5.4.5 Gesture Control The Car
Introduction
The app allows you to control a robot's movements using hand gestures, including left and right rotation and forward and backward translation. The app consists of MIPI image capture, human detection and tracking, hand keypoint detection, gesture recognition, gesture control strategy, image encoding and decoding, and web display. The workflow is shown in the following diagram:
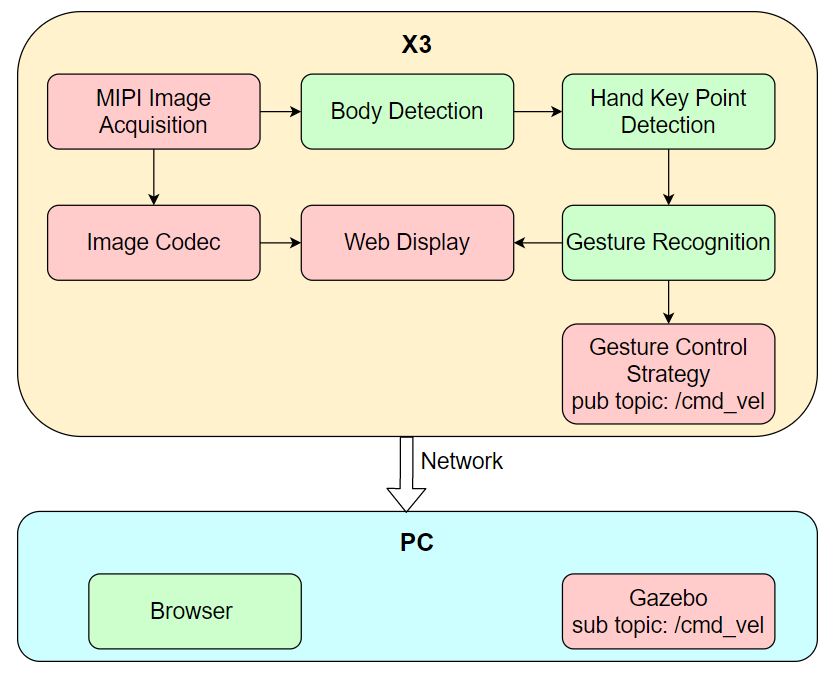
The supported control gestures, their corresponding functionalities, and examples of the gestures are as follows:
| Control Gesture | Function | Gesture Action Example |
|---|---|---|
| 666 Gesture/Awesome | Move forward |  |
| yeah/Victory | Move backward |  |
| Thumb Right | Turn right |  |
| Thumb Left | Turn left | 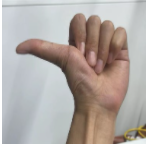 |
The app is demonstrated using a virtual car in the PC Gazebo simulation environment, but the control commands can also be directly used to control a physical robot.
Code repository: (https://github.com/D-Robotics/gesture_control)
Supported Platforms
| Platform | System | Function |
|---|---|---|
| RDK X3, RDK X3 Module, RDK X5 | Ubuntu 20.04 (Foxy), Ubuntu 22.04 (Humble) | Start MIPI/USB camera to capture images, perform gesture recognition and control, and finally show the control effect through Gazebo |
Preparation
RDK
-
RDK is flashed the Ubuntu 20.04/22.04 system image.
-
TogetheROS.Bot successfully installed on RDK.
-
MIPI or USB camera installed on RDK.
-
PC on the same network segment as RDK (wired or connected to the same wireless network with the first three segments of the IP address matching). The PC needs to have the following software installed:
- Foxy
- Humble
- Ubuntu 20.04 system and ROS2 Foxy Desktop Full
- Gazebo and Turtlebot3 related packages. Installation commands:
sudo apt-get install ros-foxy-gazebo-*
sudo apt install ros-foxy-turtlebot3
sudo apt install ros-foxy-turtlebot3-simulations
- Ubuntu 22.04 system and ROS2 Humble Desktop Full
- Gazebo and Turtlebot3 related packages. Installation commands:
sudo apt-get install ros-humble-gazebo-*
sudo apt install ros-humble-turtlebot3
sudo apt install ros-humble-turtlebot3-simulations
Instructions
RDK
After running the car gesture control app, use the "666/Awesome" gesture to make the car move forward, use the "yeah/Victory" gesture to make the car move backward, use the "ThumbRight" gesture to make the car turn right, and use the "ThumbLeft" gesture to make the car turn left. The directions for turning left and right are based on the direction of the person's left and right (the direction of the thumb).
Once the app is launched, you can view the images published by the sensor and the corresponding algorithm results on the PC browser (enter http://IP:8000 in the browser, where IP is the IP address of the RDK).
Launch the simulation environment on the PC:
source /opt/ros/foxy/setup.bash
export TURTLEBOT3_MODEL=burger
ros2 launch turtlebot3_gazebo empty_world.launch.py
After successful launch, the car in the simulation environment will look like this:
![]()
Publishing Images from the MIPI Camera
# Configure the tros.b environment
source /opt/tros/setup.bash
# Copy the necessary configuration files for running the example from the installation path of tros.b.
cp -r /opt/tros/lib/mono2d_body_detection/config/ .
cp -r /opt/tros/lib/hand_lmk_detection/config/ .
cp -r /opt/tros/lib/hand_gesture_detection/config/ .
# Configure the MIPI camera
export CAM_TYPE=mipi
# Launch the launch file
ros2 launch gesture_control gesture_control.launch.py
Publishing Images from the USB Camera
# Configure the tros.b environment
source /opt/tros/setup.bash
# Copy the necessary configuration files for running the example from the installation path of tros.b.
cp -r /opt/tros/lib/mono2d_body_detection/config/ .
cp -r /opt/tros/lib/hand_lmk_detection/config/ .
cp -r /opt/tros/lib/hand_gesture_detection/config/ .
# Configure USB camera
export CAM_TYPE=usb
# Launch the launch file
ros2 launch gesture_control gesture_control.launch.py
Result Analysis
The terminal output on the RDK shows the following information:
[gesture_control-7] [WARN] [1652965757.159500951] [GestureControlEngine]: frame_ts_ms: 3698315358, track_id: 2, tracking_sta: 1, gesture: 14
[gesture_control-7] [WARN] [1652965757.159660358] [GestureControlEngine]: do move, direction: 0, step: 0.500000
[gesture_control-7] [WARN] [1652965757.211420964] [GestureControlEngine]: frame_ts_ms: 3698315425, track_id: 2, tracking_sta: 1, gesture: 14
[gesture_control-7] [WARN] [1652965757.211624899] [GestureControlEngine]: do move, direction: 0, step: 0.500000
[gesture_control-7] [WARN] [1652965757.232051230] [GestureControlEngine]: frame_ts_ms: 3698315457, track_id: 2, tracking_sta: 1, gesture: 14
[gesture_control-7] [WARN] [1652965757.232207513] [GestureControlEngine]: do move, direction: 0, step: 0.500000
The above log snippet shows the processing results of controlling the movement of the car through gestures. The value of tracking_sta is 1, indicating that gesture control is enabled, while a value of 0 indicates gesture recognition.
Starting from the timestamp frame_ts_ms: 3698315358, the car is controlled to move forward at a speed of 0.5m/s using the 666 gesture (gesture: 14) (do move, direction: 0, step: 0.500000).
On the PC, the command ros2 topic list can be used in the terminal to query the topic information of the RDK:
$ ros2 topic list
/camera_info
/cmd_vel
/hbmem_img04054242060426080500012020112713
/hobot_hand_gesture_detection
/hobot_hand_lmk_detection
/hobot_mono2d_body_detection
/image
/parameter_events
/rosout
Among them, /image is the image captured by the MIPI sensor and encoded in JPEG format, /hobot_hand_gesture_detection is the algorithm message published by the RDK containing gesture recognition information, and /cmd_vel is the motion control command published by the RDK.
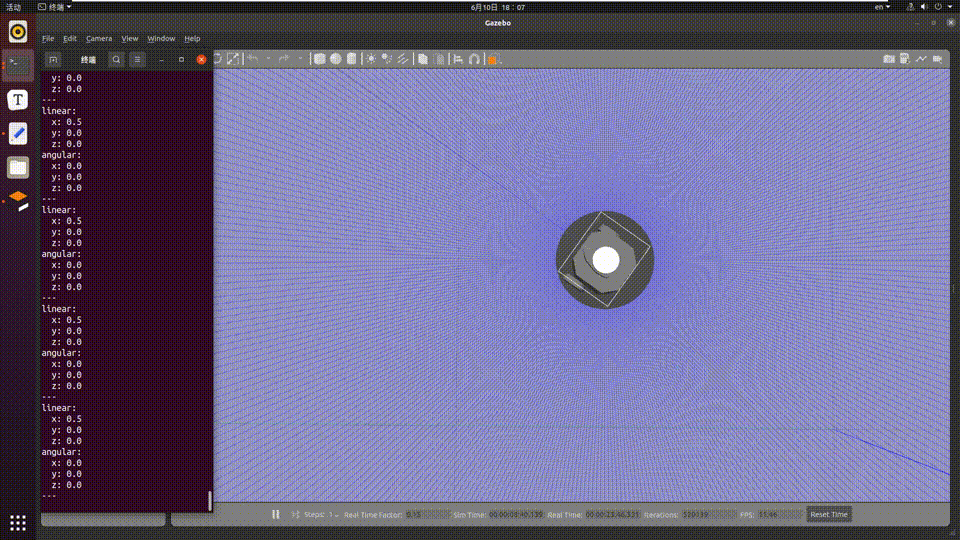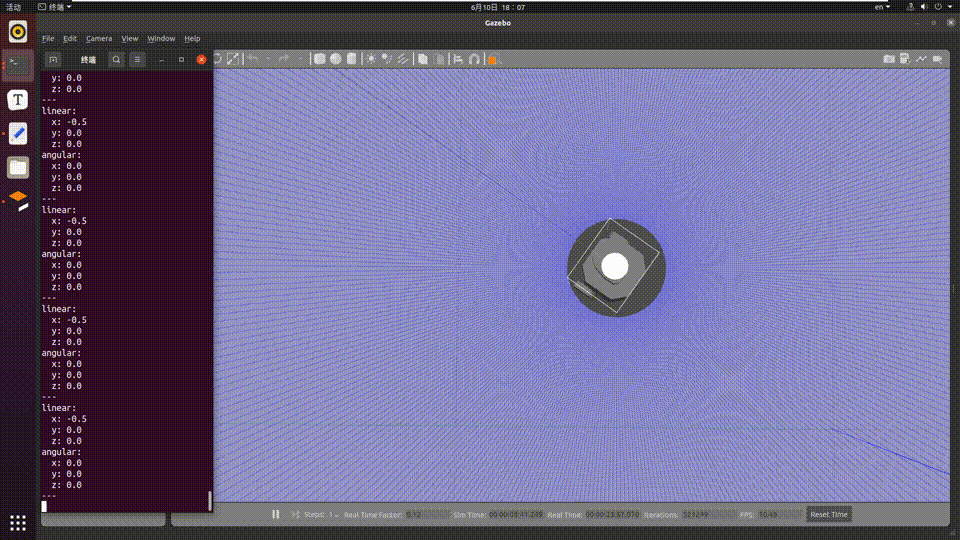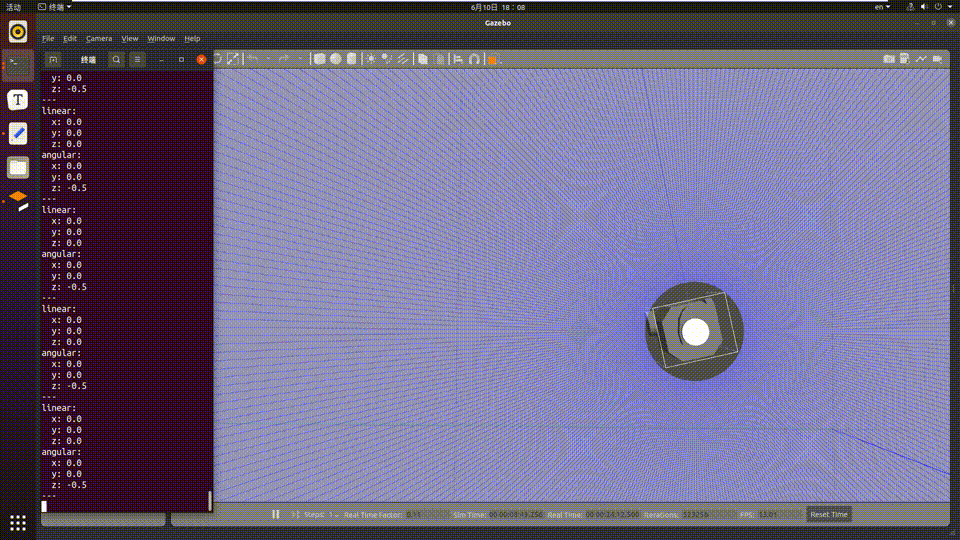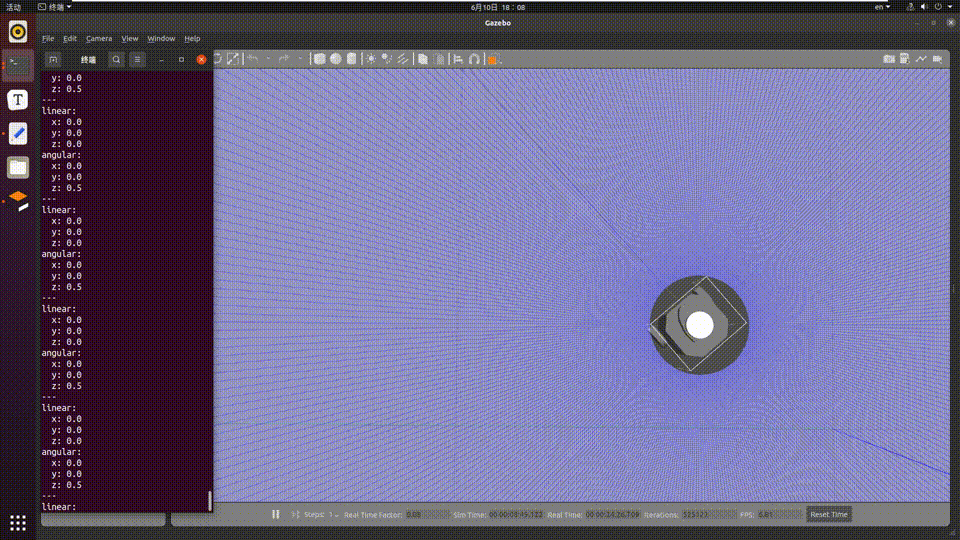
On the PC, the command ros2 topic echo /cmd_vel can be used in the terminal to view the motion control command published by the RDK:
linear:
x: -0.5
y: 0.0
z: 0.0
angular:
x: 0.0
y: 0.0
z: 0.0
---
linear:
x: 0.0
y: 0.0
z: 0.0
angular:
x: 0.0
y: 0.0
z: -0.5
---
The car moves according to the gestures in the PC simulation environment, and the simulated car movement is as follows: