UART Stress Test
Test Principle
UART stress testing is a method used to verify the stability and performance of UART communication by exchanging large volumes of data and performing high-load operations. Its principle mainly involves sending and receiving massive amounts of data to simulate real-world UART usage scenarios. Specifically, it includes the following aspects:
- Data Transmission and Reception: The core principle of UART stress testing is to send large amounts of data to a UART device and then receive data back from it.
- Data Transmission: A script or program generates large data packets and sends them to the target device via the UART interface.
- Data Reception: The target device returns the received data (e.g., through a UART loopback test or an external device’s response). The stress test program receives this data and performs comparison and validation.
- Baud Rate and Data Frame Configuration: Baud rate defines the transmission speed of UART communication, typically expressed in bits per second (bps). UART communication also involves other parameters, such as:
- Data Bits: The number of data bits in each data frame (commonly 8 or 7 bits).
- Stop Bits: Bits indicating the end of data transmission (typically 1 or 2 bits).
- Parity Bits: Used for error checking during data transmission (odd/even parity).
Test Content
1. Test Procedure:
The uartstress.sh script uses a loopback test—a common UART testing method—where data sent from the transmitter is physically or logically routed back to the receiver to verify correct data transmission. In the source code uart_test.c, the function perform_single_loopback_test() implements this test with the following steps:
- Open the UART port and configure its parameters using
open_uart(). - Initialize a semaphore using
sem_init()to ensure proper thread synchronization. - Create three threads:
- Send thread (
uart_send_thread): Responsible for transmitting data. - Receive thread (
uart_recv_thread): Responsible for receiving data and storing it in a buffer. - Data verification thread (
check_recv_thread): Compares received data against the originally sent data for consistency.
- Send thread (
- Once all threads complete their tasks,
pthread_join()waits for all threads to finish before concluding the test.
2. Command Analysis:
- Test command:
uart_test -l -s 1024 -c "$StressCount" -b "$Baudrate" -d "$Device" > "$uart_test_log_file" - Parameter explanation:
-l: Perform a loopback test.-s 1024: Specify the data size per test as 1024 bytes.-c "$StressCount": Define the number of stress test iterations (i.e., how many times the test repeats).-b "$Baudrate": Set the UART baud rate; the variable$Baudratewill be replaced with the actual value provided.-d "$Device": Specify the UART device path via the variable$Device.> "$uart_test_log_file": Redirect test output to the specified log file$uart_test_log_file.
Preparation
Usage Instructions for the Stress Test Script
UART stress testing supports the -h suffix to display command parameter descriptions. For example:
sunrise@ubuntu:/app/chip_base_test/03_uart_test$ ./uartstress.sh -h
Usage: ./uartstress.sh [options]
Options:
-b <baudrate> Set the UART baud rate (default: 115200).
-d <device> Set the UART device (default: /dev/ttyS2).
-c <count> Set the stress count (default: 100).
-o <directory> Set the output directory for logs (default: ../log).
-h Show this help message and exit.
Parameter details:
-b <baudrate>: Sets the baud rate (default: 115200).-d <device>: Specifies the UART device to test (default:/dev/ttyS2).-c <count>: Defines the number of stress iterations (default: 100).-o <directory>: Sets the log output directory (default:../log).
Example:
For instance, the command:
./uartstress.sh -b 115200 -d /dev/ttyS2 -c 50 -o /app/chip_base_test
configures the baud rate to 115200, uses UART device ttyS2 (corresponding to the actual UART in use), runs 50 test iterations, and outputs logs to /app/chip_base_test.
Usage Instructions for the Executable Program
The uart_test program supports multiple test modes. Supported command-line options are as follows:
Usage: uart_test [OPTIONS]
Options:
-s, --size : Specify test data size in KB (default: 1024KB, max: 20480KB / 20MB)
-b, --baudrate : Specify UART baud rate (default: 115200)
-c, --count : Specify number of test iterations (default: infinite loop)
-d, --device : Specify UART device path
-l, --loopback : Enable UART loopback test
-r, --read-only : Enable UART read-only mode test
-w, --write-only: Enable UART write-only mode test
-D, --dual-loopback : Enable dual UART bidirectional loopback test (requires --uart2)
-u, --uart2 : Specify second UART device path (mandatory for dual loopback)
-V, --verbose : Set log output mode via bitwise AND:
1 = send module logs;
2 = receive module logs;
4 = data verification logs.
Combine values (e.g., 3 = send + receive logs).
-h, --help : Display help information
To change the test mode, simply replace -l in the uartstress.sh script with another test option. For example, for UART write-only mode:
"${script_dir}/uart_test" -w -s 1024 -c "$StressCount" -b "$Baudrate" -d "$Device" > "$uart_test_log_file"
Afterwards, connect uart2_rx and uart2_tx to a PC using a TTL UART adapter module, and open a serial terminal tool to observe the transmitted data.
Test uart device:/dev/ttyS2
Test size: 2 KBytes, baudrate: 115200
Performing uart send...
Starting send thread
This is uart send test 1 times
This is uart send test 2 times
This is uart send test 3 times
Notes
For better extensibility of the RDK_S100 interface, I2C5 and UART2 can be switched via DIP switches. To run this test, you must modify the device tree pin multiplexing configuration, recompile the DTB, install it, and set the DIP switch to the correct position.
1. To test UART2, modify the device tree as follows:
diff --git a/kernel-dts/rdk-v0p5.dtsi b/kernel-dts/rdk-v0p5.dtsi
index 504b21b..8d72794 100644
--- a/kernel-dts/rdk-v0p5.dtsi
+++ b/kernel-dts/rdk-v0p5.dtsi
@@ -210,6 +210,10 @@
status = "okay";
};
+&i2c5 {
+ status = "disabled";
+};
&i2c4 {
status = "okay";
@@ -267,6 +271,10 @@
};
};
+&uart2 {
+ status="okay";
+};
+
2. Refer to the RDK_S100 physical diagram below, locate UART2, and switch the DIP switch to the right to connect UART2:
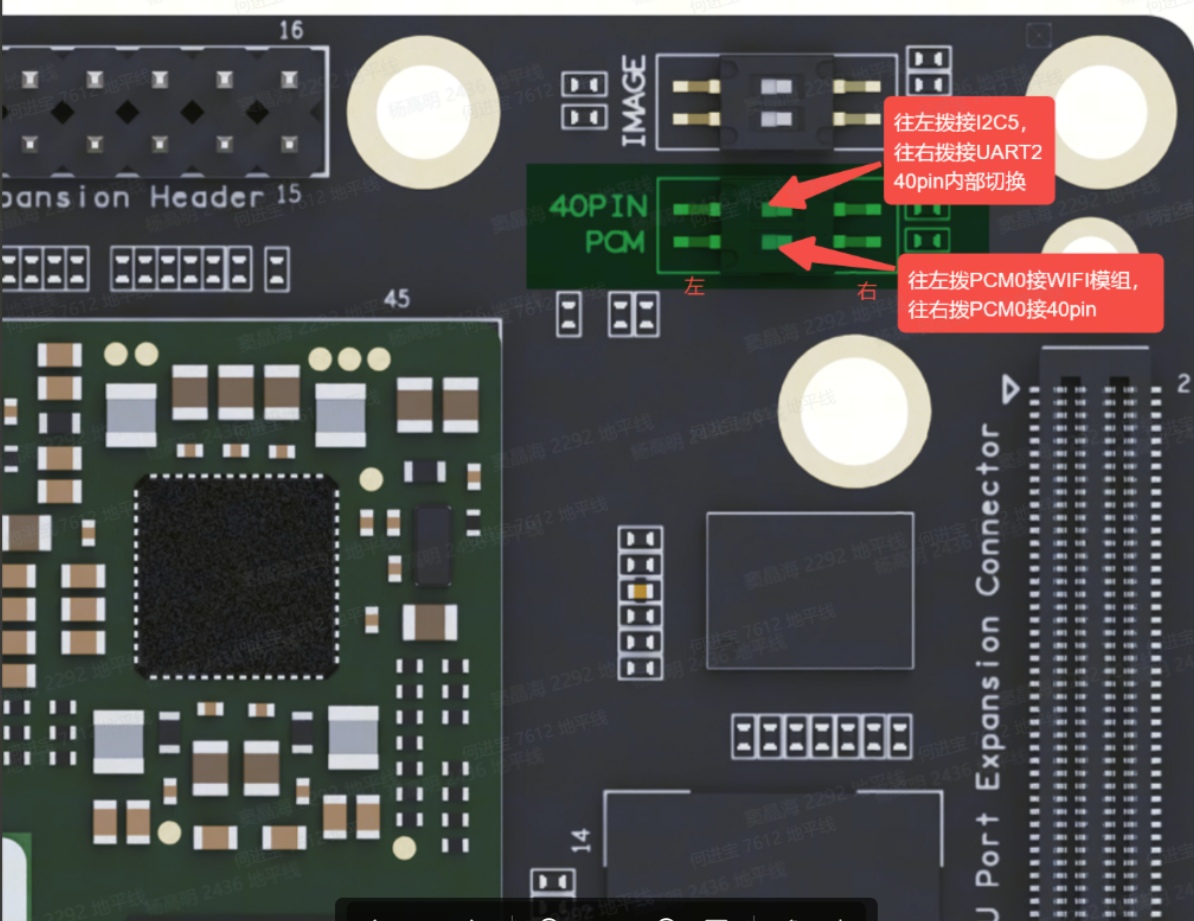
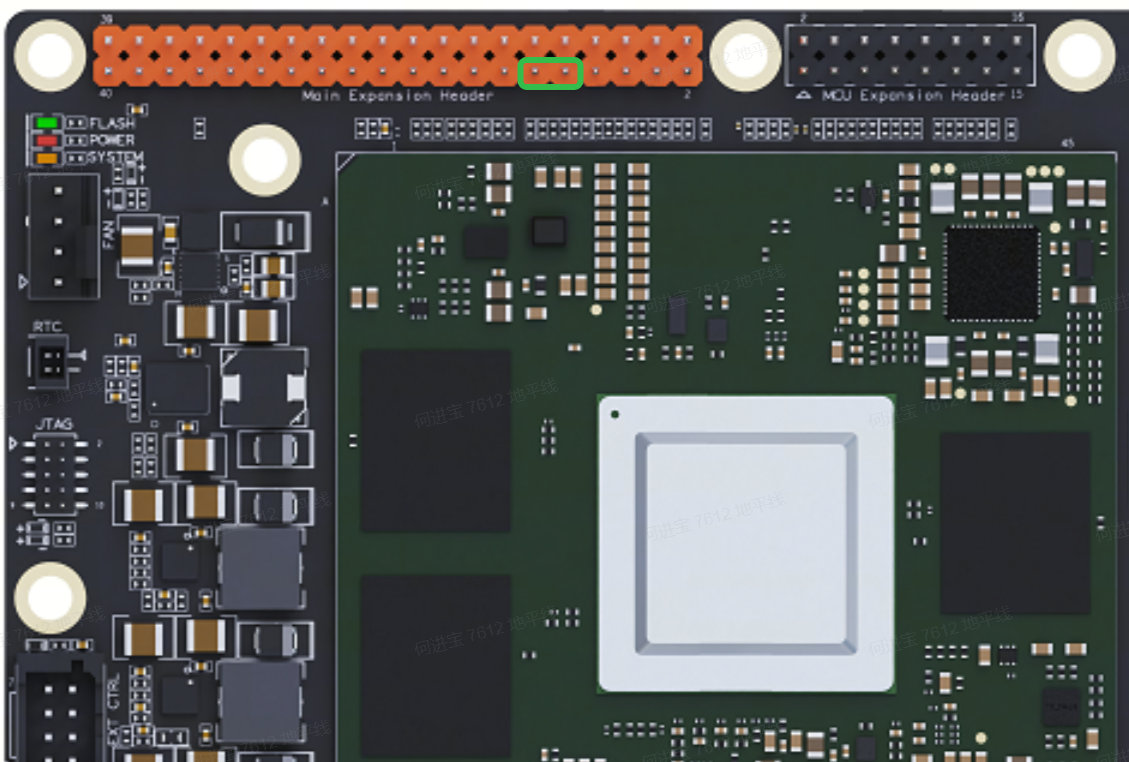
3. Consult the RDK_S100 schematic to identify the UART2 pins and connector locations, as shown:
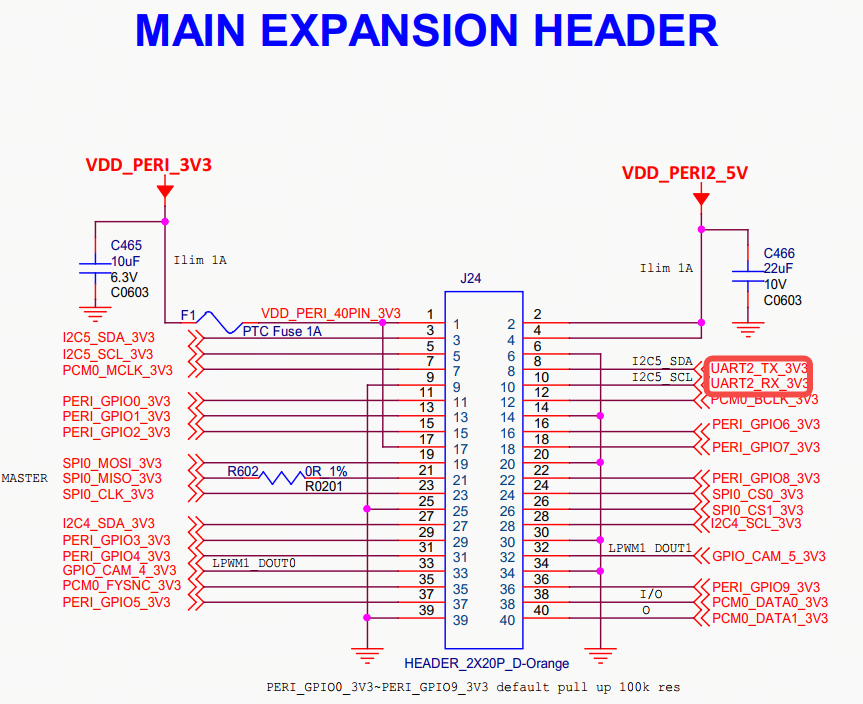
Then, use a female-to-female Dupont jumper wire to connect uart2_tx and uart2_rx.
4. Confirm that the following three files exist in the /app/chip_base_test/03_uart_test directory: uartstress.sh, uart_test.c, and uart_test.
sunrise@ubuntu:/app/chip_base_test/03_uart_test$ tree
.
├── Makefile
├── Readme.md
├── uart_test.c
└── uartstress.sh
5. You can regenerate the executable using the following compilation command:
gcc -o uart_test uart_test.c
After completing all preparations, run the test command:
./uartstress.sh
After running for a while, the log output will appear as follows:
sunrise@ubuntu:/app/chip_base_test/03_uart_test# ./uartstress.sh
Uart test starting...
Test configuration:
Baudrate: 115200
Device: /dev/ttyS2
Stress count: 100
Output directory: /app/chip_base_test/log
Log file: /app/chip_base_test/log/uart_test_log2.txt
If no additional messages appear in the console, check the log file directly under /app/chip_base_test/log/:
sunrise@ubuntu:# cat /app/chip_base_test/log/uart_test_log2.txt
Test uart device:/dev/ttyS2
Test size: 512 KBytes, baudrate: 115200
Performing uart recv...
Performing uart send...
Performing data check...
Starting send thread
Starting receive thread
This is receive test 1 times
This is uart send test 1 times
This is receive test 2 times
Data verification successful. Received data matches sent data. Test total data count: 0x80000
This is uart send test 2 times
This is receive test 3 times
Data verification successful. Received data matches sent data. Test total data count: 0x100000
This is uart send test 3 times
This is receive test 4 times
Data verification successful. Received data matches sent data. Test total data count: 0x180000
This is uart send test 4 times
Test Metrics
After the test program starts, it generates the following files in the /app/chip_base_test/log/ directory:
- uart_test_log*.txt: Records print messages and current status during stress testing.
The test objective is to ensure the system can operate stably for 48 hours without rebooting or hanging. To verify stability during the test, you can use the following command to check whether the log files contain abnormal messages such as fail, error, or timeout:
cd "/app/chip_base_test/log/" && grep -iE 'error|fail|timeout' uart_test_log*.txt
UART Stress Test Results
After the test script finishes execution, the log files were inspected and no abnormal status messages were found, indicating that the stress test has passed.
This is receive test 48 times
Data verification successful. Received data matches sent data. Test total data count: 0x1780000
This is uart send test 48 times
This is receive test 49 times
Data verification successful. Received data matches sent data. Test total data count: 0x1800000
This is uart send test 49 times
This is receive test 50 times
Data verification successful. Received data matches sent data. Test total data count: 0x1880000
This is uart send test 50 times