5.5.2 Model Inference
Supported Platforms
| Platform | Supported OS & ROS 2 Version |
|---|---|
| RDK X3, RDK X3 Module | Ubuntu 20.04 (Foxy), Ubuntu 22.04 (Humble) |
The content introduced in this chapter is theoretically applicable to all platforms. The code examples are based on the RDK X3 platform, and code adaptation will be required if used on other platforms.
Model Inference Development
Background
hobot_dnn is the edge algorithm inference framework in TogetheROS.Bot software stack. It utilizes the BPU processor on RDK to achieve algorithm inference. Based on the D-Robotics algorithm inference framework and ROS2 Node, it provides a simpler and easier-to-use model integration development interface for robot application development. This includes model management, model description-based input processing and result parsing, and model output memory allocation management.
By reading this chapter, users can use the models provided by D-Robotics to create and run a human detection algorithm Node based on hobot_dnn on RDK. With the help of the components provided by tros.b, it subscribes to the images captured and published by the camera, performs algorithm inference to detect human bounding boxes, and uses the Multi-Object Tracking (MOT) algorithm to track and assign target numbers to the detection boxes. Finally, it achieves real-time rendering and display of images, human bounding box detection, and target tracking results in a web browser on a PC.
Preparation
-
RDK development board with relevant software installed, including:
- Ubuntu 20.04/22.04 system image provided by D-Robotics.
- tros.b software package.
- Development tools: Compilers and other tools to build ROS packages.
sudo apt install ros-dev-tools
-
RDK with F37 or GC4663 camera installed.
-
PC that can access RDK through the network.
For detailed instructions on how to use hobot_dnn, please refer to the README.md and API documentation in the hobot_dnn code. The workflow of using hobot_dnn is as follows:
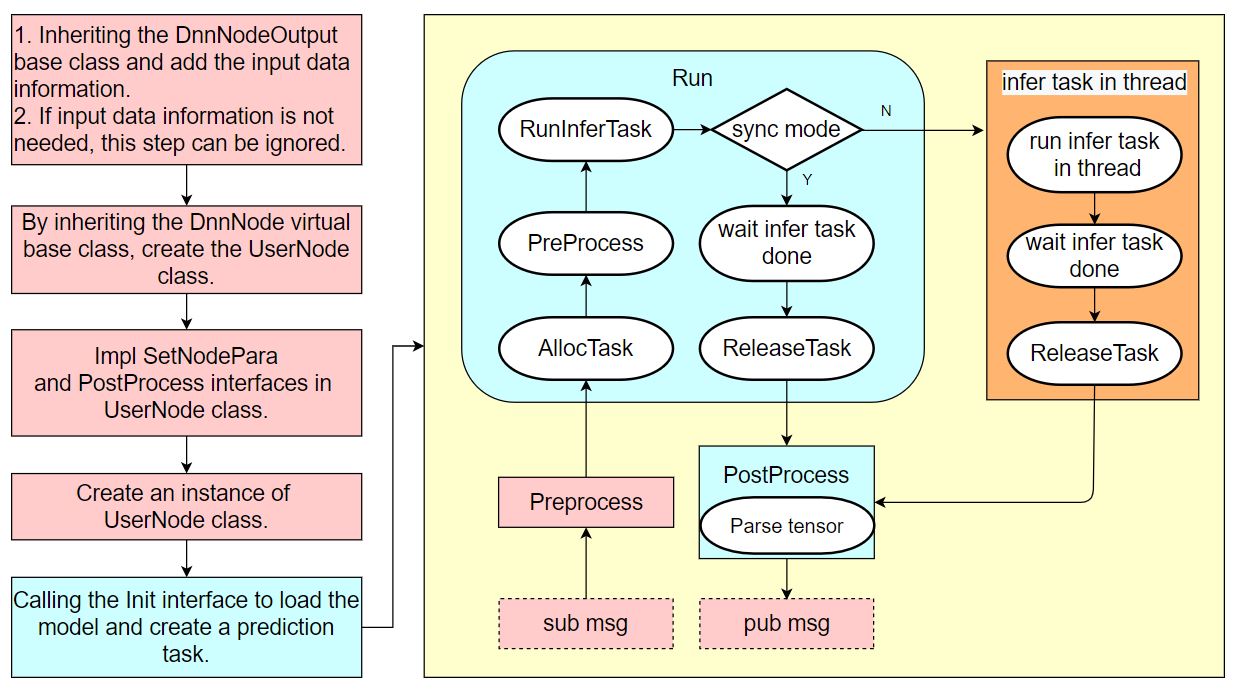
Without understanding the workflow of using hobot_dnn, users can also follow the steps in this chapter to develop a model inference example using hobot_dnn.
The following content in this chapter uses the tros.b Foxy version as an example. If you are using the tros.b Humble version, just replace the source /opt/tros/setup.bash command with source /opt/tros/humble/ setup.bash.
Usage
1. Create package
mkdir -p ~/dev_ws/src
cd ~/dev_ws/src
source /opt/tros/setup.bash
ros2 pkg create --build-type ament_cmake cpp_dnn_demo --dependencies rclcpp sensor_msgs hbm_img_msgs ai_msgs dnn_node hobot_mot
cd cpp_dnn_demo
touch src/body_det_demo.cpp
2. Write exampleThe created project path can be viewed as follows:
root@ubuntu:~# cd ~
root@ubuntu:~# tree dev_ws/
dev_ws/
└── src
└── cpp_dnn_demo
├── CMakeLists.txt
├── include
│ └── cpp_dnn_demo
├── package.xml
└── src
└── body_det_demo.cpp
5 directories, 3 files
Open the created source code file body_det_demo.cpp using tools like vi/vim on the RDK: vi ~/dev_ws/src/cpp_dnn_demo/src/body_det_demo.cpp
Copy the following code into the file:
#include "dnn_node/dnn_node.h"
#include "dnn_node/util/image_proc.h"
#include "dnn_node/util/output_parser/detection/fasterrcnn_output_parser.h"
#include "sensor_msgs/msg/image.hpp"
#include "ai_msgs/msg/perception_targets.hpp"
#include "hbm_img_msgs/msg/hbm_msg1080_p.hpp"
#include "hobot_mot/hobot_mot.h"
// Create an algorithm inference output data structure and add message header information as a member
struct FasterRcnnOutput : public hobot::dnn_node::DnnNodeOutput {
std::shared_ptr<std_msgs::msg::Header> image_msg_header = nullptr;
};
// Inherit from the DnnNode base class and create an algorithm inference node
class BodyDetNode : public hobot::dnn_node::DnnNode {
public:
BodyDetNode(const std::string &node_name = "body_det",
const rclcpp::NodeOptions &options = rclcpp::NodeOptions());
protected:
// Implement the pure virtual interface of the base class to configure Node parameters
int SetNodePara() override;
// Implement the virtual interface of the base class to encapsulate the parsed model output data into ROS Msg and publish it
int PostProcess(const std::shared_ptr<hobot::dnn_node::DnnNodeOutput> &node_output)
override;
```private:
// Width and height of the input image data for the algorithm model
int model_input_width_ = -1;
int model_input_height_ = -1;
// Model output index corresponding to the body detection box result
const int32_t box_output_index_ = 1;
// Collection of detection box output indexes
const std::vector<int32_t> box_outputs_index_ = {box_output_index_};
// Image message subscriber
rclcpp::Subscription<hbm_img_msgs::msg::HbmMsg1080P>::ConstSharedPtr
ros_img_subscription_ = nullptr;
// Algorithm inference result message publisher
rclcpp::Publisher<ai_msgs::msg::PerceptionTargets>::SharedPtr
msg_publisher_ = nullptr;
// Multi-target tracking algorithm engine
std::shared_ptr<HobotMot> hobot_mot_ = nullptr;
// Image message subscription callback
void FeedImg(const hbm_img_msgs::msg::HbmMsg1080P::ConstSharedPtr msg);
};
BodyDetNode::BodyDetNode(const std::string & node_name, const rclcpp::NodeOptions & options) :
hobot::dnn_node::DnnNode(node_name, options) {
// Initialize the algorithm inference using the SetNodePara() method implemented in the BodyDetNode subclass
if (Init() != 0 ||
GetModelInputSize(0, model_input_width_, model_input_height_) < 0) {
RCLCPP_ERROR(rclcpp::get_logger("dnn_demo"), "Node init fail!");
rclcpp::shutdown();
}
// Create a message subscriber to subscribe image messages from the camera node
ros_img_subscription_ =
this->create_subscription<hbm_img_msgs::msg::HbmMsg1080P>(
"/hbmem_img", 10, std::bind(&BodyDetNode::FeedImg, this, std::placeholders::_1));
// Create a message publisher to publish algorithm inference messages
msg_publisher_ = this->create_publisher<ai_msgs::msg::PerceptionTargets>(
"/cpp_dnn_demo", 10);
// Create a multi-target tracking (MOT) algorithm engine
hobot_mot_ = std::make_shared<HobotMot>("config/iou2_method_param.json");
}
int BodyDetNode::SetNodePara() {
if (!dnn_node_para_ptr_) return -1;
// Specify the model file path and model name to be used for the algorithm inference
dnn_node_para_ptr_->model_file = "config/multitask_body_kps_960x544.hbm";
dnn_node_para_ptr_->model_name = "multitask_body_kps_960x544";
return 0;
}void BodyDetNode::FeedImg(const hbm_img_msgs::msg::HbmMsg1080P::ConstSharedPtr img_msg) {
if (!rclcpp::ok()) {
return;
}
// Validate the subscribed image message, this example only supports processing NV12 format image data
if (!img_msg) return;
if ("nv12" != std::string(reinterpret_cast<const char*>(img_msg->encoding.data()))) {
RCLCPP_ERROR(rclcpp::get_logger("dnn_demo"), "Only support nv12 img encoding!");
return;
}
// Create model input data based on the model input resolution using the methods provided by DnnNode
auto inputs = std::vector<std::shared_ptr<hobot::dnn_node::DNNInput>>{
hobot::dnn_node::ImageProc::GetNV12PyramidFromNV12Img(
reinterpret_cast<const char*>(img_msg->data.data()),
img_msg->height, img_msg->width, model_input_height_, model_input_width_)};
// Create model output data and fill in message header information
auto dnn_output = std::make_shared<FasterRcnnOutput>();
dnn_output->image_msg_header = std::make_shared<std_msgs::msg::Header>();
dnn_output->image_msg_header->set__frame_id(std::to_string(img_msg->index));
dnn_output->image_msg_header->set__stamp(img_msg->time_stamp);
// Run inference asynchronously
Run(inputs, dnn_output, nullptr, false);
}
int BodyDetNode::PostProcess(const std::shared_ptr<hobot::dnn_node::DnnNodeOutput> &node_output) {
if (!rclcpp::ok()) {
return 0;
}
// Validate the output data
if (node_output->output_tensors.empty() ||
static_cast<int32_t>(node_output->output_tensors.size()) < box_output_index_) {
RCLCPP_ERROR(rclcpp::get_logger("dnn_demo"), "Invalid outputs");
return -1;
}
// Create parsing output data
// Dimension of detection box results is equal to the number of detected object categories
std::vector<std::shared_ptr<hobot::dnn_node::parser_fasterrcnn::Filter2DResult>>
results;
// Keypoint data
std::shared_ptr<hobot::dnn_node::parser_fasterrcnn::LandmarksResult> output_body_kps = nullptr;
// Use the built-in Parse method in hobot dnn to parse the algorithm output
if (hobot::dnn_node::parser_fasterrcnn::Parse(node_output, nullptr,
box_outputs_index_, -1, -1, results, output_body_kps) < 0) {
RCLCPP_ERROR(rclcpp::get_logger("dnn_node_sample"), "Parse node_output fail!");
return -1;
}
auto filter2d_result = results.at(box_output_index_);
if (!filter2d_result) return -1;
// Convert the human detection boxes inferred by the algorithm into the MOT algorithm input data type
std::vector<MotBox> in_box_list;
for (auto& rect : filter2d_result->boxes) {
in_box_list.emplace_back(
MotBox(rect.left, rect.top, rect.right, rect.bottom, rect.conf));
}
// Calculate the timestamp of the current frame based on the message header
auto fasterRcnn_output =
std::dynamic_pointer_cast<FasterRcnnOutput>(node_output);
time_t time_stamp =
fasterRcnn_output->image_msg_header->stamp.sec * 1000 +
fasterRcnn_output->image_msg_header->stamp.nanosec / 1000 / 1000;
// Create the output of the MOT algorithm: human detection boxes with target IDs and disappeared target IDs
std::vector<MotBox> out_box_list;
std::vector<std::shared_ptr<MotTrackId>> disappeared_ids;
// Run the multi-object tracking algorithm
if (hobot_mot_->DoProcess(in_box_list,
out_box_list,
disappeared_ids,
time_stamp,
model_input_width_,
model_input_height_) < 0) {
RCLCPP_ERROR(rclcpp::get_logger("dnn_demo"), "Do mot fail");
return -1;
}
// Create an ROS Msg for publishing the inference results
ai_msgs::msg::PerceptionTargets::UniquePtr pub_data(
new ai_msgs::msg::PerceptionTargets());
// Fill in the message header for the ROS Msg
pub_data->header.set__stamp(fasterRcnn_output->image_msg_header->stamp);
pub_data->header.set__frame_id(fasterRcnn_output->image_msg_header->frame_id);
// Fill in the algorithm inference output frame rate to the ROS Msg
if (node_output->rt_stat) {
pub_data->set__fps(round(node_output->rt_stat->output_fps));
// If the algorithm inference statistics are updated, output the frame rate statistics of the algorithm model input and output
if (node_output->rt_stat->fps_updated) {RCLCPP_WARN(rclcpp::get_logger("dnn_demo"),
"input fps: %.2f, out fps: %.2f",
node_output->rt_stat->input_fps,
node_output->rt_stat->output_fps);
}
}
for (auto& rect : out_box_list) {
// Validate the effectiveness of the target tracking result
if (rect.id < 0) {
continue;
}
// Fill the target tracking result and detection box into ROS Msg
ai_msgs::msg::Target target;
target.set__type("person");
target.set__track_id(rect.id);
ai_msgs::msg::Roi roi;
roi.type = "body";
roi.rect.set__x_offset(rect.x1);
roi.rect.set__y_offset(rect.y1);
roi.rect.set__width(rect.x2 - rect.x1);
roi.rect.set__height(rect.y2 - rect.y1);
target.rois.emplace_back(roi);
pub_data->targets.emplace_back(std::move(target));
}
// Fill the disappeared targets into ROS Msg
for (const auto& id_info : disappeared_ids) {
if (id_info->value < 0 ||
hobot_mot::DataState::INVALID == id_info->state_) {
continue;
}
ai_msgs::msg::Target target;
target.set__type("person");
target.set__track_id(id_info->value);
ai_msgs::msg::Roi roi;
roi.type = "body";
target.rois.emplace_back(roi);
pub_data->disappeared_targets.emplace_back(std::move(target));
}
// Publish ROS Msg
msg_publisher_->publish(std::move(pub_data));
return 0;
}
int main(int argc, char** argv) {
rclcpp::init(argc, argv);
rclcpp::spin(std::make_shared<BodyDetNode>());```cpp
#include "dnn_node/dnn_node.h"
#include "dnn_node/util/image_proc.h"
#include "dnn_node/util/output_parser/detection/fasterrcnn_output_parser.h"
#include "sensor_msgs/msg/image.hpp"
#include "ai_msgs/msg/perception_targets.hpp"
#include "hbm_img_msgs/msg/hbm_msg1080_p.hpp"
#include "hobot_mot/hobot_mot.h"
rclcpp::shutdown();
return 0;
}
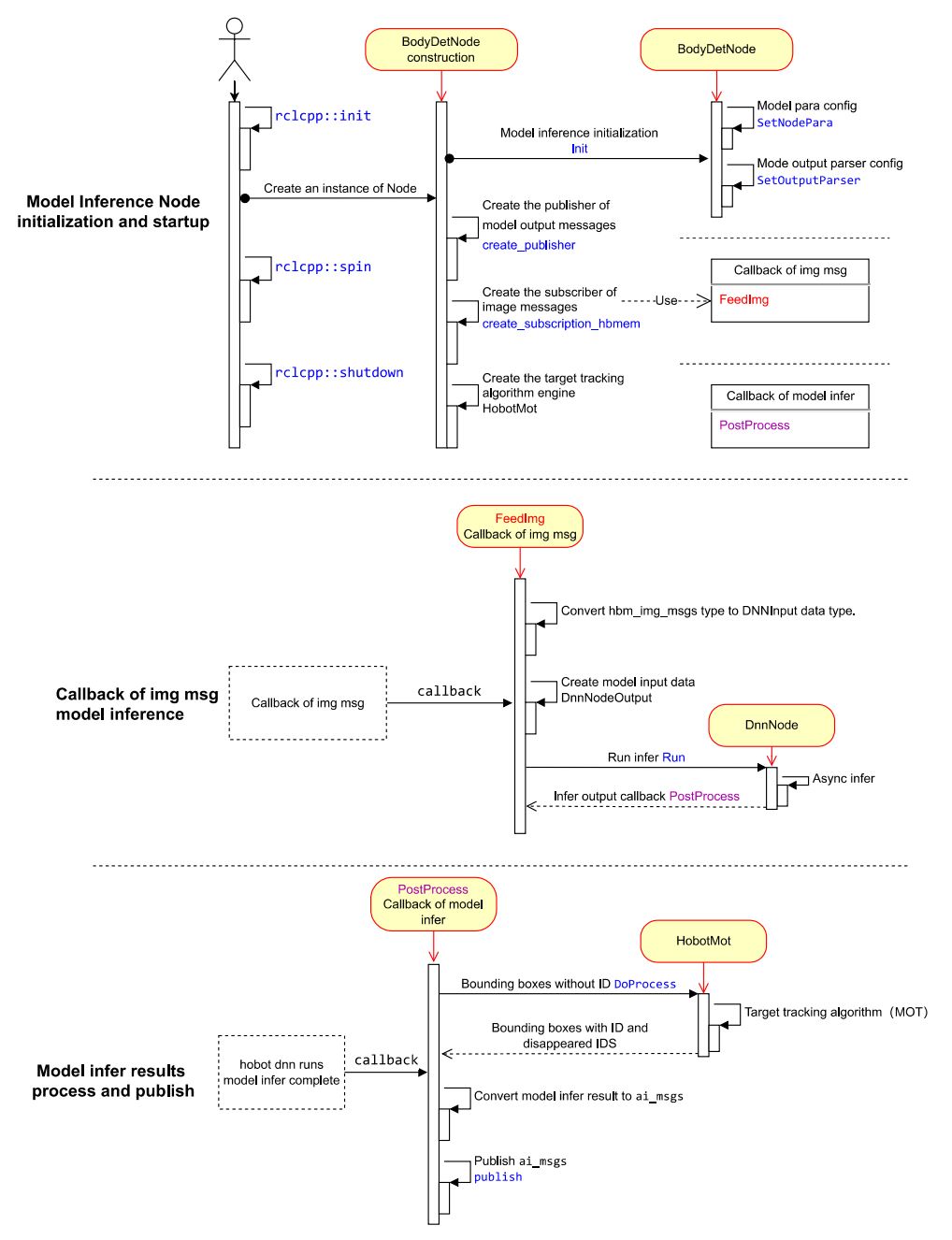
2.1 Node Design
The main body detection algorithm node in the example consists of three logically independent functionalities.
(1) Node Initialization and Startup
Configure the model information used by the algorithm, create the publisher for algorithm inference messages and the subscriber for image messages, and start the target tracking algorithm engine.
(2) Message Subscription and Algorithm Inference
When creating the subscriber for image messages, a message callback FeedImg is registered to process the image data for algorithm model inference. The callback does not wait for the algorithm inference to complete.
(3) Processing and Publishing of Inference Results
After the algorithm inference is completed, the inference results are output through the registered callback PostProcess. In the callback, the detection results are processed using the multi-object tracking algorithm (HobotMot), and the algorithm inference result messages are published.
The design and flow logic of the Node are shown in the following figure:
2.2 Code Explanation
Add Header Files
-
dnn_node/dnn_node.h: Header file for the inference framework, used for algorithm model management and inference. -
dnn_node/util/image_proc.h: Header file for algorithm model input image processing. -
dnn_node/util/output_parser/detection/fasterrcnn_output_parser.h: Header file for algorithm model output parsing method, used to parse structured data (in this example, it corresponds to the human detection bounding boxes) from the output address after model inference. -
ROS Msg header files: Used for message subscription and publishing.
-
hobot_mot/hobot_mot.h: Header file for the MOT (Multi-Object Tracking) algorithm engine, used for tracking the detected human bounding boxes.
#include "dnn_node/dnn_node.h"
#include "dnn_node/util/image_proc.h"
#include "dnn_node/util/output_parser/detection/fasterrcnn_output_parser.h"
#include "sensor_msgs/msg/image.hpp"
#include "ai_msgs/msg/perception_targets.hpp"
#include "hbm_img_msgs/msg/hbm_msg1080_p.hpp"
#include "hobot_mot/hobot_mot.h"
```**Creating algorithm inference output data structure**
Inheriting the `DnnNodeOutput` base class from `hobot_dnn`, adding a message header information member to represent the image information corresponding to the inference output.
```C++
struct FasterRcnnOutput : public hobot::dnn_node::DnnNodeOutput {
std::shared_ptr<std_msgs::msg::Header> image_msg_header = nullptr;
};
Creating algorithm inference Node
Inheriting the virtual base class DnnNode from hobot_dnn, defining the algorithm inference node BodyDetNode and implementing the virtual interfaces defined in DnnNode.
int SetNodePara(): Configuring model parameters.
int PostProcess(const std::shared_ptr<hobot::dnn_node::DnnNodeOutput>& node_output): Callback for inference results, packaging the parsed and structured model output data into ROS Msg and publishing them.
class BodyDetNode : public hobot::dnn_node::DnnNode {
public:
BodyDetNode(const std::string& node_name = "body_det",
const rclcpp::NodeOptions& options = rclcpp::NodeOptions());
protected:
int SetNodePara() override;
int PostProcess(const std::shared_ptr<hobot::dnn_node::DnnNodeOutput>& node_output) override;
Implementing the constructor of the BodyDetNode subclass
The constructor of the BodyDetNode subclass initializes the Node and retrieves the size of the model's input image through the GetModelInputSize interface, including the width model_input_width_ and height model_input_height_ of the image. This is used for model pre-processing as different models generally have different input image sizes.
Creating a subscriber for image messages using zero-copy communication method, subscribing to image messages from camera node for algorithm model inference. The subscribed topic is /hbmem_img and the message type is the image message type defined in tros.b, hbm_img_msgs::msg::HbmMsg1080P.
Creating a publisher for algorithm inference messages. The published topic is /cpp_dnn_demo and the message type is the algorithm message type defined in tros.b, ai_msgs::msg::PerceptionTargets.
Creating a Multiple Object Tracking (MOT) algorithm engine for tracking each person detection box.
Constructor of BodyDetNode:
BodyDetNode::BodyDetNode(const std::string& node_name, const rclcpp::NodeOptions& options) :
hobot::dnn_node::DnnNode(node_name, options) {
// Initialize algorithm inference using the SetNodePara() method implemented in the BodyDetNode subclass
if (Init() != 0 ||
GetModelInputSize(0, model_input_width_, model_input_height_) < 0) {
```RCLCPP_ERROR(rclcpp::get_logger("dnn_demo"), "Node init fail!");
rclcpp::shutdown();
}
// Create message subscriber, subscribe to image messages from camera node
ros_img_subscription_ =
this->create_subscription<hbm_img_msgs::msg::HbmMsg1080P>(
"/hbmem_img", 10, std::bind(&BodyDetNode::FeedImg, this, std::placeholders::_1));
// Create message publisher, publish algorithm inference messages
msg_publisher_ = this->create_publisher<ai_msgs::msg::PerceptionTargets>(
"/cpp_dnn_demo", 10);
// Create multi-object tracking (MOT) algorithm engine
hobot_mot_ = std::make_shared<HobotMot>("config/iou2_method_param.json");
}
Where Init() is an interface defined and implemented in the DnnNode base class, which performs algorithm inference initialization, only concatenates the pipeline, and the specific SetNodePara() steps are implemented by the user (in the subclass). The initialization process of the concatenation is as follows:
int DnnNode::Init() {
RCLCPP_INFO(rclcpp::get_logger("dnn"), "Node init.");
int ret = 0;
// 1. set model info in node para
ret = SetNodePara();
if (ret != 0) {
RCLCPP_ERROR(rclcpp::get_logger("dnn"), "Set node para failed!");
return ret;
}
// check node para
if (ModelTaskType::InvalidType == dnn_node_para_ptr_->model_task_type) {
RCLCPP_ERROR(rclcpp::get_logger("dnn"), "Invalid model task type");
return -1;
}
// 2. model init
ret = dnn_node_impl_->ModelInit();
if (ret != 0) {
RCLCPP_ERROR(rclcpp::get_logger("dnn"), "Model init failed!");
return ret;
}
// 3. set output parser
ret = SetOutputParser();
if (ret != 0) {
RCLCPP_ERROR(rclcpp::get_logger("dnn"), "Set output parser failed!");
return ret;
}
```// 4. task init
ret = dnn_node_impl_->TaskInit();
if (ret != 0) {
RCLCPP_ERROR(rclcpp::get_logger("dnn"), "Task init failed!");
return ret;
}
return ret;
}
Set model parameters
Set the path and name of the model file used for algorithm inference.
int BodyDetNode::SetNodePara() {
if (!dnn_node_para_ptr_) return -1;
dnn_node_para_ptr_->model_file = "config/multitask_body_kps_960x544.hbm";
dnn_node_para_ptr_->model_name = "multitask_body_kps_960x544";
return 0;
}
Implement the image subscription callback
Create DNNInput type model input data. The subscribed message contains image information (such as encoding method, content data, resolution, etc.). Use the image processing interface hobot::dnn_node::ImageProc::GetNV12PyramidFromNV12Img in hobot_dnn algorithm module to convert the subscribed nv12 format image to the data type required by the model input, according to the model input resolution (model_input_width_ and model_input_height_, obtained from the loaded model by querying with the GetModelInputSize interface in the constructor of BodyDetNode). The interface is defined as follows:
// - [in] in_img_data: image data
// - [in] in_img_height: height of the image
// - [in] in_img_width: width of the image
// - [in] scaled_img_height: height of the model input
// - [in] scaled_img_width: width of the model input
std::shared_ptr<NV12PyramidInput> GetNV12PyramidFromNV12Img(
const char* in_img_data,
const int& in_img_height,
const int& in_img_width,
const int& scaled_img_height,
const int& scaled_img_width);
Create FasterRcnnOutput type model output data. The subscribed message contains message headers (frame_id and timestamp). Use the subscribed message headers to fill in the message headers of the output data, which represent the image information corresponding to the algorithm inference output.
Start inference. Use the Run interface in the base class DnnNode to run the inference asynchronously, with the fourth parameter of the interface set as false indicating the more efficient asynchronous inference mode. The Run interface is defined as follows:
// - Parameters
// - [in] inputs: shared pointers to input data
// - [in] outputs: shared pointer to output data
struct Filter2DResult {
int track_id; // Target number
hbm_common_msgs::msg::BBox2D bbox; // bounding box
};
// Algorithm inference result callback, converting model output data into human detection boxes with target numbers
void BodyDetNode::OnInferenceResult(const std::shared_ptr<hobot::dnn_node::DNNOutput>& output) {
if (!output || !output->FrameStamps().size()) {
return;
}
// Fill structured inference result data of type 'Filter2DResult' based on algorithm inference results
std::vector<Filter2DResult> results;
const auto* dnn_output = static_cast<const FasterRcnnOutput*>(output.get());
for (size_t i = 0; i < dnn_output->bboxes.size(); ++i) {
Filter2DResult result;
result.track_id = dnn_output->track_ids[i];
result.bbox.x = dnn_output->bboxes[i].tl().x;
result.bbox.y = dnn_output->bboxes[i].tl().y;
result.bbox.width = dnn_output->bboxes[i].br().x - dnn_output->bboxes[i].tl().x;
result.bbox.height = dnn_output->bboxes[i].br().y - dnn_output->bboxes[i].tl().y;
results.push_back(result);
}
// Process the inference results using the MOT algorithm to obtain missing target number data
std::vector<int> disappear_ids;
// TODO: MOT Algorithm processing
// Publish the parsed structured reasoning results and disappearing target numbers
PublishDetection(results);
PublishDisappearingTarget(disappear_ids);
}
In the inference result callback 'OnInferenceResult', fill in structured inference result data of type 'Filter2DResult' based on the model output data. Then, use the MOT algorithm to process the inference results and obtain the missing target number data. Finally, publish the parsed structured reasoning results and the missing target number.Using the built-in Parse parsing method in hobot dnn, parse the output of the human detection algorithm.
Run the multi-target tracking algorithm. Convert the human detection boxes outputted by the algorithm into the data type required by the MOT algorithm. Calculate the timestamp of the current frame based on the message header. After processing with the MOT algorithm, obtain the human detection boxes with target ID and the disappeared target ID.
Publish the results of the algorithm inference. Create a ROS Msg, fill in the image message header (frame ID and timestamp) corresponding to the results of the algorithm inference, the human detection boxes with target ID, the frame rate statistics outputted by the algorithm inference, and the disappeared target ID. The published ROS Msg can be subscribed and used by other ROS Nodes.
int BodyDetNode::PostProcess(const std::shared_ptr<hobot::dnn_node::DnnNodeOutput> &node_output) {
if (!rclcpp::ok()) {
return 0;
}
// Validate the validity of the output data
if (node_output->output_tensors.empty() ||
static_cast<int32_t>(node_output->output_tensors.size()) < box_output_index_) {
RCLCPP_ERROR(rclcpp::get_logger("dnn_demo"), "Invalid outputs");
return -1;
}
// Create the parsing output data
// The dimension of detection box results is equal to the number of detected target categories
std::vector<std::shared_ptr<hobot::dnn_node::parser_fasterrcnn::Filter2DResult>>
results;
// Key point data
std::shared_ptr<hobot::dnn_node::parser_fasterrcnn::LandmarksResult> output_body_kps = nullptr;
// Parse the algorithm output using the built-in Parse method in hobot dnn
if (hobot::dnn_node::parser_fasterrcnn::Parse(node_output, nullptr,
box_outputs_index_, -1, -1, results, output_body_kps) < 0) {
RCLCPP_ERROR(rclcpp::get_logger("dnn_node_sample"),
"Parse node_output fail!");
return -1;
}
auto filter2d_result = results.at(box_output_index_);
if (!filter2d_result) return -1;
// Convert the human detection boxes outputted by the algorithm inference into the data type required by MOT algorithm
std::vector<MotBox> in_box_list;
for (auto& rect : filter2d_result->boxes) {
in_box_list.emplace_back(
MotBox(rect.left, rect.top, rect.right, rect.bottom, rect.conf));
}
// Calculate the timestamp of the current frame based on the message header
auto fasterRcnn_output =
std::dynamic_pointer_cast<FasterRcnnOutput>(node_output);
time_t time_stamp =
fasterRcnn_output->image_msg_header->stamp.sec * 1000 +
```fasterRcnn_output->image_msg_header->stamp.nanosec / 1000 / 1000;
// Create output of MOT algorithm: detection boxes with object IDs and disappeared object IDs
std::vector<MotBox> out_box_list;
std::vector<std::shared_ptr<MotTrackId>> disappeared_ids;
// Run multi-object tracking algorithm
if (hobot_mot_->DoProcess(in_box_list,
out_box_list,
disappeared_ids,
time_stamp,
model_input_width_,
model_input_height_) < 0) {
RCLCPP_ERROR(rclcpp::get_logger("dnn_demo"), "Do mot fail");
return -1;
}
// Create ROS Msg for publishing inference results
ai_msgs::msg::PerceptionTargets::UniquePtr pub_data(
new ai_msgs::msg::PerceptionTargets());
// Fill message header to ROS Msg
pub_data->header.set__stamp(fasterRcnn_output->image_msg_header->stamp);
pub_data->header.set__frame_id(fasterRcnn_output->image_msg_header->frame_id);
// Fill algorithm inference output FPS to ROS Msg
if (node_output->rt_stat) {
pub_data->set__fps(round(node_output->rt_stat->output_fps));
// If there is an update in algorithm inference statistics, output the statistics of input and output FPS of the algorithm model
if (node_output->rt_stat->fps_updated) {
RCLCPP_WARN(rclcpp::get_logger("dnn_demo"),
"input fps: %.2f, out fps: %.2f",
node_output->rt_stat->input_fps,
node_output->rt_stat->output_fps);
}
}
for (auto& rect : out_box_list) {
// Validate the validity of the target tracking result
if (rect.id < 0) {
continue;
}
// Fill target tracking result and detection box to ROS Msg
ai_msgs::msg::Target target;
target.set__type("person");
target.set__track_id(rect.id);
ai_msgs::msg::Roi roi;
roi.type = "body";
roi.rect.set__x_offset(rect.x1);
roi.rect.set__y_offset(rect.y1);roi.rect.set__width(rect.x2 - rect.x1);
roi.rect.set__height(rect.y2 - rect.y1);
target.rois.emplace_back(roi);
pub_data->targets.emplace_back(std::move(target));
}
// Fill in the disappeared targets to ROS Msg
for (const auto& id_info : disappeared_ids) {
if (id_info->value < 0 ||
hobot_mot::DataState::INVALID == id_info->state_) {
continue;
}
ai_msgs::msg::Target target;
target.set__type("person");
target.set__track_id(id_info->value);
ai_msgs::msg::Roi roi;
roi.type = "body";
target.rois.emplace_back(roi);
pub_data->disappeared_targets.emplace_back(std::move(target));
}
// Publish ROS Msg
msg_publisher_->publish(std::move(pub_data));
return 0;
}
The dnn node contains built-in methods for parsing the output of various detection, classification, and segmentation algorithms. After installing tros.b on the RDK, the supported parsing methods can be queried as follows:
root@ubuntu:~# tree /opt/tros/include/dnn_node/util/output_parser
/opt/tros/include/dnn_node/util/output_parser
├── classification
│ └── ptq_classification_output_parser.h
├── detection
│ ├── fasterrcnn_output_parser.h
│ ├── fcos_output_parser.h
│ ├── nms.h
│ ├── ptq_efficientdet_output_parser.h
│ ├── ptq_ssd_output_parser.h
│ ├── ptq_yolo2_output_parser.h
│ ├── ptq_yolo3_darknet_output_parser.h
│ └── ptq_yolo5_output_parser.h
├── perception_common.h
├── segmentation
│ └── ptq_unet_output_parser.h
└── utils.h
3 directories, 12 files
You can see that there are three paths under the /opt/tros/include/dnn_node/util/output_parser directory, which correspond to the output parsing methods for classification, detection, and segmentation algorithms.
perception_common.h defines the data type of the parsed perception results.
The algorithm models and their corresponding output parsing methods are as follows:
| Algorithm Category | Algorithm | Output Parsing Method |
|---|---|---|
| Object Detection | FCOS | fcos_output_parser.h |
| Object Detection | EfficientNet_Det | ptq_efficientdet_output_parser.h |
| Object Detection | MobileNet_SSD | ptq_ssd_output_parser.h |
| Object Detection | YoloV2 | ptq_yolo2_output_parser.h |
| Object Detection | YoloV3 | ptq_yolo3_darknet_output_parser.h |
| Object Detection | YoloV5 | ptq_yolo5_output_parser.h |
| Human Detection | FasterRcnn | fasterrcnn_output_parser.h |
| Image Classification | mobilenetv2 | ptq_classification_output_parser.h |
| Semantic Segmentation | mobilenet_unet | ptq_unet_output_parser.h |
Entrance Function
Create an instance of BodyDetNode, initialize and start the inference task in the constructor of BodyDetNode, and stop the inference only when the user inputs the exit signal.
int main(int argc, char** argv) {
rclcpp::init(argc, argv);
rclcpp::spin(std::make_shared<BodyDetNode>());
rclcpp::shutdown();
return 0;
}
2.3 Compilation Dependencies
In step 1, the cpp_dnn_demo package was created using the ros2 pkg create command. The CMakeLists.txt and package.xml files have been automatically created in the dev_ws/src/cpp_dnn_demo directory.
The package.xml file automatically adds the compiled dependencies, which include rclcpp, sensor_msgs, ai_msgs, hbm_img_msgs, dnn_node, and hobot_mot. ai_msgs defines the message format of the algorithm output in TogatherROS, hbm_img_msgs defines the image message format used for zero-copy communication, dnn_node is the algorithm inference framework, and hobot_mot is the multi-object tracking algorithm. These packages are installed when TogatherROS is installed.
2.4 Compilation Script
Add package dependencies and compilation installation information in CMakeLists.txt.
(1) Add dependencies on the multi-object tracking algorithm and the algorithm inference engine library.
link_directories(
/opt/tros/lib/
``````cmake
# CMakeLists.txt
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.5)
project(cpp_dnn_demo)
# Default to C99
if(NOT CMAKE_C_STANDARD)
set(CMAKE_C_STANDARD 99)
endif()
# Default to C++14
if(NOT CMAKE_CXX_STANDARD)
set(CMAKE_CXX_STANDARD 14)
endif()
if(CMAKE_COMPILER_IS_GNUCXX OR CMAKE_CXX_COMPILER_ID MATCHES "Clang")
add_compile_options(-Wall -Wextra -Wpedantic)
endif()
# (1) Set the library path to "/usr/lib/hbbpu/"
set(LIBHB_PATH /usr/lib/hbbpu/)
# (2) Add pkg compilation information
add_executable(${PROJECT_NAME}
src/body_det_demo.cpp
)
ament_target_dependencies(
${PROJECT_NAME}
rclcpp
dnn_node
sensor_msgs
ai_msgs
hobot_mot
hbm_img_msgs
)
# (3) Add pkg installation information to enable running the compiled pkg with "ros2 run"
install(
TARGETS ${PROJECT_NAME}
RUNTIME DESTINATION lib/${PROJECT_NAME}
)# find dependencies
find_package(ament_cmake REQUIRED)
find_package(rclcpp REQUIRED)
find_package(sensor_msgs REQUIRED)
find_package(ai_msgs REQUIRED)
find_package(hbm_img_msgs REQUIRED)
find_package(dnn_node REQUIRED)
find_package(hobot_mot REQUIRED)
link_directories(
/opt/tros/lib/
/usr/lib/hbbpu/
)
add_executable(${PROJECT_NAME}
src/body_det_demo.cpp
)
ament_target_dependencies(
${PROJECT_NAME}
rclcpp
dnn_node
sensor_msgs
ai_msgs
hobot_mot
hbm_img_msgs
)
# Install executables
install(
TARGETS ${PROJECT_NAME}
RUNTIME DESTINATION lib/${PROJECT_NAME}
)
ament_package()
3 Build and Run
3.1 Build
In the RDK with tros.b installed, execute the following command to build the package:
cd ~/dev_ws
# Configure tros.b environment
source /opt/tros/setup.bash
```# Compiling pkg
colcon build --packages-select cpp_dnn_demo
If the compilation is successful, an installation package called "install" will be generated in the compilation path for the cpp_dnn_demo pkg. The following information will be displayed in the compilation terminal:
Starting >>> cpp_dnn_demo
[Processing: cpp_dnn_demo]
Finished <<< cpp_dnn_demo [32.7s]
Summary: 1 package finished [33.4s]
3.2 Common Compilation Errors
- ModuleNotFoundError: No module named 'ament_package'
Specific error message:
# colcon build --packages-select cpp_dnn_demo
Starting >>> cpp_dnn_demo
--- stderr: cpp_dnn_demo
CMake Error at CMakeLists.txt:19 (find_package):
By not providing "Findament_cmake.cmake" in CMAKE_MODULE_PATH this project
has asked CMake to find a package configuration file provided by
"ament_cmake", but CMake did not find one.
Could not find a package configuration file provided by "ament_cmake" with
any of the following names:
ament_cmakeConfig.cmake
ament_cmake-config.cmake
Add the installation prefix of "ament_cmake" to CMAKE_PREFIX_PATH or set
"ament_cmake_DIR" to a directory containing one of the above files. If
"ament_cmake" provides a separate development package or SDK, be sure it
has been installed.
---
Failed <<< cpp_dnn_demo [2.83s, exited with code 1]
Summary: 0 packages finished [3.44s]
1 package failed: cpp_dnn_demo
1 package had stderr output: cpp_dnn_demo
This indicates that the ROS2 environment is not configured successfully. Enter the "ros2" command in the terminal to check the environment:
# ros2
-bash: ros2: command not found
If you receive the "command not found" prompt, it means that the ROS2 environment has not been configured successfully. Please check if the command source /opt/tros/setup.bash has been executed successfully. The successful output information is as follows:
# ros2
usage: ros2 [-h] Call `ros2 <command> -h` for more detailed usage. ...
ros2 is an extensible command-line tool for ROS 2.
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
- Cannot find the dnn_node package
The specific error message is as follows:
colcon build --packages-select cpp_dnn_demo
Starting >>> cpp_dnn_demo
[Processing: cpp_dnn_demo]
--- stderr: cpp_dnn_demo
CMake Error at CMakeLists.txt:22 (find_package):
By not providing "Finddnn_node.cmake" in CMAKE_MODULE_PATH this project has
asked CMake to find a package configuration file provided by "dnn_node",
but CMake did not find one.
Could not find a package configuration file provided by "dnn_node" with any
of the following names:
dnn_nodeConfig.cmake
dnn_node-config.cmake
Add the installation prefix of "dnn_node" to CMAKE_PREFIX_PATH or set
"dnn_node_DIR" to a directory containing one of the above files. If
"dnn_node" provides a separate development package or SDK, be sure it has
been installed.
Failed <<< cpp_dnn_demo [59.7s, exited with code 1]
Summary: 0 packages finished [1min 1s]
1 package failed: cpp_dnn_demo
1 package had stderr output: cpp_dnn_demo
This indicates that the hobot_dnn environment has not been configured successfully. Please check if /opt/tros/share/dnn_node exists.
3.3 Running
In order to better display the effect of algorithm reasoning and experience perception ability, the MIPI camera image capture, image encoding, and WEB data display Node in tros.b are used to provide the ability of data sensing and display. The system can publish the captured images from the camera on RDK, perform algorithm reasoning to detect human body frames, and render and display the images and human body frame detection results in real time on the WEB browser on the PC side.
The runtime system process diagram is as follows:
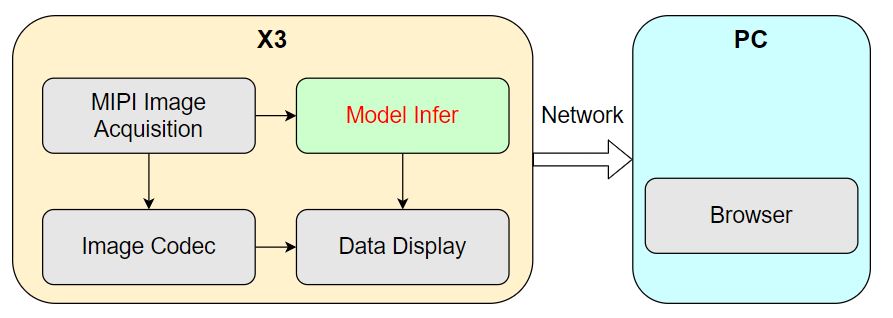
There are 4 nodes running on RDK, and algorithm reasoning is one of them in this example.
The system startup process is as follows:
(1) Open terminal one on RDK and start the algorithm reasoning node:
cd ~/dev_ws
# Configure the tros.b environment
source /opt/tros/setup.bash
# Configure the cpp_dnn_demo environment
source ./install/setup.bash
# Copy the necessary configuration files for running the example from the tros.b installation path
# Model file
mkdir -p config && cp /opt/tros/lib/dnn_benchmark_example/config/X3/multitask_body_kps_960x544.hbm config/
# Multi-object tracking configuration file
cp -r /opt/tros/lib/hobot_mot/config/iou2_method_param.json config/
# Run the cpp_dnn_demo pkg
ros2 run cpp_dnn_demo cpp_dnn_demo --ros-args --log-level warn
(2) Open terminal 2 on RDK and start the image publishing, encoding, and display Node in tros.b:
Since multiple Nodes need to be started, a launch script is used to start the Nodes in batches. Create a launch script cpp_dnn_demo.launch.py in any path on RDK, with the following content:
import os
from launch import LaunchDescription
from launch_ros.actions import Node
from launch.actions import IncludeLaunchDescription
from launch.launch_description_sources import PythonLaunchDescriptionSource
from ament_index_python import get_package_share_directory
from ament_index_python.packages import get_package_prefix
def generate_launch_description():
web_service_launch_include = IncludeLaunchDescription(
PythonLaunchDescriptionSource(
```os.path.join(
get_package_share_directory('websocket'),
'launch/websocket_service.launch.py'))
)
return LaunchDescription([
web_service_launch_include,
# Start image publishing package
Node(
package='mipi_cam',
executable='mipi_cam',
output='screen',
parameters=[
{"out_format": "nv12"},
{"image_width": 960},
{"image_height": 544},
{"io_method": "shared_mem"},
{"video_device": "F37"}
],
arguments=['--ros-args', '--log-level', 'error']
),
# Start jpeg image encoding & publishing package
Node(
package='hobot_codec',
executable='hobot_codec_republish',
output='screen',
parameters=[
{"channel": 1},
{"in_mode": "shared_mem"},
{"in_format": "nv12"},
{"out_mode": "ros"},
{"out_format": "jpeg"},
{"sub_topic": "/hbmem_img"},
{"pub_topic": "/image_jpeg"}
],
arguments=['--ros-args', '--log-level', 'error']
),
# Start web display package
Node(
package='websocket',
executable='websocket',
output='screen',
parameters=[
{"image_topic": "/image_jpeg"},
{"image_type": "mjpeg"},
{"smart_topic": "/cpp_dnn_demo"}
],
arguments=['--ros-args', '--log-level', 'error']
)
])Using startup script:
```shell
# Configure tros.b environment
source /opt/tros/setup.bash
# Launch the nodes for image publishing, encoding, and display
ros2 launch cpp_dnn_demo.launch.py
3.4 Common Errors
If the following error message is displayed during startup:
error while loading shared libraries: libdnn_node.so: cannot open shared object file: No such file or directory
Indicates failure to configure the hobot_dnn environment. Use the command ros2 pkg prefix dnn_node to check if dnn_node exists.
3.5 Results
After successful execution, the terminal outputs the following information:
root@ubuntu:~/dev_ws# ros2 run cpp_dnn_demo cpp_dnn_demo
[BPU_PLAT]BPU Platform Version(1.3.1)!
[C][154775][10-25][00:33:53:266][configuration.cpp:49][EasyDNN]EasyDNN version: 0.4.11
[HBRT] set log level as 0. version = 3.14.5
[DNN] Runtime version = 1.9.7_(3.14.5 HBRT)
[WARN] [1666629233.325690884] [dnn]: Run default SetOutputParser.
[WARN] [1666629233.326263403] [dnn]: Set output parser with default dnn node parser, you will get all output tensors and should parse output_tensors in PostProcess.
(MOTMethod.cpp:34): MOTMethod::Init config/iou2_method_param.json
(IOU2.cpp:29): IOU2 Mot::Init config/iou2_method_param.json
[WARN] [1666629234.410291616] [dnn_demo]: input fps: 31.22, out fps: 31.28
[WARN] [1666629235.410357068] [dnn_demo]: input fps: 30.00, out fps: 30.00
[WARN] [1666629236.444863458] [dnn_demo]: input fps: 30.01, out fps: 29.98
[WARN] [1666629237.476656118] [dnn_demo]: input fps: 30.00, out fps: 30.07
[WARN] [1666629238.478156431] [dnn_demo]: input fps: 30.01, out fps: 29.97
[WARN] [1666629239.510039629] [dnn_demo]: input fps: 30.01, out fps: 30.07
[WARN] [1666629240.511561150] [dnn_demo]: input fps: 30.00, out fps: 29.97
[WARN] [1666629241.543333811] [dnn_demo]: input fps: 30.01, out fps: 30.07
[WARN] [1666629242.544654089] [dnn_demo]: input fps: 30.01, out fps: 29.97
[WARN] [1666629243.576435625] [dnn_demo]: input fps: 30.01, out fps: 30.07
The log output shows that the model used for algorithm inference during initialization has an input image resolution of 960x544. The MOT algorithm engine is using the configuration file config/iou2_method_param.json. During inference, the input and output frame rate of the algorithm is 30fps, and the statistics are refreshed once per second.
Use the ros2 command on RDK to query and output the contents of the /cpp_dnn_demo topic messages published by the inference node.
root@ubuntu:~# source /opt/tros/setup.bash
root@ubuntu:~# ros2 topic list
/cpp_dnn_demo
/hbmem_img08172824022201080202012021072315
/image_jpeg
/parameter_events
/rosout
root@ubuntu:~# ros2 topic echo /cpp_dnn_demo
header:
stamp:
sec: 1659938514
nanosec: 550421888
frame_id: '7623'
fps: 30
perfs: []
targets:
- type: person
track_id: 1
rois:
- type: body
rect:
x_offset: 306
y_offset: 106
height: 416
width: 151
do_rectify: false
attributes: []
points: []
captures: []
- type: person
track_id: 2
rois:
- type: body
rect:
x_offset: 135
y_offset: 89
height: 423
width: 155
do_rectify: false
attributes: []
points: []
captures: []
- type: person
track_id: 3
rois:
- type: body
rect:
x_offset: 569y_offset: 161
height: 340
width: 123
do_rectify: false
attributes: []
points: []
captures: []
- type: person
track_id: 4
rois:
- type: body
rect:
x_offset: 677
y_offset: 121
height: 398
width: 123
do_rectify: false
attributes: []
points: []
captures: []
- type: person
track_id: 5
rois:
- type: body
rect:
x_offset: 478
y_offset: 163
height: 348
width: 103
do_rectify: false
attributes: []
points: []
captures: []
disappeared_targets: []
---
The output /cpp_dnn_demo topic message indicates that the algorithm detected 5 human body boxes , and output the coordinates and corresponding target tracking results (track_id) for each detection box.
Enter http://IP:8000 (IP is the IP address of RDK, for example, the IP address used in this example is 10.64.28.88) on the PC's web browser to view real-time images and algorithm inference rendering effects:

Each detection box is rendered with the detection box type (such as body indicating human body detection box) and the target tracking result. The fps field in the lower left corner of the browser indicates the real-time algorithm inference output frame rate.
Enter the Ctrl+C command to exit the program.
Summary of this sectionThis chapter introduces how to use the models provided by D-Robotics to create and run an algorithm inference example for human detection based on hobot_dnn. It uses images published from the camera, obtains the algorithm output, and renders and displays the image and algorithm inference results in real-time on the PC browser.
Users can refer to the README.md and the API Manual in hobot_dnn to learn about the richer algorithm inference capabilities.
Algorithm Workflow Construction
Background
ROS2 nodes decompose complex robot software systems into multiple functional and logically independent modules. For example, a robot application may include multiple nodes for sensing and algorithm perception functions. Nodes exchange data through "topics". Nodes with different functions in the robot software system are connected through topics to form a directed acyclic graph (DAG).
The D-Robotics TogetheROS.Bot software stack includes rich robot development components and algorithm nodes. The sensing nodes support capturing image data from the camera and publishing it for use in perception algorithm inference. The human bounding box detection algorithm node in the perception algorithm library performs inference on image data and outputs human bounding box detection results. The human keypoint detection algorithm node performs inference on image data and the human bounding box detection results to output human keypoint detection results. Therefore, the human keypoint detection algorithm node needs to communicate with the human bounding box detection algorithm node by subscribing to the human bounding box messages published by that node.
By reading this chapter, users can use the sensing nodes, human bounding box detection algorithm nodes, and human keypoint detection algorithm nodes in RDK, connect the sensing nodes and perception nodes through ROS2 topics, and achieve the goal of developing complex robot algorithm applications.
Preparation
- RDK development board with the following software installed:
-
D-Robotics-provided Ubuntu 20.04/22.04 system image
-
tros.bsoftware package
-
RDK with F37 or GC4663 camera installed
-
A PC in the same network segment (wired or connected to the same wireless network, with the first three segments of the IP address consistent with RDK). The PC needs to have the following environment installed:
-
Ubuntu 20.04/22.04 system
Usage
1. Start Data Collection Node
On the RDK, open a terminal and start the image publishing node, which captures image data from the F37 camera and publishes it for algorithm inference:
# Configure the tros.b environment
source /opt/tros/setup.bash
# Start the node
ros2 run mipi_cam mipi_cam --ros-args -p out_format:=nv12 -p image_width:=960 -p image_height:=544 -p video_device:=F37 -p io_method:=shared_mem --log-level warn
2. Start Human Bounding Box Detection Algorithm Node
On the RDK, open a terminal and start the human bounding box detection algorithm node, which subscribes to the image messages published by the data collection node, detects and publishes human bounding box messages.The publishing topic specified in the launch command is hobot_hand_detection.
# Set up tros.b environment
source /opt/tros/setup.bash
# Copy the required configuration files from the installation path of tros.b.
cp -r /opt/tros/lib/mono2d_body_detection/config/ .
# Start Node
ros2 run mono2d_body_detection mono2d_body_detection --ros-args --log-level warn --ros-args -p ai_msg_pub_topic_name:=hobot_hand_detection
3 Start the Node for Hand Keypoint Detection Algorithm
Open a terminal on the RDK and start the Node for hand keypoint detection algorithm. It subscribes to image messages published by the data collection Node and hand bounding box messages published by the hand bounding box detection algorithm Node.
The publishing topic is specified as hobot_hand_lmk_detection, and the subscribing topic is specified as hobot_hand_detection in the launch command.
# Set up tros.b environment
source /opt/tros/setup.bash
# Copy the required configuration files from the installation path of tros.b.
cp -r /opt/tros/lib/hand_lmk_detection/config/ .
# Start Node
ros2 run hand_lmk_detection hand_lmk_detection --ros-args --log-level warn --ros-args -p ai_msg_pub_topic_name:=hobot_hand_lmk_detection -p ai_msg_sub_topic_name:=hobot_hand_detection
4 View the Output of the Algorithm Inference
Open a terminal on the RDK and use the ROS2 command to view the Topic messages published by the algorithm inference Node.
View the hand bounding box detection messages published by the hand bounding box detection algorithm Node
Query command:
# Set up tros.b environment
source /opt/tros/setup.bash
# Start Node
ros2 topic echo /hobot_hand_detection
Output:
header:
stamp:
sec: 1660034025
nanosec: 429969208
frame_id: '8049'
fps: 30
targets:
- type: person
track_id: 10
rois:
- type: hand
rect:
x_offset: 619
y_offset: 128
height: 229
width: 168
do_rectify: false
attributes: []
points: []
captures: []
disappeared_targets: []
The message contains the results of a person's hand detection algorithm (roi type: hand) published by the fps: 30 target detection algorithm Node.
View the hand keypoint detection message published by the hand keypoint detection algorithm Node
Query command:
# Configure the tros.b environment
source /opt/tros/setup.bash
# Start the Node
ros2 topic echo /hobot_hand_lmk_detection
Output result:
header:
stamp:
sec: 1660034025
nanosec: 429969208
frame_id: '8049'
fps: 30
targets:
- type: person
track_id: 10
rois:
- type: hand
rect:
x_offset: 619
y_offset: 128
height: 229
width: 168do_rectify: false
attributes: []
points:
- type: hand_kps
point:
- x: 715.2421875
y: 348.0546875
z: 0.0
- x: 673.4921875
y: 315.8515625
z: 0.0
- x: 655.2265625
y: 294.3828125
z: 0.0
- x: 639.5703125
y: 262.1796875
z: 0.0
- x: 621.3046875
y: 229.9765625
z: 0.0
- x: 686.5390625
y: 247.8671875
z: 0.0
- x: 683.9296875
y: 201.3515625
z: 0.0
- x: 683.9296875
y: 176.3046875
z: 0.0
- x: 681.3203125
y: 147.6796875
z: 0.0
- x: 712.6328125
y: 240.7109375
z: 0.0
- x: 717.8515625
y: 194.1953125
z: 0.0
- x: 720.4609375
y: 161.9921875
z: 0.0
- x: 723.0703125
y: 129.7890625
z: 0.0
- x: 736.1171875
y: 247.8671875
z: 0.0
- x: 743.9453125
y: 201.3515625
z: 0.0- x: 749.1640625
y: 172.7265625
z: 0.0
- x: 749.1640625
y: 140.5234375
z: 0.0
- x: 759.6015625
y: 262.1796875
z: 0.0
- x: 770.0390625
y: 226.3984375
z: 0.0
- x: 775.2578125
y: 204.9296875
z: 0.0
- x: 775.2578125
y: 179.8828125
z: 0.0
confidence: []
captures: []
disappeared_targets: []
We can see that the published message contains the bounding box and keypoint detection results of the hand. The bounding box information is consistent with the subscribed message.The Rqt's Node Graph function on the PC side (the PC needs to be in the same network segment as the RDK) can visualize the Nodes running on the RDK, the topics published and subscribed by the Nodes, and the graph composed of these topics, as shown in the figure below:

In the figure, the ellipses represent the Node names, and the rectangles represent the Topic names. It can be seen that the entire graph consists of 3 Nodes and 2 Topics.
The "mipi_cam" (sensing Node) is the starting point, responsible for capturing and publishing images from the camera.
The "mono2d_body_det" (algorithm perception Node) is the middle node, subscribing to the image data published by the "mipi_cam" Node and performing human body box detection.
The "hand_lmk_det" (algorithm perception Node) is the end node, subscribing to the image data published by the "mipi_cam" Node and the human body box detection data published by the "mono2d_body_det" Node, and performing hand keypoint detection.
Summary
This chapter introduces the use of sensing Nodes, human body box detection Nodes, and hand keypoint detection algorithm Nodes in the RDK, based on ROS2 topic communication. By connecting two perception algorithm Nodes, images captured from the camera are used for algorithm inference and the detected hand keypoints are published as messages.
Based on the algorithm chaining principle introduced in this chapter, users can connect more algorithm Nodes on the RDK and develop feature-rich robot algorithm applications.