeStamps/V201.txt
The program will take some time to load the bag-of-words library. After a while, the program will print the current frame rate.
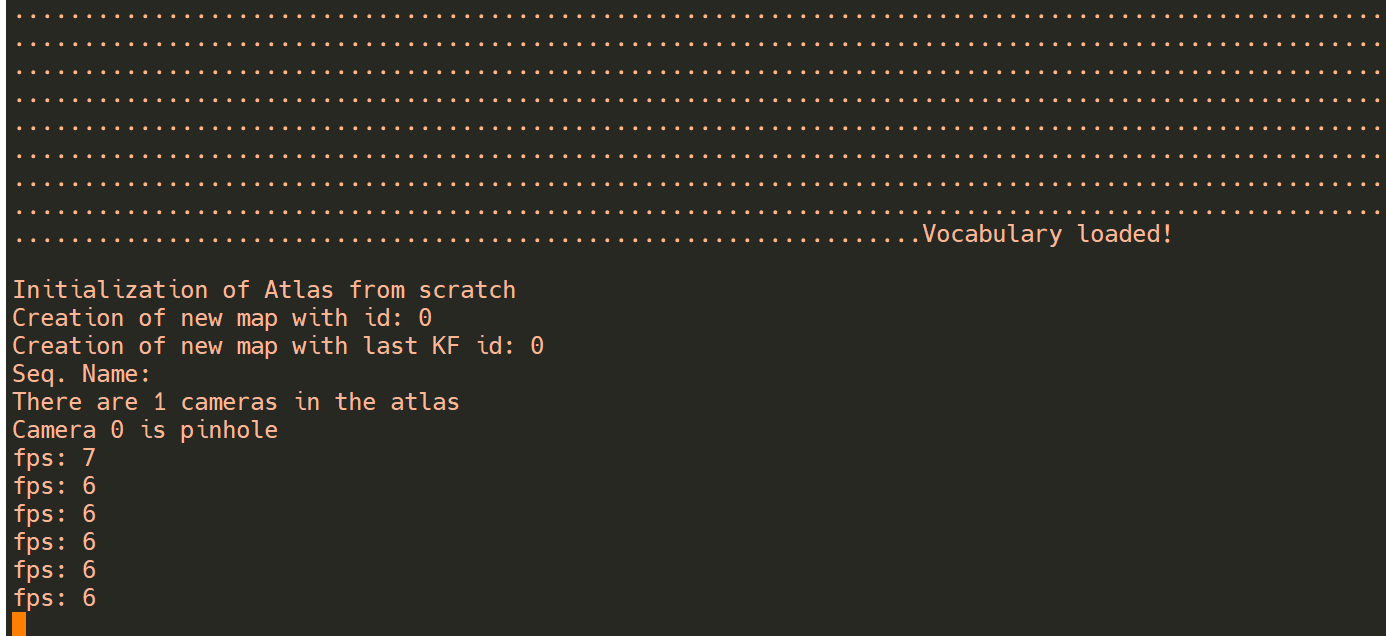
Use RealSense D435i Camera
The tros.b has developed a set of sample programs based on ORB-SLAM3 and ROS2, which integrate image and IMU data subscriptions and publish map point clouds, poses, and travel trajectories as topics. It is convenient to observe the running result of the program through the visualization software Rviz2, which helps developers in ROS2 development and debugging of ORB-SLAM3.
The latest version of the image has applied UVC and HID driver patches for the RealSense series camera to the kernel. After installing the RealSense SDK and ROS2 package using the apt command, you can directly use the test program. The installation method for ROS2 package coexisting with tros.b can be found in Using ROS2 package
- Foxy
- Humble
# Configure the tros.b environment
source /opt/tros/setup.bash
# Configure the tros.b environment
source /opt/tros/humble/setup.bash
echo $ROS_DISTRO
sudo apt-get install ros-$ROS_DISTRO-librealsense2* -y
sudo apt-get install ros-$ROS_DISTRO-realsense2-camera -y
sudo apt-get install ros-$ROS_DISTRO-realsense2-description -y
After installation, we start the Realsense camera as an image publishing node and the visual SLAM node as an image subscriber. It subscribes to the image topic and publishes pose and point cloud information.
Next, we log in to RDK using the root account (password: root) and start the Realsense D435i camera. Otherwise, insufficient permissions will prevent the camera from starting correctly.
- Foxy
- Humble
# Configure the tros.b environment
source /opt/tros/setup.bash
# Configure the tros.b environment
source /opt/tros/humble/setup.bash
ros2 launch realsense2_camera rs_launch.py enable_depth:=false enable_color:=false enable_infra1:=true depth_module.profile:=640x480x15
After the camera is started, you can observe the following logs from the console:
Next, we start the visual SLAM node:
- Foxy
- Humble
source /opt/tros/setup.bash
source /opt/tros/humble/setup.bash
# Overclock X3 CPU to 1.5GHz
sudo bash -c 'echo 1 > /sys/devices/system/cpu/cpufreq/boost'
# Enable X3 CPU performance mode
sudo bash -c 'echo performance > /sys/devices/system/cpu/cpufreq/policy0/scaling_governor'
# Enter working directory
cd /opt/tros/${TROS_DISTRO}/share/orb_slam3
# Unzip the bag-of-words library
tar -xvf ./Vocabulary/ORBvoc.txt.tar.gz
# Start ORB-SLAM3 monocular processing node
ros2 run orb_slam3_example_ros2 mono ./ORBvoc.txt ./Examples/Monocular/RealSense_D435i.yaml
The visual SLAM node on the RDK starts and receives camera image data, and then starts printing the current frame rate "fps".
At the same time, open the Rviz2 visualization software on the PC (in the same network segment as the tros.b), add relevant visualization information, and subscribe to the following topics:
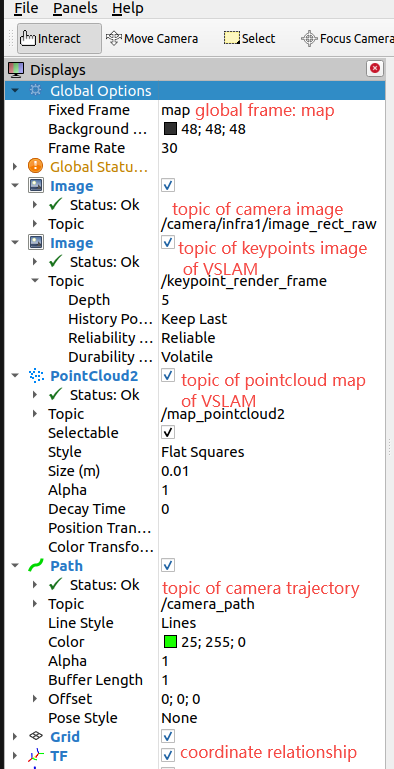
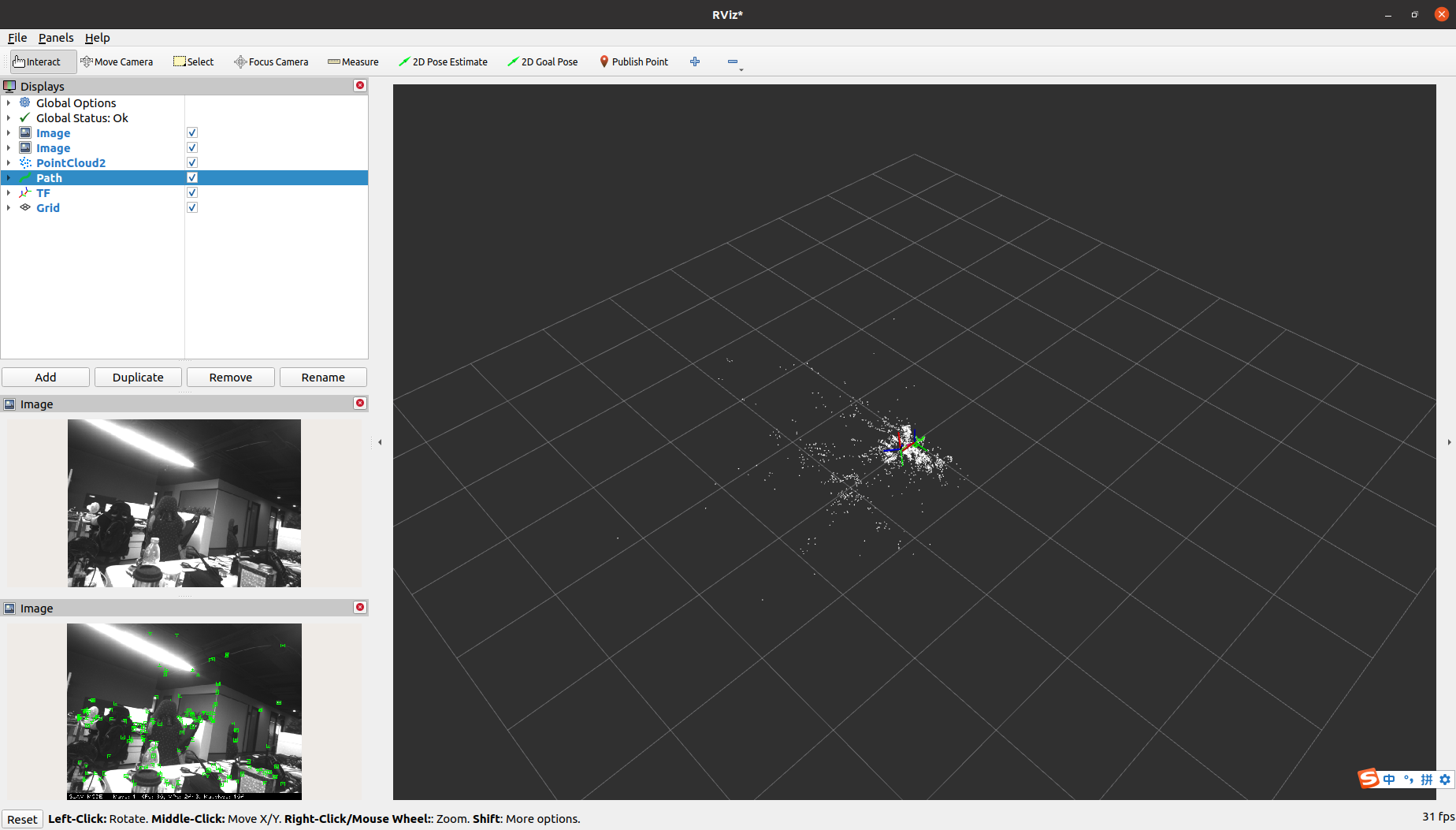
After subscribing to the topics, you can observe the rendering results of the feature points in the RVIZ2 software, and also observe the generated white map point cloud and green camera trajectory information on the right side of the window as the camera moves.
Using SuperPoint optimized ORB-SLAM3
As we all know, deep learning methods have shown amazing advantages and potential compared to traditional algorithms, especially in terms of stability, efficiency, and accuracy in detection and classification tasks. In the field of visual SLAM, many works have emerged that use deep learning methods to replace traditional SLAM front-ends and back-ends, and have demonstrated significant advantages.
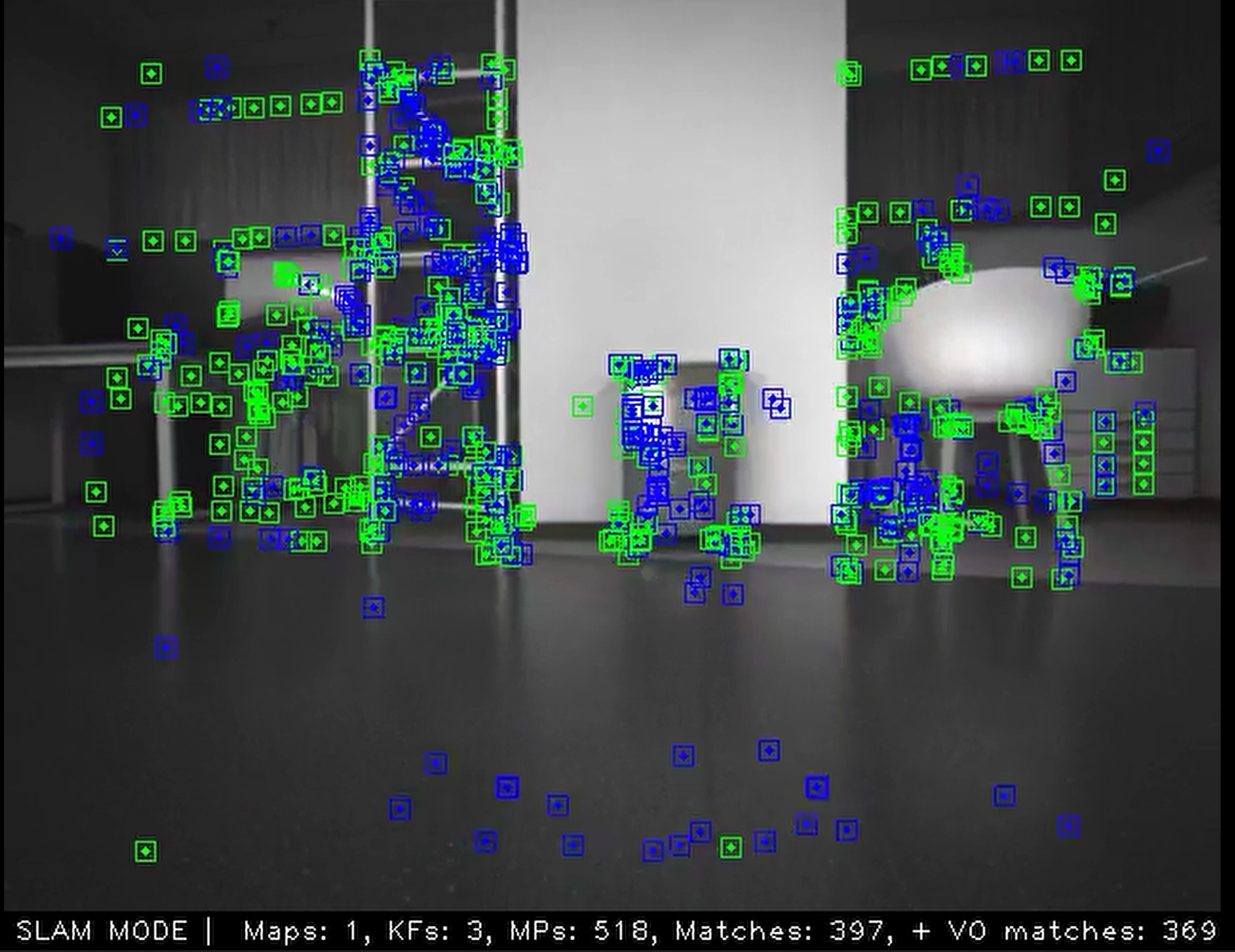
SuperPoint and SuperGlue are examples of such methods. SuperPoint is a self-supervised deep learning network model that can extract both the position and descriptor of image feature points. TROS.b integrates SuperPoint with ORB-SLAM3, and developers can freely switch between feature point extraction methods in the configuration files located in /opt/tros/share/orb_slam3/Examples/\*/*.yaml. As shown in the figure below, the feature point extraction algorithm used is "SUPERPOINT":
The result of using the SuperPoint feature extraction algorithm is shown in the following figure. It can be seen that the feature points are extracted very densely and the contours of objects are detected.
