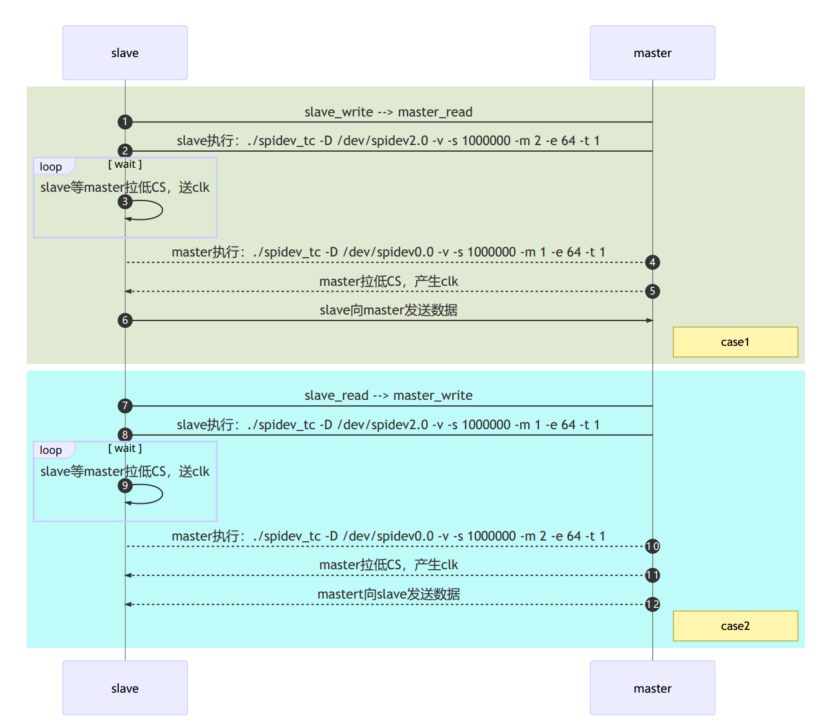
SPI Debugging Guide
Driver Code
Code Path
drivers/spi/spidev.c # Generate character device node for user space operations
drivers/spi/spi.c # SPI framework layer code
drivers/spi/spi-hobot.c # SPI driver layer code
Kernel Configuration
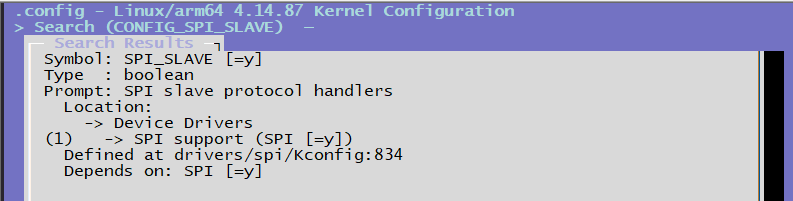
CONFIG_SPI_SPIDEV=y # Configuration option for spidev.c
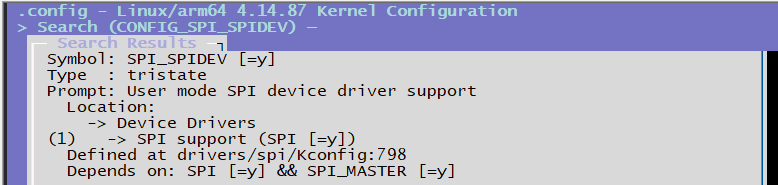
CONFIG_SPI_SLAVE=y # Configuration option that CONFIG_SPI_SPIDEV depends on
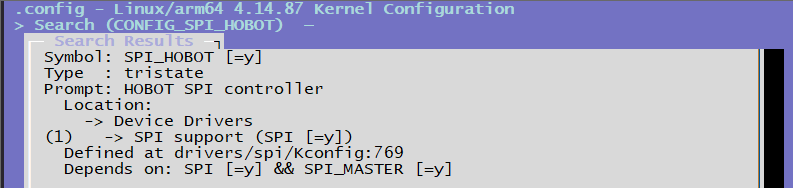
CONFIG_SPI_HOBOT=y # Configuration option for spi-hobot.c driver layer
DTS Device Node Configuration
Add the appropriate device node in the following file and compile the kernel. File path: arch/arm64/boot/dts/hobot/hobot-xj3.dtsi
spi0: spi@0xA5004000 {
compatible = "hobot,hobot-spi";
reg = <0 0xA5004000 0 0x1000>;
clocks = <&spi0_mclk>;
clock-names = "spi_mclk";
interrupt-parent = <&gic>;
interrupts = <0 33 4>;
resets = <&rst 0x50 4>;
reset-names = "spi0";
pinctrl-names = "default";
pinctrl-0 = <&spi0_func>;
status = "disabled";
#address-cells = <1>;
#size-cells = <0>;
File path: arch/arm64/boot/dts/hobot/hobot-x3-sdb.dts
/* Configure as master */
&spi0 {
status = "okay";
spidev@0x00 {
compatible = "rohm,dh2228fv";
spi-max-frequency = <20000000>;
reg = <0>;
};
};
/* Configure as slave */
&spi2 {
status = "okay";
slave = <1>;
slave@0x00 {
compatible = "rohm,dh2228fv";
spi-max-frequency = <20000000>;
reg = <0>;
};
};
Using spi0 and spi2 configurations as examples
- The nodes in hobot-x3.dtsi are shared nodes and generally do not need to be modified. For different hardware, modifications will be made in the corresponding dts files.
- spi0 is configured as spi master and spi2 is configured as spi slave. The attribute isslave = <1> in spi2 represents that it is configured as a slave.
- The nodes spidev@0x00 and slave@0x00 in both nodes will be recognized as /dev/spidev0.0 and /dev/spidev2.0 devices in spidev.c and can be accessed by user space.
SPI Driver
The driver is located at: drivers/spi/spi-hobot.c
SPI master/slave configuration
static int hb_spi_probe(struct platform_device *pdev)
{
...
/* master or slave mode select */
isslave = of_property_read_bool(pdev->dev.of_node, "slave");
if (isslave == MASTER_MODE) {
ctlr = spi_alloc_master(&pdev->dev, sizeof(*hbspi));
if (!ctlr) {
dev_err(&pdev->dev, "failed to alloc spi master\n");
return -ENOMEM;
}
} else if (isslave == SLAVE_MODE) {
ctlr = spi_alloc_slave(&pdev->dev, sizeof(*hbspi));
if (!ctlr) {
dev_err(&pdev->dev, "failed to alloc spi slave, try master\n");
return -ENOMEM;
}
}
...
}
SPI Registration
Register SPI controller with the kernel
static int hb_spi_probe(struct platform_device *pdev)
{
...
if (isslave == MASTER_MODE) {
hbspi->isslave = MASTER_MODE;
snprintf(ctrl_mode, sizeof(ctrl_mode), "%s", "master");
ctlr->bus_num = pdev->id;
// ctlr->num_chipselect = HB_SPI_MAX_CS;
ctlr->mode_bits = SPI_CPOL | SPI_CPHA | SPI_LSB_FIRST | SPI_CS_HIGH |
SPI_NO_CS;
ctlr->setup = hb_spi_setup;
ctlr->prepare_transfer_hardware = hb_spi_prepare_xfer_hardware;
ctlr->transfer_one = hb_spi_transfer_one;
ctlr->unprepare_transfer_hardware = hb_spi_unprepare_xfer_hardware;
ctlr->set_cs = hb_spi_chipselect;
ctlr->dev.of_node = pdev->dev.of_node;
} else if (isslave == SLAVE_MODE) {
hbspi->isslave = SLAVE_MODE;
snprintf(ctrl_mode, sizeof(ctrl_mode), "%s", "slave");
ctlr->mode_bits = SPI_CPOL | SPI_CPHA | SPI_LSB_FIRST;
ctlr->setup = hb_spi_slave_setup;
ctlr->prepare_message = hb_spi_slave_prepare_message;
ctlr->transfer_one = hb_spi_slave_transfer_one;
ctlr->slave_abort = hb_spi_slave_abort;
}
/* register spi controller */
ret = devm_spi_register_controller(&pdev->dev, ctlr);
if (ret) {
dev_err(&pdev->dev, "failed to register %s controller(%d)\n",
ctrl_mode, ret);
goto clk_dis_mclk;
}
···
}
Hardware initialization
The hardware initialization function is as follows. The meaning of the registers can be confirmed by checking with the D-Robotics related information.
/* spi hw init */
static void hb_spi_init_hw(struct hb_spi *hbspi)
{
u32 val = 0;
/* First, should reset the whole controller */
hb_spi_reset(hbspi);
hb_spi_en_ctrl(hbspi, HB_SPI_OP_CORE_DIS, HB_SPI_OP_NONE,
HB_SPI_OP_NONE);
hb_spi_wr(hbspi, HB_SPI_INTSETMASK_REG, HB_SPI_INT_ALL);
/* clear all interrupt pending */
hb_spi_wr(hbspi, HB_SPI_SRCPND_REG, HB_SPI_INT_ALL);
/* init rfto */
hb_spi_wr(hbspi, HB_SPI_RFTO_REG, 0x27F);
/* no instruction */
hb_spi_wr(hbspi, HB_SPI_INST_REG, 0x0);
hb_spi_wr(hbspi, HB_SPI_INST_MASK_REG, 0xFFFFFFFF);
/* spi master mode */
val = hb_spi_rd(hbspi, HB_SPI_CTRL_REG);
if (hbspi->isslave == SLAVE_MODE)
val |= HB_SPI_SLAVE_MODE;
else
val &= (~HB_SPI_SLAVE_MODE);
if (hbspi->isslave == MASTER_MODE)
val &= (~HB_SPI_SAMP_SEL);
hb_spi_wr(hbspi, HB_SPI_CTRL_REG, val);
if (debug)
dev_err(hbspi->dev, "%s CTRL=%08X\n",
__func__, hb_spi_rd(hbspi, HB_SPI_CTRL_REG));
hb_spi_config(hbspi);
hb_spi_en_ctrl(hbspi, HB_SPI_OP_CORE_EN, 0, 0);
}
Debug parameters
The following are the debug parameters outputted in the spi driver:
static int debug;
static int slave_tout = 2000;
static int master_tout = 1000;
```module_param(debug, int, 0644);
MODULE_PARM_DESC(debug, "spi: 0 close debug, other open debug");
module_param(slave_tout, int, 0644);
MODULE_PARM_DESC(slave_tout, "spi: slave timeout(sec), default 10 s");
module_param(master_tout, int, 0644);
MODULE_PARM_DESC(master_tout, "spi: master timeout(sec), default 2 s");
- The debug level can be set to 0, 1, or 2, with a default value of 0.
- The default timeout for slave is 2s, and the maximum valid value is 100s.
- The default timeout for master is 1s, and the maximum valid value is 10s.
To modify the parameters using sysfs in the kernel command line, follow the steps below. The units in sysfs are all in milliseconds. Find the available parameters, which include 3 parameters.
ls /sys/module/spi_hobot/parameters/
The output should be as follows:
root@x3dvbj3-hynix2G-2666:~# ls /sys/module/spi_hobot/parameters/
debug master_tout slave_tout
Get the current value of the debug parameter. The default value is 0, which means debug is not enabled.
cat /sys/module/spi_hobot/parameters/debug
The output should be as follows:
root@x3dvbj3-hynix2G-2666:~# cat /sys/module/spi_hobot/parameters/debug
0
Set the debug parameter value to 1 and confirm the setting is successful:
echo 1 > /sys/module/spi_hobot/parameters/debug
cat /sys/module/spi_hobot/parameters/debug
The output should be as follows:
root@x3dvbj3-hynix2G-2666:~# echo 1 > /sys/module/spi_hobot/parameters/debugroot@x3dvbj3-hynix2G-2666:~# cat /sys/module/spi_hobot/parameters/debug
1
Get the current master_tout parameter, which is the value of the master timeout: default is 2s
cat /sys/module/spi_hobot/parameters/master_tout
The following should be printed:
root@x3dvbj3-hynix2G-2666:~# cat /sys/module/spi_hobot/parameters/master_tout
1000
Get the current slave_tout parameter, which is the value of the slave timeout: default is 1s
cat /sys/module/spi_hobot/parameters/slave_tout
The following should be printed:
root@x3dvbj3-hynix2G-2666:~# cat /sys/module/spi_hobot/parameters/slave_tout
2000
SPI Testing
Hardware Loopback Test
Kernel dts enables spi0 as master mode:
/* Configure as master */
&spi0 {
status = "okay";
spidev@0x00 {
compatible = "rohm,dh2228fv";
spi-max-frequency = <20000000>;
reg = <0>;
};
};
You can observe the spidev0.0 device node
# ls /dev/spidev0.0
/dev/spidev0.0
Connect the MOSI and MISO pins of the SPI using a connector.

Test Code
Compile the spidev_tc.c code, the specific code is as follows:
/opt/gcc-ubuntu-9.3.0-2020.03-x86_64-aarch64-linux-gnu/bin/aarch64-linux-gnu-gcc -o spidev_tc spidev_tc.c -lpthread
Loopback test command: open /dev/spidev0.0, set the speed to 12MHz, perform read and write operations simultaneously, read and write 1000 bytes each time, test 50 rounds.
# ./spidev_tc -D /dev/spidev0.0 -s 12000000 -m 3 -e 1000 -t 50
spi mode: 0x0
bits per word: 8
max speed: 12000000 Hz (12000 KHz)
userspace spi read and write test, len=1000 times=50
test: OK, times=0
test: OK, times=1
...
test: OK, times=49
The spidev_tc command is a command set for testing SPI, and you can read its help information for more usage methods.
Appendix
spidev_tc.c Test Code
/*
* SPI testing utility (using spidev driver)
*
* Copyright (c) 2007 MontaVista Software, Inc.
* Copyright (c) 2007 Anton Vorontsov <avorontsov@ru.mvista.com>
*
* This program is free software; you can redistribute it and/or modify
* it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by
* the Free Software Foundation; either version 2 of the License.
*
* Cross-compile with cross-gcc -I/path/to/cross-kernel/include
*/
#include <stdint.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <getopt.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <time.h>
#include <sys/ioctl.h>
#include <linux/ioctl.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <linux/types.h>
#include <linux/spi/spidev.h>
#define ARRAY_SIZE(a) (sizeof(a) / sizeof((a)[0]))
static void pabort(const char *s)
{
perror(s);
abort();
}
static const char *device = "/dev/spidev0.0";
static uint32_t mode;
static uint8_t bits = 8;
static char *input_file;
static char *output_file;
static uint32_t speed = 500000;
static uint16_t delay;
static int verbose;
static int transfer_size;
static int iterations;
static int interval = 5; /* interval in seconds for showing transfer rate */
static int rw_mode = 0; //1: read, 2: write, 3: write and read
static int rw_len = 4;
static int rw_times = 5;
uint8_t default_tx[] = {
0xFF, 0xFF, 0xFF, 0xFF, 0xFF, 0xFF,
0x40, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x95,
0xFF, 0xFF, 0xFF, 0xFF, 0xFF, 0xFF,
0xFF, 0xFF, 0xFF, 0xFF, 0xFF, 0xFF,
0xFF, 0xFF, 0xFF, 0xFF, 0xFF, 0xFF,
0xF0, 0x0D,
};
uint8_t default_rx[ARRAY_SIZE(default_tx)] = {0, };
char *input_tx;
static void hex_dump(const void *src, size_t length, size_t line_size,
char *prefix)
{
int i = 0;
const unsigned char *address = src;
const unsigned char *line = address;
unsigned char c;
printf("%s | ", prefix);
while (length-- > 0) {
printf("%02X ", *address++);
if (!(++i % line_size) || (length == 0 && i % line_size)) {
if (length == 0) {
while (i++ % line_size)
printf("__ ");
}
printf(" | "); /* right close */
while (line < address) {
c = *line++;
printf("%c", (c < 33 || c == 255) ? 0x2E : c);
}
printf("\n");
if (length > 0)
printf("%s | ", prefix);
}
}
}
static void hex_dump2(const void *src, size_t length, size_t line_size,
char *prefix)
{
int i = 0;
const unsigned char *address = src;
const unsigned char *line = address;
unsigned char c;
printf("%s | ", prefix);
while (length-- > 0) {
printf("%02X ", *address++);
if (!(++i % line_size) || (length == 0 && i % line_size)) {
if (length == 0) {
while (i++ % line_size)
printf("__ ");
}
printf("\n");
if (length > 0)
printf("%s | ", prefix);
}
}
printf("\n");
}/*
* Unescape - process hexadecimal escape character
* converts shell input "\x23" -> 0x23
*/
static int unescape(char *_dst, char *_src, size_t len)
{
int ret = 0;
int match;
char *src = _src;
char *dst = _dst;
unsigned int ch;
while (*src) {
if (*src == '\\' && *(src+1) == 'x') {
match = sscanf(src + 2, "%2x", &ch);
if (!match)
pabort("malformed input string");
src += 4;
*dst++ = (unsigned char)ch;
} else {
*dst++ = *src++;
}
ret++;
}
return ret;
}
static void transfer(int fd, uint8_t const *tx, uint8_t const *rx, size_t len)
{
int ret;
int out_fd;
struct spi_ioc_transfer tr = {
.tx_buf = (unsigned long)tx,
.rx_buf = (unsigned long)rx,
.len = len,
.delay_usecs = delay,
.speed_hz = speed,
.bits_per_word = bits,
};
if (mode & SPI_TX_QUAD)
tr.tx_nbits = 4;
else if (mode & SPI_TX_DUAL)
tr.tx_nbits = 2;
if (mode & SPI_RX_QUAD)
tr.rx_nbits = 4;
else if (mode & SPI_RX_DUAL)
tr.rx_nbits = 2;
}
tr.rx_nbits = 2;
if (!(mode & SPI_LOOP)) {
if (mode & (SPI_TX_QUAD | SPI_TX_DUAL))
tr.rx_buf = 0;
else if (mode & (SPI_RX_QUAD | SPI_RX_DUAL))
tr.tx_buf = 0;
}
ret = ioctl(fd, SPI_IOC_MESSAGE(1), &tr);
if (ret < 1)
pabort("can't send spi message");
if (verbose)
hex_dump(tx, len, 32, "TX");
if (output_file) {
out_fd = open(output_file, O_WRONLY | O_CREAT | O_TRUNC, 0666);
if (out_fd < 0)
pabort("could not open output file");
ret = write(out_fd, rx, len);
if (ret != len)
pabort("not all bytes written to output file");
close(out_fd);
}
if (verbose)
hex_dump(rx, len, 32, "RX");
}
static void transfer2(int fd, uint8_t const *tx, uint8_t const *rx, size_t len)
{
int ret;
int out_fd;
struct spi_ioc_transfer tr = {
.tx_buf = (unsigned long)tx,
.rx_buf = (unsigned long)rx,
.len = len,
.delay_usecs = delay,
.speed_hz = speed,
.bits_per_word = bits,
};
if (mode & SPI_TX_QUAD)
tr.tx_nbits = 4;
else if (mode & SPI_TX_DUAL)
tr.tx_nbits = 2;
if (mode & SPI_RX_QUAD)
tr.rx_nbits = 4;else if (mode & SPI_RX_DUAL)
tr.rx_nbits = 2;
if (!(mode & SPI_LOOP)) {
if (mode & (SPI_TX_QUAD | SPI_TX_DUAL))
tr.rx_buf = 0;
else if (mode & (SPI_RX_QUAD | SPI_RX_DUAL))
tr.tx_buf = 0;
}
if (verbose && rw_mode >> 1)
hex_dump2(tx, len, 32, "TX");
ret = ioctl(fd, SPI_IOC_MESSAGE(1), &tr);
if (ret < 1) {
//pabort("can't send spi message");
printf("can't send spi message");
} else {
if (output_file) {
out_fd = open(output_file, O_WRONLY | O_CREAT | O_TRUNC, 0666);
if (out_fd < 0)
pabort("could not open output file");
ret = write(out_fd, rx, len);
if (ret != len)
pabort("not all bytes written to output file");
close(out_fd);
}
if (verbose && rw_mode&0x01)
hex_dump2(rx, len, 32, "RX");
}
}
static void print_usage(const char *prog)
{
printf("Usage: %s [-DsbdlHOLC3vpNR24SImet]\n", prog);
puts(" -D --device 设备使用地址(默认 /dev/spidev1.1)\n"
" -s --speed 最大速度(Hz)\n"
" -d --delay 延迟时间(微秒)\n"
" -b --bpw 字长\n"
" -i --input 从文件中输入数据(例如 \"test.bin\")\n"
" -o --output 输出数据到文件(例如 \"results.bin\")\n"
" -l --loop 环回测试\n"
" -H --cpha 时钟相位\n"
" -O --cpol 时钟极性\n"
" -L --lsb 最低有效位\n"
" -C --cs-high 片选信号激活高电平\n"
" -3 --3wire SI/SO信号共用\n"" -v --verbose Verbose (show tx buffer)\n" -> "-v --verbose 详细信息(显示发送缓冲区)\n"
" -p Send data (e.g. \"1234\\xde\\xad\")\n" -> " -p 发送数据(例如\"1234\\xde\\xad\")\n"
" -N --no-cs no chip select\n" -> " -N --no-cs 不使用芯片选择\n"
" -R --ready slave pulls low to pause\n" -> " -R --ready 从机拉低以暂停\n"
" -2 --dual dual transfer\n" -> " -2 --dual 双通道传输\n"
" -4 --quad quad transfer\n" -> " -4 --quad 四通道传输\n"
" -S --size transfer size\n" -> " -S --size 传输大小\n"
" -I --iter iterations\n" -> " -I --iter 迭代次数\n"
" -m --rw-mode 1 read, 2 write, 3 write and read\n" -> " -m --rw-mode 1 读取, 2 写入, 3 写入和读取\n"
" -e --rw-len read or write len\n" -> " -e --rw-len 读取或写入长度\n"
" -t --rw-times read or write times\n" -> " -t --rw-times 读取或写入次数\n");
exit(1);
}
static void parse_opts(int argc, char *argv[])
{
while (1) {
static const struct option lopts[] = {
{ "device", 1, 0, 'D' },
{ "speed", 1, 0, 's' },
{ "delay", 1, 0, 'd' },
{ "bpw", 1, 0, 'b' },
{ "input", 1, 0, 'i' },
{ "output", 1, 0, 'o' },
{ "loop", 0, 0, 'l' },
{ "cpha", 0, 0, 'H' },
{ "cpol", 0, 0, 'O' },
{ "lsb", 0, 0, 'L' },
{ "cs-high", 0, 0, 'C' },
{ "3wire", 0, 0, '3' },
{ "no-cs", 0, 0, 'N' },
{ "ready", 0, 0, 'R' },
{ "dual", 0, 0, '2' },
{ "verbose", 0, 0, 'v' },
{ "quad", 0, 0, '4' },
{ "size", 1, 0, 'S' },
{ "iter", 1, 0, 'I' },
{ "rw-mode", 1, 0, 'm' },
{ "rw-len", 1, 0, 'e' },
{ "rw-times", 1, 0, 't' },
{ NULL, 0, 0, 0 },
};
int c;
c = getopt_long(argc, argv, "D:s:d:b:i:o:lHOLC3NR24p:vS:I:m:e:t:",
lopts, NULL);
//printf("optind: %d\n", optind);
//printf("optarg: %s\n", optarg);
//printf("option: %c\n", c);
if (c == -1)
break;
switch (c) {
case 'D':
device = optarg;
break;
case 's':
speed = atoi(optarg);
break;
case 'd':
delay = atoi(optarg);
break;
case 'b':
bits = atoi(optarg);
break;
case 'i':
input_file = optarg;
break;
case 'o':
output_file = optarg;
break;
case 'l':
mode |= SPI_LOOP;
break;
case 'H':
mode |= SPI_CPHA;
break;
case 'O':
mode |= SPI_CPOL;
break;
case 'L':
mode |= SPI_LSB_FIRST;
break;
case 'C':
mode |= SPI_CS_HIGH;
break;
case '3':
mode |= SPI_3WIRE;
break;
case 'N':
mode |= SPI_NO_CS;
break;
case 'v':
verbose = 1;
break;
case 'R':
mode |= SPI_READY;
break;
case 'p':input_tx = optarg;
break;
case '2':
mode |= SPI_TX_DUAL;
break;
case '4':
mode |= SPI_TX_QUAD;
break;
case 'S':
transfer_size = atoi(optarg);
break;
case 'I':
iterations = atoi(optarg);
break;
case 'm':
rw_mode = atoi(optarg);
break;
case 'e':
rw_len = atoi(optarg);
break;
case 't':
rw_times = atoi(optarg);
break;
default:
print_usage(argv[0]);
break;
}
}
if (mode & SPI_LOOP) {
if (mode & SPI_TX_DUAL)
mode |= SPI_RX_DUAL;
if (mode & SPI_TX_QUAD)
mode |= SPI_RX_QUAD;
}
}
static void transfer_escaped_string(int fd, char *str)
{
size_t size = strlen(str);
uint8_t *tx;
uint8_t *rx;
tx = malloc(size);
if (!tx)
pabort("can't allocate tx buffer");
rx = malloc(size);
if (!rx)
pabort("can't allocate rx buffer");
size = unescape((char *)tx, str, size);
printf("size: %d\n", size);
transfer(fd, tx, rx, size);
free(rx);
free(tx);
}
static void transfer_file(int fd, char *filename)
{
ssize_t bytes;
struct stat sb;
int tx_fd;
uint8_t *tx;
uint8_t *rx;
if (stat(filename, &sb) == -1)
pabort("can't stat input file");
tx_fd = open(filename, O_RDONLY);
if (tx_fd < 0)
pabort("can't open input file");
tx = malloc(sb.st_size);
if (!tx)
pabort("can't allocate tx buffer");
rx = malloc(sb.st_size);
if (!rx)
pabort("can't allocate rx buffer");
bytes = read(tx_fd, tx, sb.st_size);
if (bytes != sb.st_size)
pabort("failed to read input file");
transfer(fd, tx, rx, sb.st_size);
free(rx);
free(tx);
close(tx_fd);
}
static uint64_t _read_count;
static uint64_t _write_count;
static void show_transfer_rate(void)
{
static uint64_t prev_read_count, prev_write_count;
double rx_rate, tx_rate;
rx_rate = ((_read_count - prev_read_count) * 8) / (interval*1000.0);
tx_rate = ((_write_count - prev_write_count) * 8) / (interval*1000.0);printf("rate: tx %.1fkbps, rx %.1fkbps\n", rx_rate, tx_rate);
prev_read_count = _read_count;
prev_write_count = _write_count;
}
static void transfer_buf(int fd, int len)
{
uint8_t *tx;
uint8_t *rx;
int i;
tx = malloc(len);
if (!tx)
pabort("can't allocate tx buffer");
for (i = 0; i < len; i++)
tx[i] = random();
rx = malloc(len);
if (!rx)
pabort("can't allocate rx buffer");
transfer(fd, tx, rx, len);
_write_count += len;
_read_count += len;
if (mode & SPI_LOOP) {
if (memcmp(tx, rx, len)) {
fprintf(stderr, "transfer error !\n");
hex_dump(tx, len, 32, "TX");
hex_dump(rx, len, 32, "RX");
exit(1);
}
}
free(rx);
free(tx);
}
static void transfer_read_write(int fd)
{
uint8_t *tx;
uint8_t *rx;
int i, j;
int len, times;
char str[64] = {0};
len = rw_len > 0 ? rw_len : 4;times = rw_times > 0 ? rw_times : 4;
if (rw_mode == 2)
sprintf(str, "write");
else if (rw_mode == 3)
sprintf(str, "read and write");
else {
rw_mode = 1;
sprintf(str, "read");
}
printf("userspace spi %s test, len=%d times=%d\n", str, len, times);
tx = malloc(len + 4);
if (!tx)
pabort("can't allocate tx buffer");
rx = malloc(len + 4);
if (!rx)
pabort("can't allocate rx buffer");
for (j = 0; j < rw_times; j++) {
memset(tx, 0 ,len);
memset(rx, 0, len);
if (rw_mode >> 1) {
for (i = 0; i < len; i++)
tx[i] = random();
} else {
for (i = 0; i < len; i++)
tx[i] = i << 2;
}
transfer2(fd, tx, rx, len);
printf("test: %s, times=%d\n", strncmp(tx, rx, len) == 0 ? "OK" : "Failed", j);
//sleep(2);
}
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
int ret = 0;
int fd;
parse_opts(argc, argv);
fd = open(device, O_RDWR);
if (fd < 0)
pabort("can't open device");
/*
* spi mode
*/
ret = ioctl(fd, SPI_IOC_WR_MODE32, &mode);
if (ret == -1)
pabort("can't set spi mode");
ret = ioctl(fd, SPI_IOC_RD_MODE32, &mode);
if (ret == -1)
pabort("can't get spi mode");
/*
* bits per word
*/
ret = ioctl(fd, SPI_IOC_WR_BITS_PER_WORD, &bits);
if (ret == -1)
pabort("can't set bits per word");
ret = ioctl(fd, SPI_IOC_RD_BITS_PER_WORD, &bits);
if (ret == -1)
pabort("can't get bits per word");
/*
* max speed hz
*/
ret = ioctl(fd, SPI_IOC_WR_MAX_SPEED_HZ, &speed);
if (ret == -1)
pabort("can't set max speed hz");
ret = ioctl(fd, SPI_IOC_RD_MAX_SPEED_HZ, &speed);
if (ret == -1)
pabort("can't get max speed hz");
printf("spi mode: 0x%x\n", mode);
printf("bits per word: %d\n", bits);
printf("max speed: %d Hz (%d KHz)\n", speed, speed/1000);
if (input_tx && input_file)
pabort("only one of -p and --input may be selected");
if (input_tx)
transfer_escaped_string(fd, input_tx);
else if (input_file)
transfer_file(fd, input_file);
else if (transfer_size) {
struct timespec last_stat;
clock_gettime(CLOCK_MONOTONIC, &last_stat);
while (iterations-- > 0) {
struct timespec current;
transfer_buf(fd, transfer_size);```c
clock_gettime(CLOCK_MONOTONIC, ¤t);
if (current.tv_sec - last_stat.tv_sec > interval) {
show_transfer_rate();
last_stat = current;
}
}
printf("total: tx %.1fKB, rx %.1fKB\n",
_write_count/1024.0, _read_count/1024.0);
} else if (rw_mode) {
transfer_read_write(fd);
} else
transfer(fd, default_tx, default_rx, sizeof(default_tx));
close(fd);
return ret;
}
SPI Timing