7.2.6 OTA
Overview
OTA (Over-the-Air Technology) refers to the technology that enables remote software updates via wireless networks. Initially introduced by the Android system for mobile devices, OTA technology has significantly simplified the traditional software update process. Users no longer need to connect their devices to a computer; instead, they can directly download and install updates on the device itself. This greatly enhances user convenience and improves device maintenance efficiency.
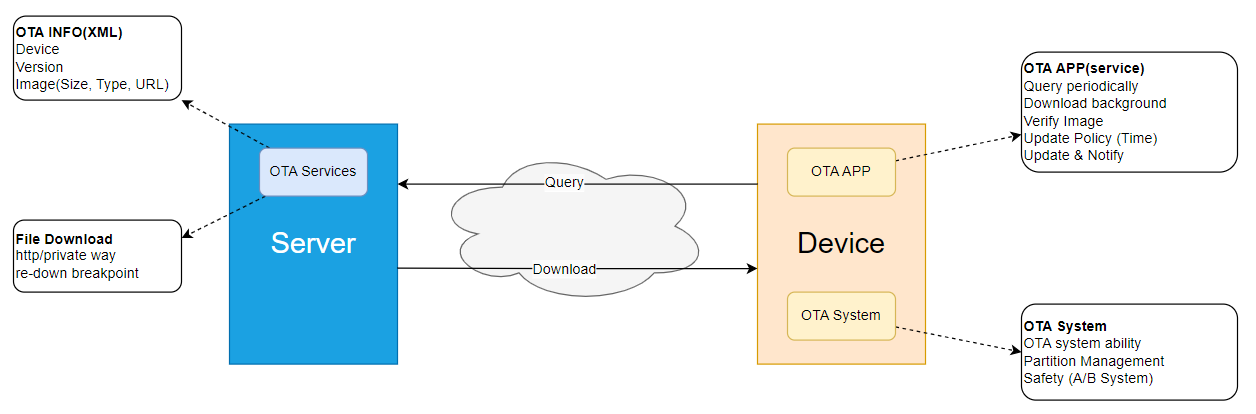
- In a broad sense, OTA consists of two main components: the cloud side and the device side. The cloud side handles device update requests, including performing update verification, delivering update packages, and collecting update results. The device side primarily relies on update packages delivered from the cloud to perform updates for system software (FOTA, Firmware Over-the-Air) or applications (SOTA, Software Over-the-Air).
- This document aims to provide a user manual for low-level device-side OTA functionality, detailing the mechanisms and implementation methods for OTA updates of system software and applications, along with relevant development guidance. It should be noted that OTA-updated system software and applications primarily refer to data stored in external storage (e.g., eMMC).
- The primary deliverables of OTA are a set of APIs and their corresponding implementation library (e.g., libupdate.so), which implements critical low-level functions such as write verification. The upper-layer OTA service architecture is implemented by the customer to integrate with their cloud services. After successfully downloading an update package from the cloud, the OTA service calls interfaces in libupdate.so to perform version upgrades and verification, ensuring secure and smooth software updates on the device.
Abbreviations
| Abbreviation | Full English Name | Chinese Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| SoC | System on Chip | System-on-Chip |
| BL[x] | Boot Loader Stage [x] | Boot Stage x |
| SPL | Secondary Program Loader | Secondary Program Loader |
| GPT | GUID Partition Table | GUID Partition Table |
| GUID | Globally Unique IDentifier | Globally Unique Identifier |
| RSA | RSA Algorithm | RSA Public-Key Cryptosystem |
| eMMC | embedded MultiMedia Card | Embedded Non-Volatile Memory |
System Partition Table
During OTA updates, target partitions are updated on a per-partition basis, categorized by type as follows:
| Partition Type | Attributes | Update Method | Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
| Persistent Partitions | Parameter partitions: typically store configuration files and parameters required during system runtime, e.g., ubootenv in the partition table.User partitions: partitions unrelated to system boot, usually mounted after system startup, e.g., userdata partition. | Single partitions generally do not have images; partition data must be preserved long-term and do not support OTA updates. | ubootenv, veeprom, userdata |
| AB Partitions | Partitions with identical prefixes and suffixes _a and _b are called AB partitions. | AB partitions are updated alternately. | boot_a, boot_b |
| BAK Partitions | Partitions with identical prefixes and a bak suffix are called BAK partitions, typically consisting of one primary partition and several backup partitions. | Only the primary partition is updated. After successful upgrade and verification, the content of the primary partition is synchronized to the backup partitions. | SBL, SBL_bak |
Enabling OTA
OTA functionality is disabled by default in RDK. To enable it, follow these steps:
-
Before enabling OTA, if the project has not been compiled and the
outdirectory does not exist, execute the following commands to either compile the project or set up the build environment:# Compile the project and generate images
sudo ./pack_image.sh
# Only set up the build environment
sudo ./pack_image.sh -p -
In the
build_paramsdirectory, modify thePARTITION_FILEconfiguration in bothubuntu-22.04_desktop_rdk-s100_beta.confandubuntu-22.04_desktop_rdk-s100_release.confto the OTA version (PARTITION_FILE="s100-ota-gpt.json"):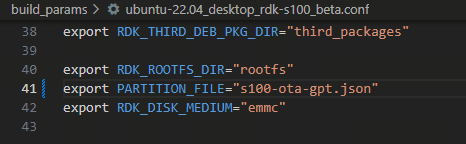
-
In the
source/bootloader/device/rdk/s100directory, set theRDK_OTAvariable to enabled (export RDK_OTA="yes") in bothboard_s100_debug.mkandboard_s100_release.mk: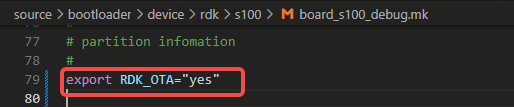
-
Compilation:
- Build a new miniboot
.debpackage:./mk_debs.sh hobot-miniboot - Recompile the local image:
sudo ./pack_image.sh -l
- Build a new miniboot
OTA Packaging Tools
Introduction to OTA Packaging Tools
The OTA packaging tools are located under the ota_tools/ directory, with the following structure:
tree
.
├── hdiffz // Diff tool for generating file differences
├── hpatchz // Diff tool for applying file differences
├── mk_otapackage.py // OTA packaging tool for generating OTA update packages
├── ota_pack_tool.sh // OTA packaging script wrapping mk_otapackage.py functionality
├── ota_process // Binary tool used during OTA updates, included in the OTA package
├── out // Output directory for OTA packaging
│ ├── deploy // Stores intermediate files during OTA package creation
│ └── ota_packages // Stores finalized OTA update packages
└── private_key.pem // Private key file used for signing OTA packages
Typically, ota_pack_tool.sh under the ota_tools/ directory is used to create required OTA update packages. It supports unpacking OTA packages, repacking after unpacking, creating full update packages, and generating incremental (differential) packages.
Usage:
Usage: ./ota_pack_tool.sh [OPTIONS]...
Options:
-x, -unpack <ota_package> Unpack the given OTA package file.
-r, -repack Repack the files into a new OTA package.
-c, -create <pack_type> -d <source_dir>
Generate OTA package by source dir or img_packages.
<pack_type>: sys, sys_signed ... etc.
<source_dir>: sys and sys_signed require img dir.
(e.g.)run "./ota_pack_tool.sh -c sys -d ../out/product/img_packages/"
-i, -inc <pack_type> -old <old_pkg> -new <new_pkg>
Create an incremental OTA package.
<pack_type>: sys, sys_signed.
<old_pkg>, <new_pkg>: OTA pack, xxx.zip.
(e.g.)run "./ota_pack_tool.sh -i sys -old out/ota_packages/all_in_one_old.zip -new out/ota_packages/all_in_one_new.zip".
-h, -help Display this help message.
Unpacking and Repacking OTA Update Packages
To unpack an update package:
./ota_pack_tool.sh -x out/ota_packages/all_in_one.zip
- After unpacking, you can update images under
ota_tools/out/ota_unpackand rebuild the OTA package. The OTA configuration file andota_processbinary used are located inota_tools/out/ota_unpack. Note that this method does not allow modification of the OTA configuration filegpt.conf.
To repack:
./ota_pack_tool.sh -r
- Source directory:
ota_tools/out/ota_unpack - Output directory:
ota_tools/out/ota_repack
Creating Full OTA Update Packages
Use the following commands to create system update packages. The partition configuration file is specified via the GPT_CONFIG variable in the ota_pack_tool.sh script, defaulting to /out/product/img_packages/s100-ota-gpt.json. Modify as needed.
# "sys" creates a non-secure update package
./ota_pack_tool.sh -c sys -d ~/s100/out/product/img_packages/
# "sys_signed" creates a secure update package
./ota_pack_tool.sh -c sys_signed -d ~/s100/out/product/img_packages/
Generated OTA packages are output to ota_tools/out/ota_packages, containing files with .zip and .signature extensions:
.zipfiles are the OTA update packages..signaturefiles are signature files for the corresponding packages.
all_in_one.signature # Signature for non-secure update package
all_in_one.zip # Non-secure update package
all_in_one_signed.signature # Signature for secure update package
all_in_one_signed.zip # Secure update package
Creating Incremental (Differential) OTA Packages
You can use ota_pack_tool to create an incremental system package named all_in_one_signed_inc.zip. The OTA configuration file and ota_process used during creation are extracted from the new package.
-
Purpose of Incremental Updates
Saves network bandwidth but does not reduce update time. -
Principle of Incremental Updates
Uses a differential algorithm to compute differences between old and new images. During update, differences are applied to the target partition. (Images on flash media are not differenced due to their small size—only a few MB—and slow flash read speeds.) The differential library used ishpatchz. Supported images include all non-flash-media images in the OTA package. -
Limitations of Incremental Updates
- Partitions on flash do not support incremental updates.
- The boot partition, due to write operations, does not support incremental updates.
- Incremental updates are only supported for image packages larger than 10 MB.
- Partitions requiring mounting during incremental updates must be mounted read-only with the
noloadoption; otherwise, MD5 verification will fail.
-
Creating an Incremental Update Package
- Incremental updates depend on a previously flashed old image package. Ensure the old image package is securely stored and not lost or corrupted.
# Create an incremental package all_in_one_signed_inc.zip based on all_in_one_signed_old.zip and all_in_one_signed_new.zip
./ota_pack_tool.sh -i sys_signed -old out/ota_packages/all_in_one_signed_old.zip -new out/ota_packages/all_in_one_signed_new.zip
Signing Keys
The private key private_key.pem used for signing is located in the project's ota_tools/ directory. The corresponding public key public_key.pem is located in source/bootloader/miniboot/ota_flash_tools/, and on the device side, the public key path is /usr/hobot/share/ota/public_key.pem.
To replace with your own keys:
-
Generate a private key:
openssl genrsa -out private_key.pem 4096 -
Generate a public key:
openssl rsa -RSAPublicKey_out -in private_key.pem -out public_key.pem -
Replace
public_key.peminsource/bootloader/miniboot/ota_flash_tools/andprivate_key.peminota_tools/. -
Recompile using the following commands:
# Navigate to the project root directory and build the miniboot .deb package
./mk_debs.sh hobot-miniboot
# Compile the local project
sudo ./pack_image.sh -l
Note:
- Generated OTA packages are named
all_in_one_xxx.zipby default. The updater validates the package name: it must contain the keyword "all_in_one" and have a.zipextension. Additionally, the package name must not contain the keywords: "app", "APP", "middleware", or "param".
OTA Update Package Overview
Package Structure
Archive: all_in_one_signed.zip
Length Date Time Name
--------- ---------- ----- ----
1047 2025-05-14 12:11 gpt.conf
5326 2025-05-14 12:11 data.json
526336 2025-05-13 20:37 HSM_FW_signed.img
264192 2025-05-13 20:37 HSM_RCA_signed.img
264192 2025-05-13 20:37 keyimage_signed.img
264192 2025-05-13 20:37 keyimage_ohp_signed.img
526336 2025-05-13 20:37 scp_signed.img
526336 2025-05-13 20:37 spl_signed.img
1312768 2025-05-13 20:37 MCU_S100_V1.0_signed.img
256288 2025-05-13 20:37 acore_cfg.img
348928 2025-05-13 20:37 bl31.img
986080 2025-05-13 20:37 optee.img
1076928 2025-05-13 20:37 uboot.img
36388864 2025-05-13 20:37 boot.img
8589934592 2025-05-13 20:37 system.img
310144 2025-05-13 19:47 ota_process
--------- -------
8632992549 16 files
The above content shows the file structure within the current OTA update package, which mainly includes the following four types of files. The number of image files may vary depending on the actual configuration.
| File | Description |
|---|---|
| gpt.conf | Partition table file |
| data.json | OTA configuration file |
| *.img | Partition images |
| ota_process | OTA flashing program |
OTA Configuration File
The OTA update package contains a configuration file named data.json. This file is generated during compilation and includes partition information and image details for the update package.
General Configuration
| Configuration | Type | Function |
|---|---|---|
| backup_dir | arr[obj] | HSM backup directory |
| ab_sync | str | Reserved field; default value is always false |
| nor_sign | bool | NOR Flash image signature verification switch |
| update_partition | arr[str] | Partitions to be updated |
| partition_info | arr[obj] | Configuration for each partition |
Partition-specific Configuration (partition_info)
| Configuration | Type | Function |
|---|---|---|
| md5sum | arr[obj] | MD5 checksums of each image |
| md5_scope | arr[obj] | Length (in bytes) used for MD5 verification of each image |
| medium | str | External storage medium (NOR/eMMC/NAND) |
| part_type | str | Partition type (AB/BAK/GOLDEN) |
| upgrade_method | str | Upgrade method (image) |
| imgname | str | Image filename; only files with .img, .bin, or .ubifs extensions are supported |
Below is an example of a data.json file:
{
"antirollbackUpdate_host": false,
"antirollbackUpdate_hsm": false,
"backup_dir": "/tmp/ota/backup",
"ab_sync": false,
"update_partition": [
"HSM_FW",
"HSM_RCA",
"keyimage",
"scp",
"spl",
"MCU",
"acore_cfg",
"bl31",
"optee",
"uboot",
"boot",
"system"
],
"nor_sign": true,
"partition_info": {
"HSM_FW": {
"md5sum": {
"HSM_FW_signed.img": "3e19e04f97e0cb4e37899958e3aec34f"
},
"md5_scope": {
"HSM_FW_signed.img": 524288
},
"medium": "nor",
"part_type": "BAK",
"have_anti_ver": null,
"upgrade_method": "image",
"imgname": "HSM_FW_signed.img"
},
"HSM_RCA": {
"md5sum": {
"HSM_RCA_signed.img": "9b2f9cb4d00586dd49112f50fdb90952"
},
"md5_scope": {
"HSM_RCA_signed.img": 262144
},
"medium": "nor",
"part_type": "BAK",
"have_anti_ver": null,
"upgrade_method": "image",
"imgname": "HSM_RCA_signed.img"
},
"keyimage": {
"md5sum": {
"keyimage_signed.img": "df28a9900fa504a90a4c85368cb7879d",
"keyimage_ohp_signed.img": "af81665e36a9a274084e2dc02b7a3830"
},
"md5_scope": {
"keyimage_signed.img": 262144,
"keyimage_ohp_signed.img": 262144
},
"medium": "nor",
"part_type": "BAK",
"have_anti_ver": null,
"upgrade_method": "image",
"imgname": "keyimage%s_signed.img"
},
"scp": {
"md5sum": {
"scp_signed.img": "6ea63e573ae3bb50dc8cb0052c29fddb"
},
"md5_scope": {
"scp_signed.img": 524288
},
"medium": "nor",
"part_type": "AB",
"have_anti_ver": null,
"upgrade_method": "image",
"imgname": "scp_signed.img"
},
"spl": {
"md5sum": {
"spl_signed.img": "ba48f24f989de1ddbc6eb3aedd139b4f"
},
"md5_scope": {
"spl_signed.img": 524288
},
"medium": "nor",
"part_type": "AB",
"have_anti_ver": null,
"upgrade_method": "image",
"imgname": "spl_signed.img"
},
"MCU": {
"md5sum": {
"MCU_S100_V1.0_signed.img": "d44784323de5f5d57fa606ea178fd854"
},
"md5_scope": {
"MCU_S100_V1.0_signed.img": 1310720
},
"medium": "nor",
"part_type": "AB",
"have_anti_ver": null,
"upgrade_method": "image",
"imgname": "MCU_S100_V1.0_signed.img"
},
"acore_cfg": {
"md5sum": {
"acore_cfg.img": "fe36a8ad522a2ca5ee811da8208828ef"
},
"md5_scope": {
"acore_cfg.img": 256288
},
"medium": "emmc",
"part_type": "AB",
"have_anti_ver": null,
"upgrade_method": "image",
"imgname": "acore_cfg.img"
},
"bl31": {
"md5sum": {
"bl31.img": "5be617cd08128e89318f61964696509a"
},
"md5_scope": {
"bl31.img": 348928
},
"medium": "emmc",
"part_type": "AB",
"have_anti_ver": null,
"upgrade_method": "image",
"imgname": "bl31.img"
},
"optee": {
"md5sum": {
"optee.img": "f0f663462f523f9e8722e0c26d29209e"
},
"md5_scope": {
"optee.img": 986080
},
"medium": "emmc",
"part_type": "AB",
"have_anti_ver": null,
"upgrade_method": "image",
"imgname": "optee.img"
},
"uboot": {
"md5sum": {
"uboot.img": "78b07c6a4264bd757c4d992e2dc0ee0b"
},
"md5_scope": {
"uboot.img": 1076928
},
"medium": "emmc",
"part_type": "AB",
"have_anti_ver": null,
"upgrade_method": "image",
"imgname": "uboot.img"
},
"boot": {
"md5sum": {
"boot.img": "aca98db8136ad4f1d55cd3e7bdb4c856"
},
"md5_scope": {
"boot.img": 36388864
},
"medium": "emmc",
"part_type": "AB",
"have_anti_ver": null,
"upgrade_method": "image",
"imgname": "boot.img"
},
"system": {
"md5sum": {
"system.img": "a6f61c86ae0045ad3167b3daf7c33b3a"
},
"md5_scope": {
"system.img": 8589934592
},
"medium": "emmc",
"part_type": "AB",
"have_anti_ver": null,
"upgrade_method": "image",
"imgname": "system.img"
}
}
}
With the above configuration, the OTA update package ensures that the image of each partition is correctly verified and updated during the upgrade process.
Detailed OTA Implementation
OTA Process
The following workflow is based on the implementation in ota_tool (developers can refer to this tool for their own implementations).
-
Preparation Phase:
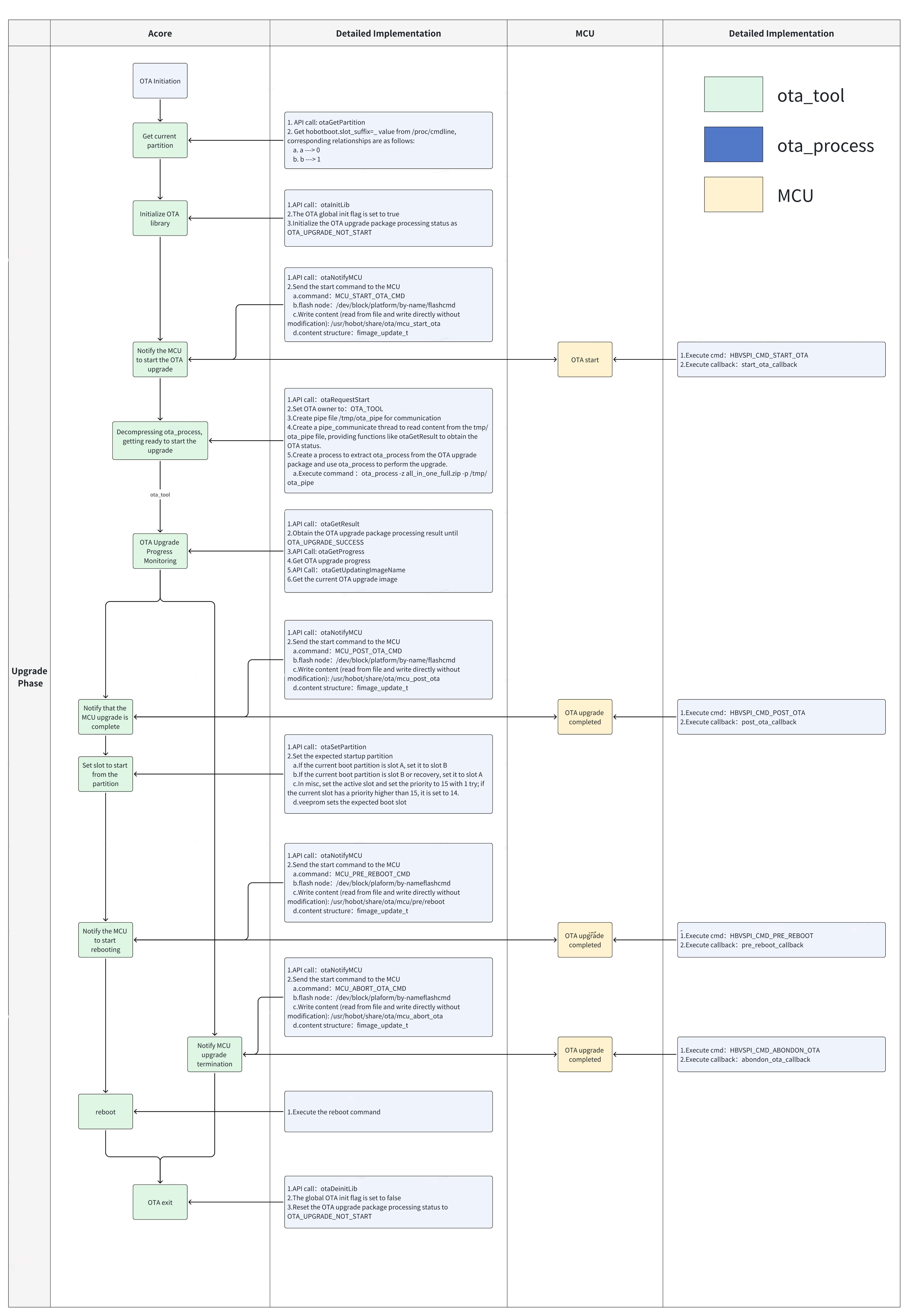
-
Upgrade Phase:
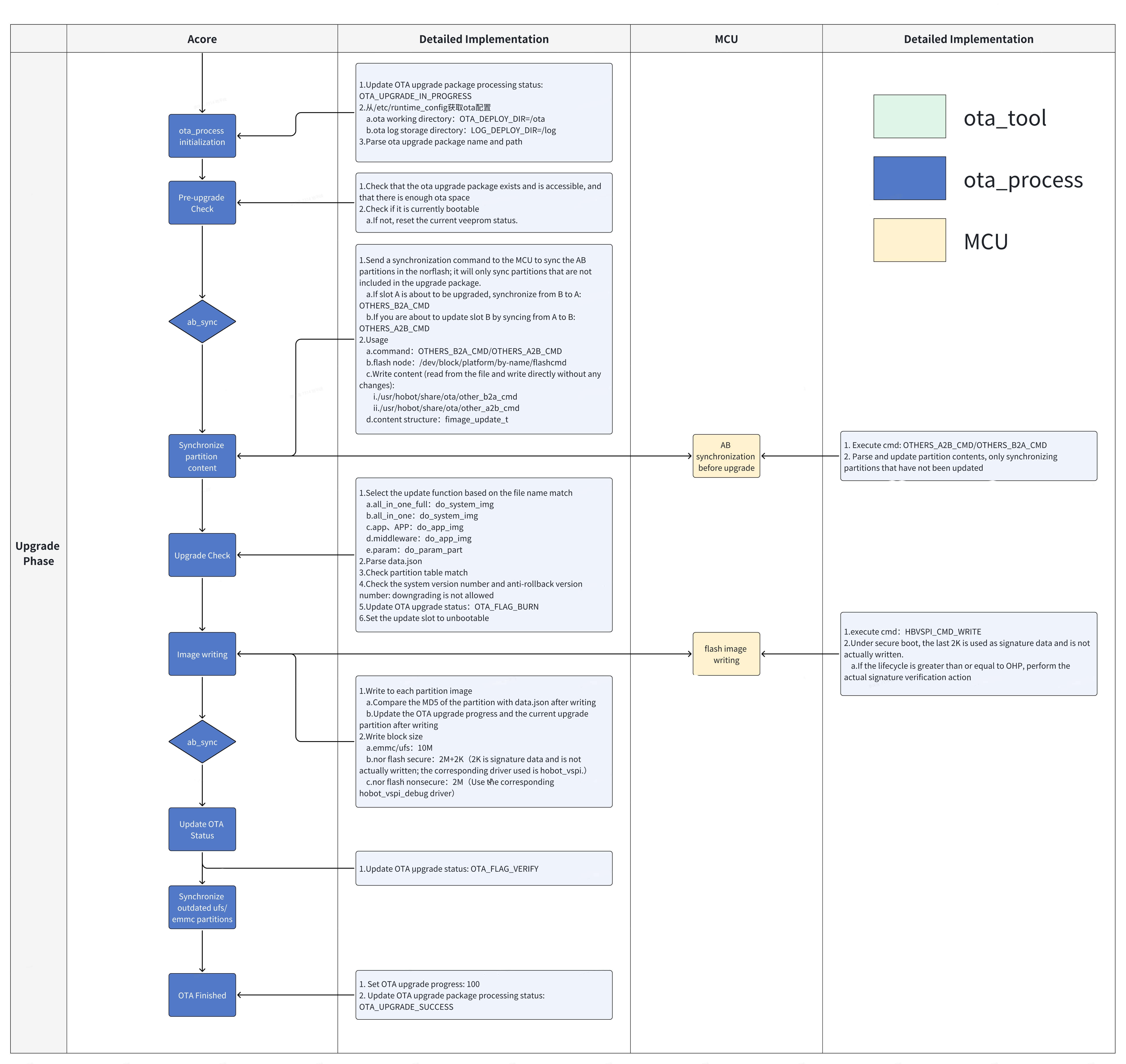
-
Verification Phase:
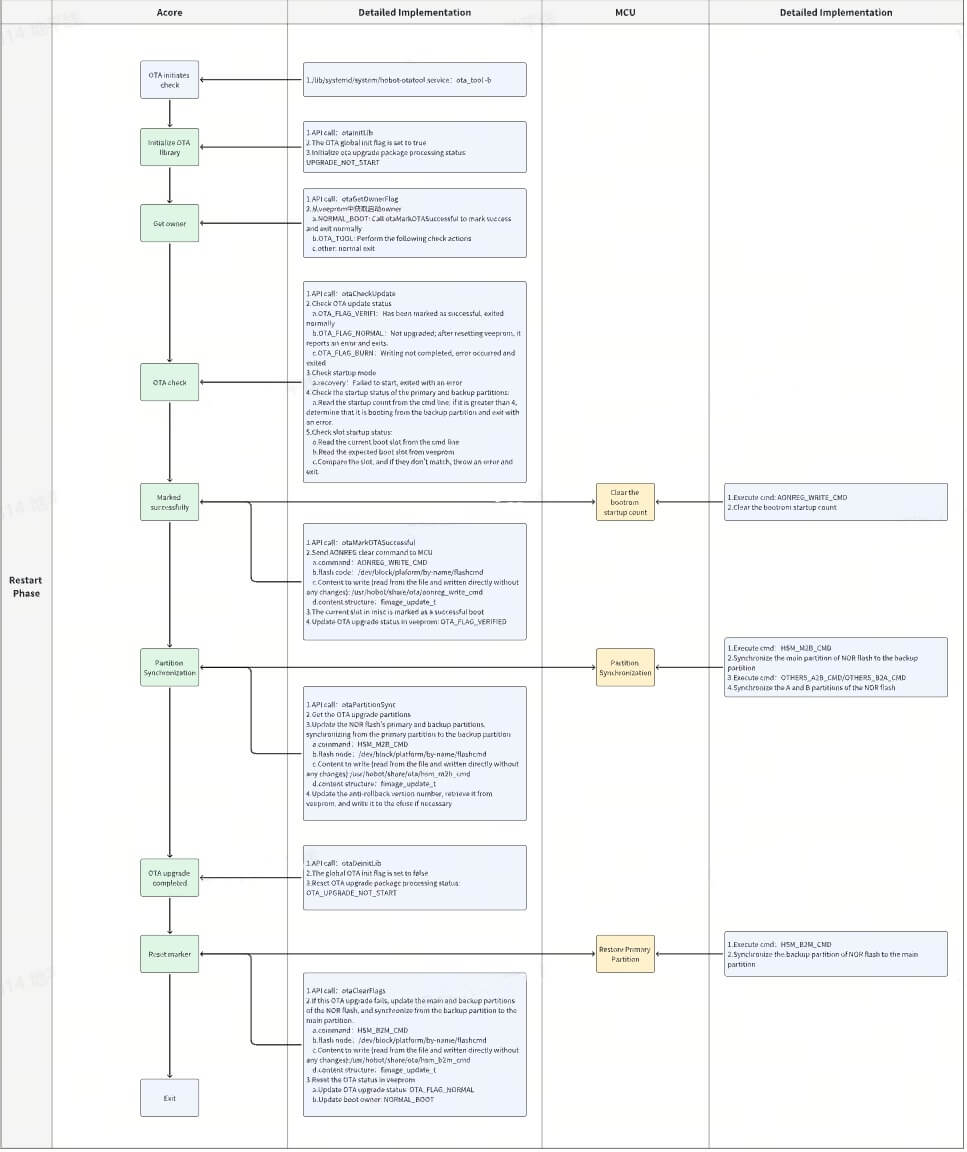
OTA State Machine
Update Package States
The state is stored in the OTA process space. Below is the state flow description:
/**
* @enum otahl_update_result
* @brief OTA upgrade result
* @NO{S21E03C02}
*/
typedef enum otahl_update_result {
OTA_UPGRADE_NOT_START = 0, /**< OTA upgrade not start */
OTA_UPGRADE_IN_PROGRESS, /**< OTA upgrading */
OTA_UPGRADE_SUCCESS, /**< OTA upgrade success*/
OTA_UPGRADE_FAILED, /**< OTA upgrade failed*/
} otahl_update_result_e;
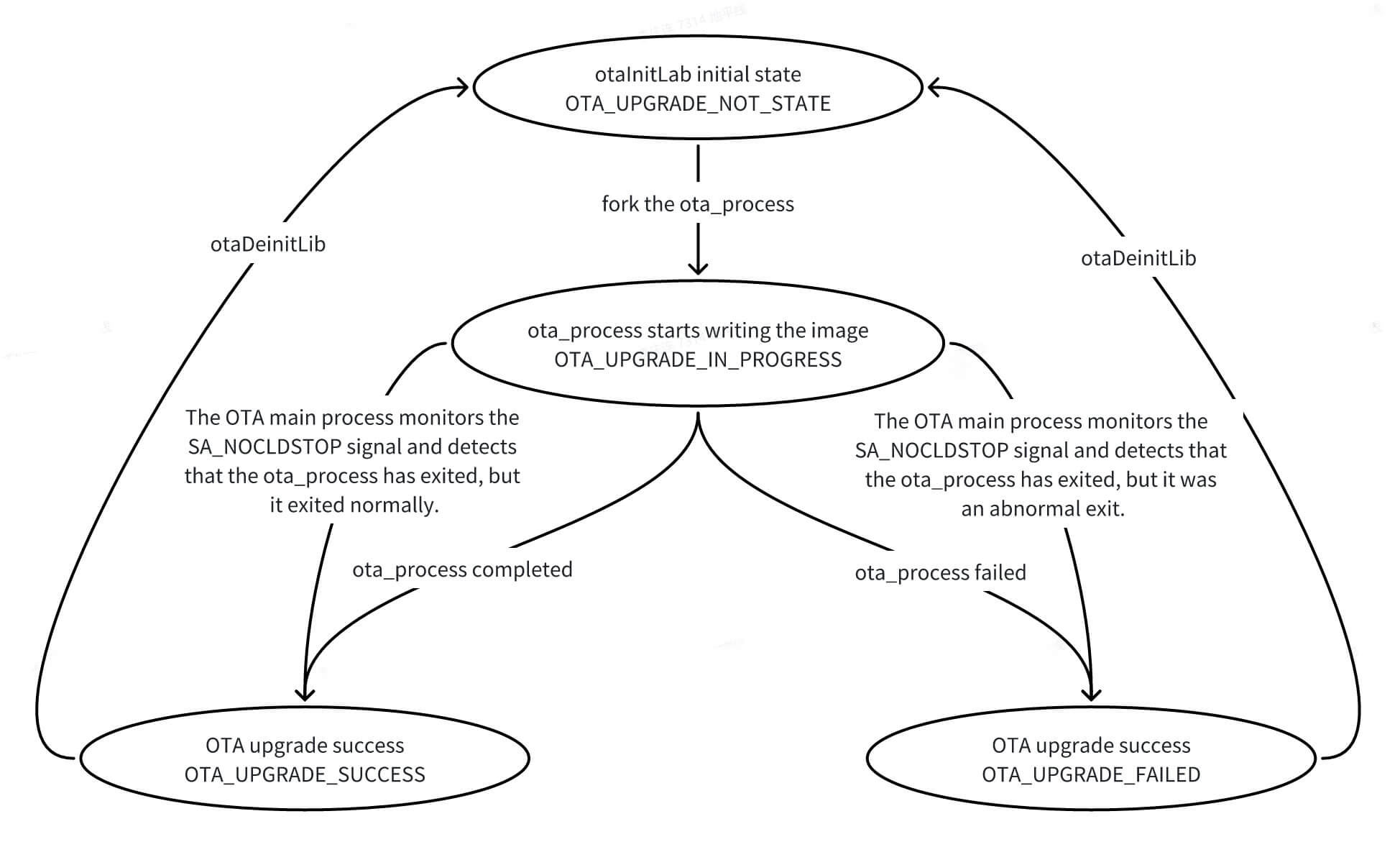
OTA Upgrade Process States
The state is stored in veeprom. Below is the state flow description:
typedef enum ota_update_flag {
OTA_FLAG_NORMAL = 0, // Normal state
OTA_FLAG_BURN, // Burning state
OTA_FLAG_VERIFY, // Pending verification state
OTA_FLAG_VERIFIED, // Verified state
} ota_update_flag_e;
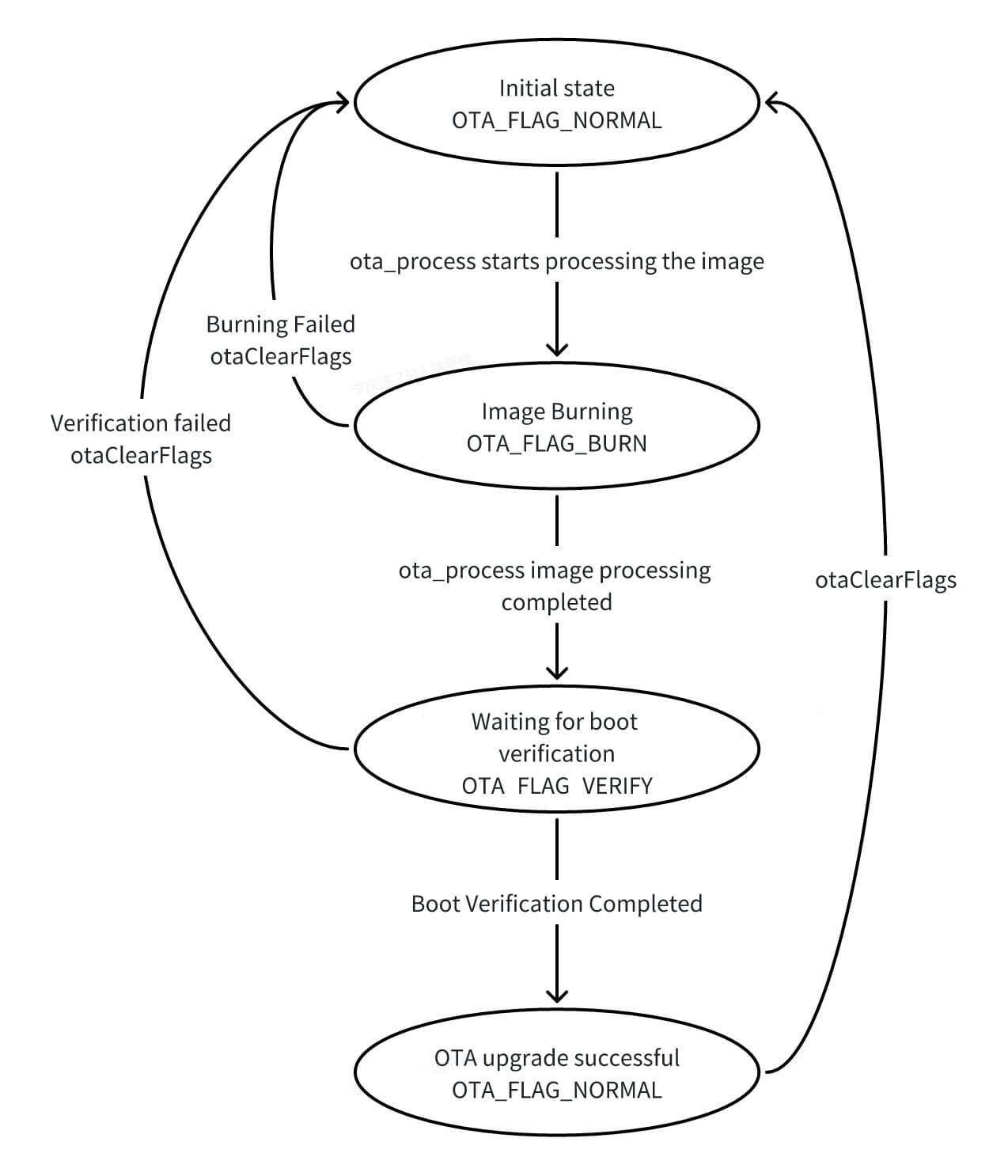
misc (AB State Machine)
-
Region Allocation
D-Robotics uses the Android A/B mechanism for A/B system implementation. The following information describes parts of this mechanism’s principles. For detailed principles, please refer to: https://source.android.google.cn/docs/core/ota?hl=en
bootloader_message_aboccupies a total of 4KB. Within this structure, thebootloader_controlused by A/B is located atstruct bootloader_message_ab->slot_suffixand occupies 32 bytes.struct bootloader_message_ab {
struct bootloader_message message;
char slot_suffix[32];
char update_channel[128];
// Round up the entire struct to 4096-byte.
char reserved[1888];
};
/**
* Be cautious about the struct size change, in case we put anything post
* bootloader_message_ab struct (b/29159185).
*/
#if (__STDC_VERSION__ >= 201112L) || defined(__cplusplus)
static_assert(sizeof(struct bootloader_message_ab) == 4096,
"struct bootloader_message_ab size changes");
#endif -
A/B Structure Data
#define ARRAY_32 (32U)
struct slot_metadata {
// Slot priority with 15 meaning highest priority, 1 lowest
// priority and 0 the slot is unbootable.
uint8_t priority : 4;
// Number of times left attempting to boot this slot.
uint8_t tries_remaining : 3;
// 1 if this slot has booted successfully, 0 otherwise.
uint8_t successful_boot : 1;
// 1 if this slot is corrupted from a dm-verity corruption, 0 otherwise.
uint8_t verity_corrupted : 1;
// Reserved for further use.
uint8_t reserved : 7;
} __attribute__((packed));
struct bootloader_control {
// NUL terminated active slot suffix.
char slot_suffix[4];
// Bootloader Control AB magic number (see BOOT_CTRL_MAGIC).
uint32_t magic;
// Version of struct being used (see BOOT_CTRL_VERSION).
uint8_t version;
// Number of slots being managed.
uint8_t nb_slot : 3;
// Number of times left attempting to boot recovery.
uint8_t recovery_tries_remaining : 3;
// Ensure 4-bytes alignment for slot_info field.
uint8_t reserved0[2];
// Per-slot information. Up to 4 slots.
struct slot_metadata slot_info[4];
// Reserved for further use.
uint8_t reserved1[8];
// CRC32 of all 28 bytes preceding this field (little endian
// format).
uint32_t crc32_le;
} __attribute__((packed)); -
State Machine Description
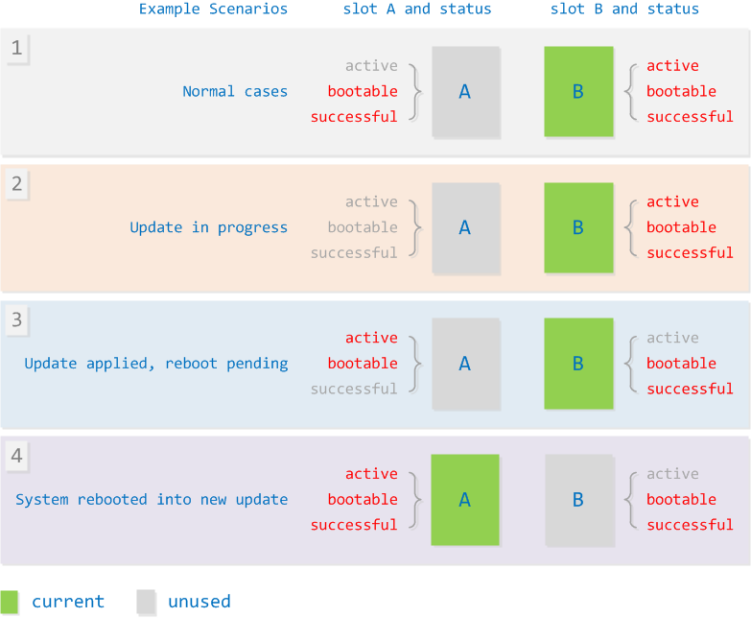
-
State 1: Default state—both A/B slots are bootable. Slot B has higher priority than slot A, so the system boots from B by default.
-
State 2: Upgrade (burning) state—slot A is unbootable, and its
boot_successflag is 0. -
State 3: Burning succeeded, but the system hasn't rebooted yet. At this point, the target slot for upgrade is set as active, and the current slot is set as inactive (by adjusting slot priorities).
-
State 4: After rebooting and successful verification, slot A is marked as successfully booted.
veeprom Region
The OTA state machine is stored in this region. Below is how OTA utilizes this region:
#define VEEPROM_OTA_STAT_OFFSET \
(1024) /**< offset of OTA status in the veeprom partition */
#define VEEPROM_OTA_STAT_SIZE \
(2048) /**< size of OTA status in the veeprom partition */
#define VEEPROM_RECOVERY_STAT_OFFSET \
(VEEPROM_OTA_STAT_OFFSET + \
VEEPROM_OTA_STAT_SIZE) /**< offset of recovery information in the veeprom partition */
#define VEEPROM_RECOVERY_STAT_SIZE \
(128) /**< size of recovery information in the veeprom partition */
-
OTA Region
Start offset: 1024
Size: 2048
Purpose: Store OTA status
Stored data is as follows:
* @ota_status_t
* @brief ota status
* @NO{S21E03C04U}
*/
typedef struct ota_status_s {
uint32_t magic; /**< magic number */
ota_update_flag_e up;
ota_update_flag_e up_system; /**< system partition update flag */
ota_update_flag_e up_backup; /**< system partition update flag */
ota_update_flag_e up_app; /**< system partition update flag */
ota_update_flag_e up_middleware; /**< system partition update flag */
ota_update_flag_e up_param; /**< system partition update flag */
ota_update_owner_e owner;
uint32_t next_slot; /**< expect slot for next boot */
update_part_t update_part;
uint8_t reserved[ARRAY_32];
uint32_t crc32_le; /**< crc verify value */
} ota_status_t;
Boot Slot Switching
The following diagram illustrates how A/B slots switch during a normal boot (this process applies regardless of whether an OTA update is present or not):
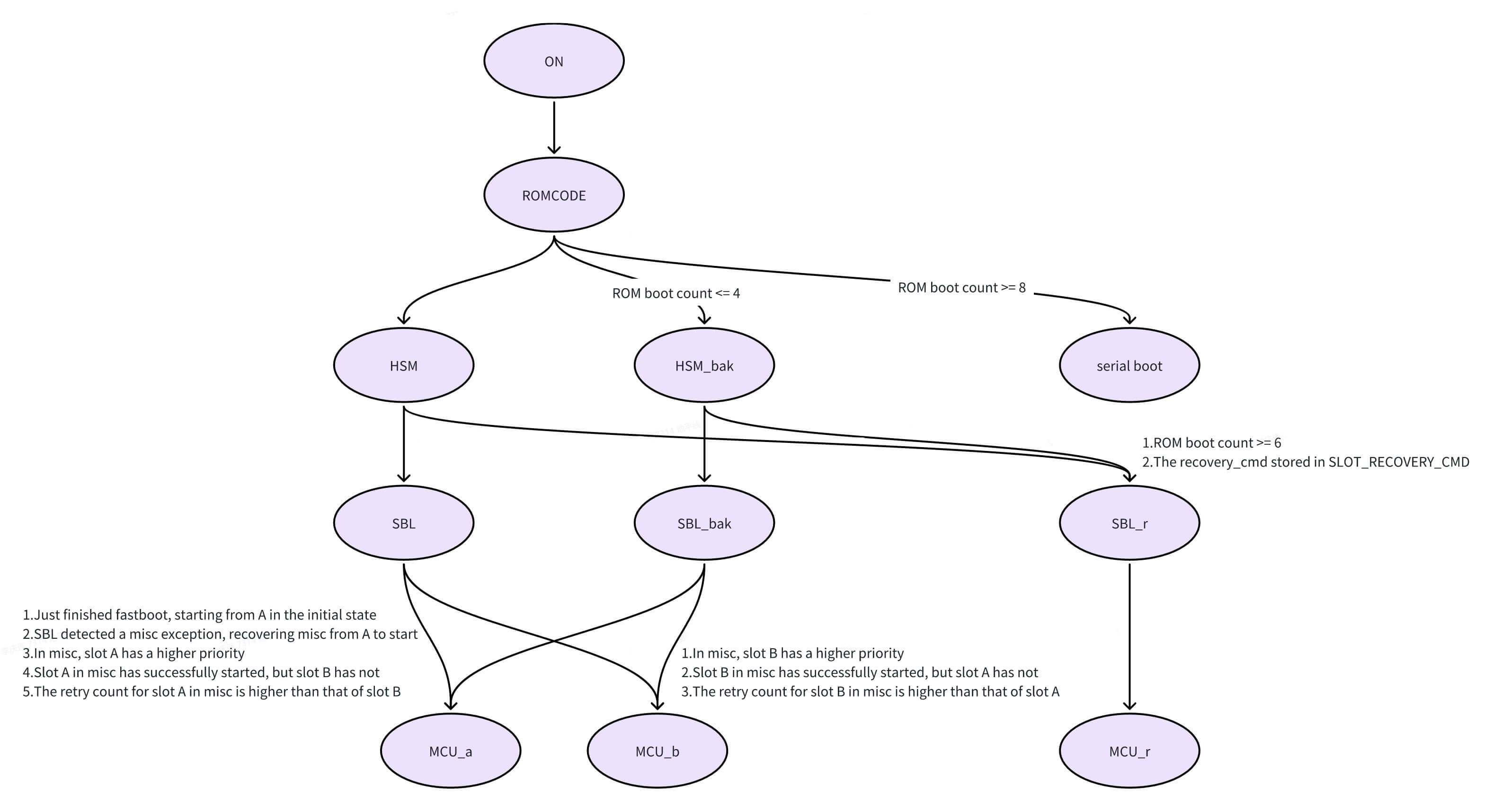
-
During boot, the ROM boot count is automatically incremented (this counter resides in the AON domain and resets upon power-off).
-
During an OTA update, the priority of the target slot is set to 15, while the other slot's priority is set to 14. The retry count for the target slot is set to 1, and a corrupted slot is marked with a retry count of 0.
-
If an OTA boot verification succeeds, the slot is marked as "successboot"; if it fails, the slot is marked as corrupted.
-
Booting from a slot that has never been marked as "successboot" consumes one retry attempt. If the retry count reaches 0 or the slot is marked as corrupted, this slot will be skipped.
Reboot Verification and Rollback
In the S100 reference implementation, after an OTA update completes and the system reboots, the kernel triggers a systemd OTA service to perform a reboot check, thereby completing the full OTA process (this essentially executes ota_tool -b).
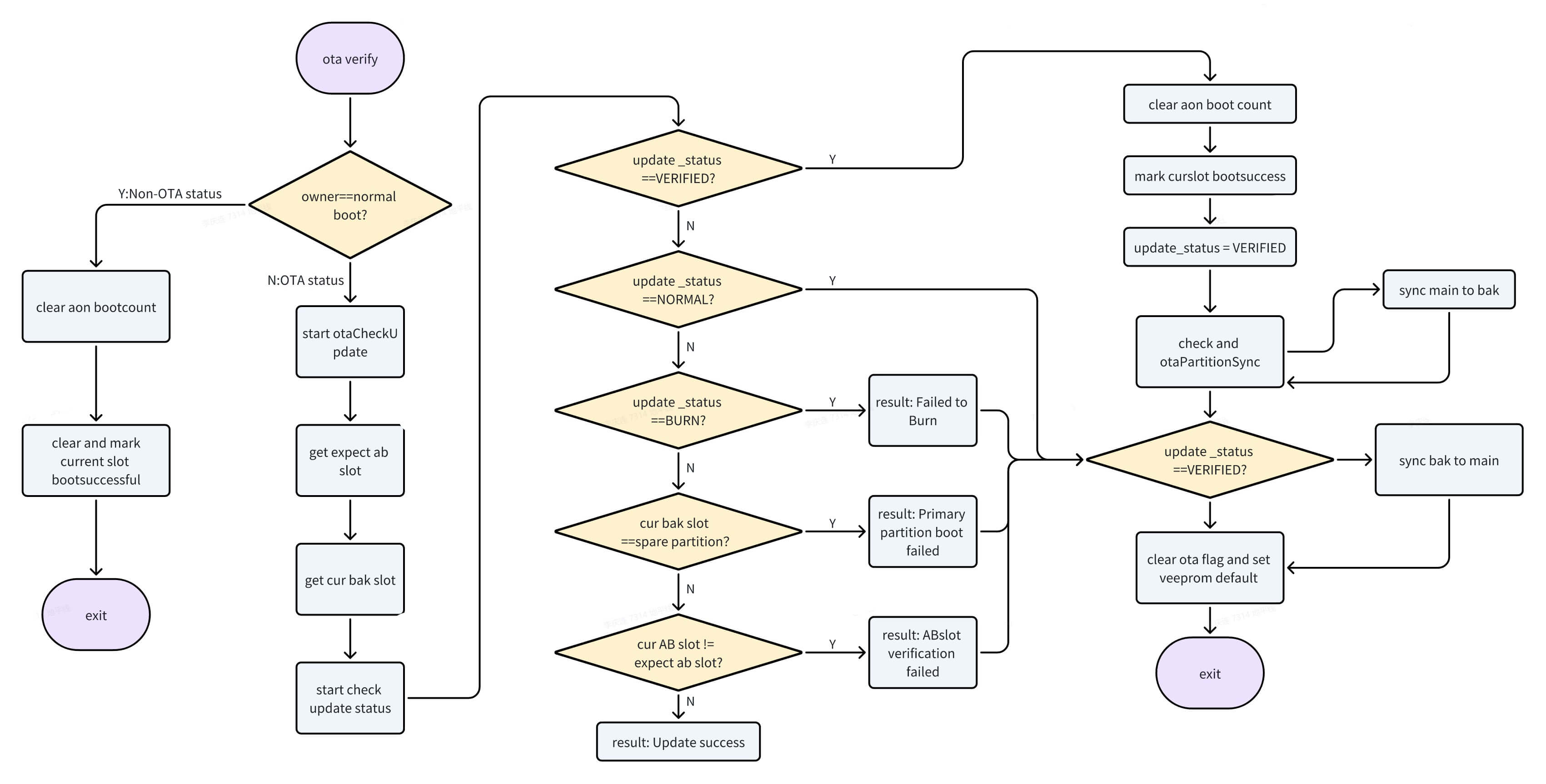
Partition Flashing Methods
OTA updates are performed on a per-partition basis. Each partition to be updated has its own image, and the update process primarily involves writing this image to the corresponding partition in external storage. Image types are categorized into full images and differential images.
Full Image Update
- A full image refers to a complete image of the target partition. During an update, this image is directly written to the corresponding partition in external storage.
Differential Image Update
-
A differential image is generated by applying a differencing algorithm to compute the differences between the original image and the target image. This process typically extracts only the differing portions between the two images and eliminates redundant data. The resulting differential image is usually significantly smaller than the full target image (the exact size depends on the degree of difference between the original and target images—the smaller the difference, the smaller the differential image), which helps save bandwidth.
-
During a differential update, the S100 OTA system reconstructs the target image by applying an inverse differencing operation using the differential image and the original partition data stored on the device, then writes the reconstructed image to the corresponding partition in external storage to complete the update.
-
The S100 uses the open-source differencing tool hdiffz/hpatch. For more details, please refer to: github | HDiffPatch.
OTA Security Measures
Partition Verification
OTA supports verification of fpt/GPT partition files within the image by comparing them against the current system's fpt/GPT partitions to check whether the partition table has been modified. If any modification is detected, the update is aborted.
- The OTA package includes a partition file
gpt.confgenerated by the build system, with the following format:fpt:0:262143:0
recovery:262144:6291455:0
misc:6291456:6553599:0
HB_APDP:6553600:6815743:0
keystorage:6815744:7340031:0
HSM_FW:7340032:7864319:0
HSM_FW_bak:7864320:8388607:0
HSM_RCA:8388608:8650751:0
··· - Since the S100 partitioning scheme supports automatic expansion of the last partition (whose end address changes dynamically), GPT verification is performed only up to the
userdatapartition. Moreover, the last partition typically does not contain an image, so this limitation does not affect normal operation.
Typical OTA Update Flow
-
The OTA Service downloads and verifies the update package from the cloud, then calls
otaInitLibto initialize the dynamic library. -
It calls
otaRequestStartto initiate the update. This API extracts theota_processprogram from the update package, forks a child process, and executesota_processto perform the actual flashing. Additionally, this API creates a file lock (to prevent concurrent updates), creates a pipe file (for communication withota_process), and spawns a thread to periodically read from the pipe to obtain real-time progress, update results, and the name of the partition currently being updated. -
During the child process update phase, the OTA Service can call
otaGetResultto retrieve the update result,otaGetProgressto get the update progress, andotaGetUpdatingImageNameto obtain the name of the image currently being updated. -
When
otaGetResultreturnsOTA_UPGRADE_SUCCESS, it indicates that the image has been successfully flashed, and the verification phase begins. -
Call
otaSetPartitionto set the next boot partition to the opposite slot, then proceed with the reboot process. -
After rebooting, the OTA Service calls
otaGetOwnerFlagto determine the update owner. If the owner is the OTA Service itself, the OTA Service assumes responsibility for verifying this update and proceeds to the verification phase. -
Call
otaCheckUpdateto obtain the update result. This API primarily checks whether the image was fully written and whether the system booted from the expected A/B slot or backup slot. -
Call
otaMarkOTASuccessfulto mark the current partition as successfully booted. This API updates the A/B state machine to mark the current slot asboot_successful, ensuring subsequent boots will use this slot. If any reboot occurs before this step, the system will boot from the slot containing the previous version, and the update will be considered failed. -
Call
otaPartitionSyncto synchronize the primary and backup BAK partitions. -
Call
otaClearFlagsto clear update flags and finalize the update process.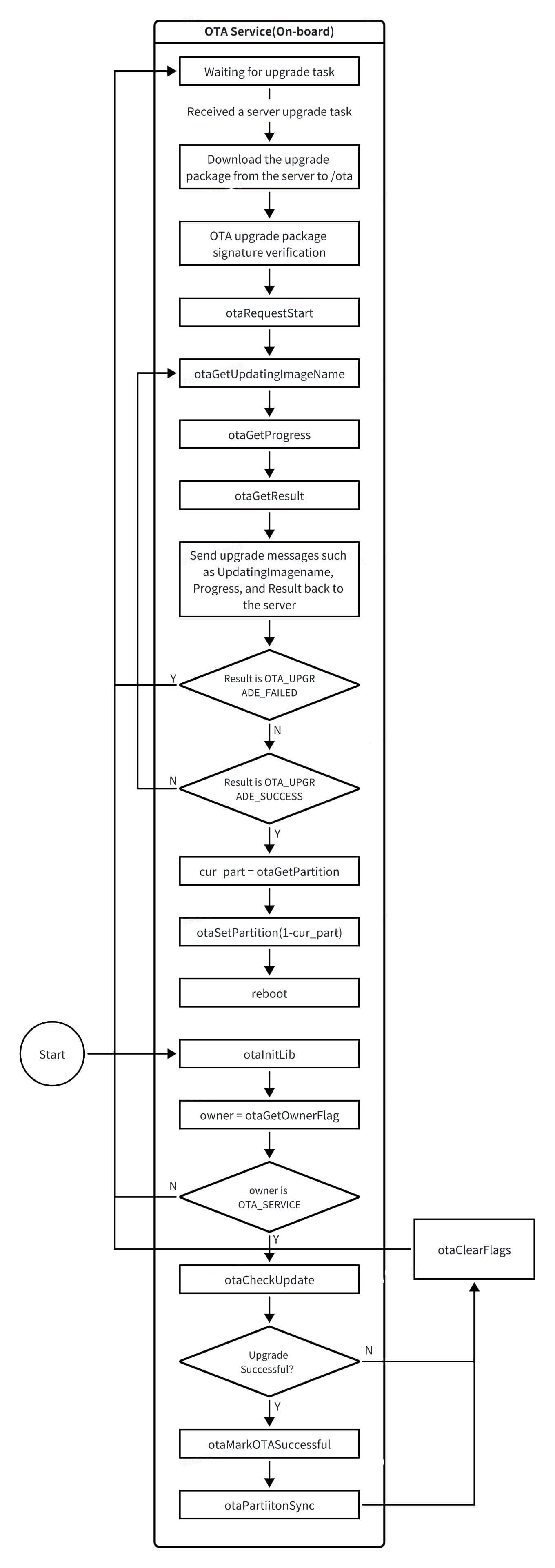
OTA Update Client Introduction
Using ota_tool
On the device, you can manually trigger an OTA update using ota_tool. Entering the command ota_tool -h displays detailed usage information.
ota_tool Usage:
-v, --version get this library's version.
-b, --boot check ota update status when boot.
-s, --setpartition [partition] set A/B slot partition, 0--A; 1--B.
-g, --getpartition get A/B slot partition, 0--A; 1--B.
-p, --package [package_path] specify the path of package, the package paths can be relative or absolute, it's length must be smaller than 64 bytes.
-n, --noreboot request ota without reboot.
-c, --checksign signature check.
-i, --signature signature information file.
-h, --help Display this help screen.
Before using ota_tool for an update, you must first upload the OTA update package to the device.
Parameter descriptions:
-hdisplays help information.-vretrieves the version oflibupdate.soand the current system software version.-bchecks the OTA update result after boot (this check is automatically performed during system startup; user intervention is not required).-ssets the A/B slot for the next boot: 0 for slot A, 1 for slot B.-gretrieves the current A/B slot.-pspecifies the update package path.-nprevents automatic reboot after a successful update.-cenables package integrity verification.-ispecifies the signature file (must follow the-pparameter).
Examples:
# Full update without package integrity verification
ota_tool -p all_in_one.zip
# Full update with package integrity verification
ota_tool -c -p all_in_one.zip -i all_in_one.signature
# Differential update without package integrity verification
ota_tool -p all_in_one_inc.zip
# Differential update with package integrity verification
ota_tool -c -p all_in_one_inc.zip -i all_in_one_inc.signature
ota_tool Implementation
ota_tool is implemented in C, with all source code contained in a single file: otainterface.c. It implements functionalities such as retrieving the system software version, checking update results, setting/getting A/B slots, performing OTA updates, forcing updates, and verifying OTA package signatures.
If the -c parameter is provided, the tool uses the specified signature file to verify the update package's signature.
Finally, it calls ota_update_all_img to start the update process.
ota_update_all_img
static int32_t ota_update_all_img(const char *zip_path)
{
int32_t progress = 0;
uint8_t slot = 0;
uint8_t next_slot = 0;
int32_t ret = 0;
ota_update_result_e result = 0;
char part_name[ARRAY_32] = { 0 };
ret = otaGetPartition(&slot);
if (ret < 0) {
return ret;
}
if (slot == 2) {
next_slot = 0;
printf("The slot [%d] to be burned\n", next_slot);
} else {
next_slot = 1 - slot;
printf("The slot [%d] to be burned\n", next_slot);
}
ret = otaInitLib();
if (ret < 0) {
printf("error:init failed!\n");
return ret;
}
ret = otaRequestStart(zip_path, OTA_TOOL);
if (ret < 0) {
printf("error: start ota update failed!\n");
ret = -1;
goto err;
}
while (otaGetResult() != OTA_UPGRADE_SUCCESS && otaGetResult() != OTA_UPGRADE_FAILED) {
progress = otaGetProgress();
result = otaGetResult();
otaGetUpdatingImageName(part_name, sizeof(part_name));
if (result == UPGRADE_FAILED) {
printf("error: ota update failed!\n");
ret = -1;
break;
}
OTA_show_Process_Bar(part_name, progress,
"OTA is upgrading ...");
usleep(100 * 1000);
}
err:
if (otaGetResult() == OTA_UPGRADE_SUCCESS) {
ret = otaSetPartition(next_slot);
if (ret < 0) {
printf("error: set partition failed!\n");
return ret;
}
if (g_is_reboot == true) {
printf("reboot system!\n");
ota_system_exe("reboot");
} else {
printf("ota update success and waiting for reboot!\n");
}
}
otaDeinitLib();
return ret;
}
-
Call
otaGetPartitionto obtain the current AB slot. -
Call
otaInitLibto initializelibupdate.so. -
Call
otaRequestStart, passing in the update package and owner (OTA_TOOL), to start the upgrade. -
Wait until
otaGetResultreturns eitherOTA_UPGRADE_SUCCESSorOTA_UPGRADE_FAILED. During this waiting period, callotaGetProgress,otaGetResult, andotaGetUpdatingImageNameto retrieve the upgrade progress, result, and the image currently being upgraded, respectively, and invokeOTA_show_Process_Barto print this information to the console. -
If the upgrade result from
otaGetResultisOTA_UPGRADE_SUCCESS, the upgrade is considered successful. Then, callotaSetPartitionto switch the AB slot to the opposite slot and reboot the SoC.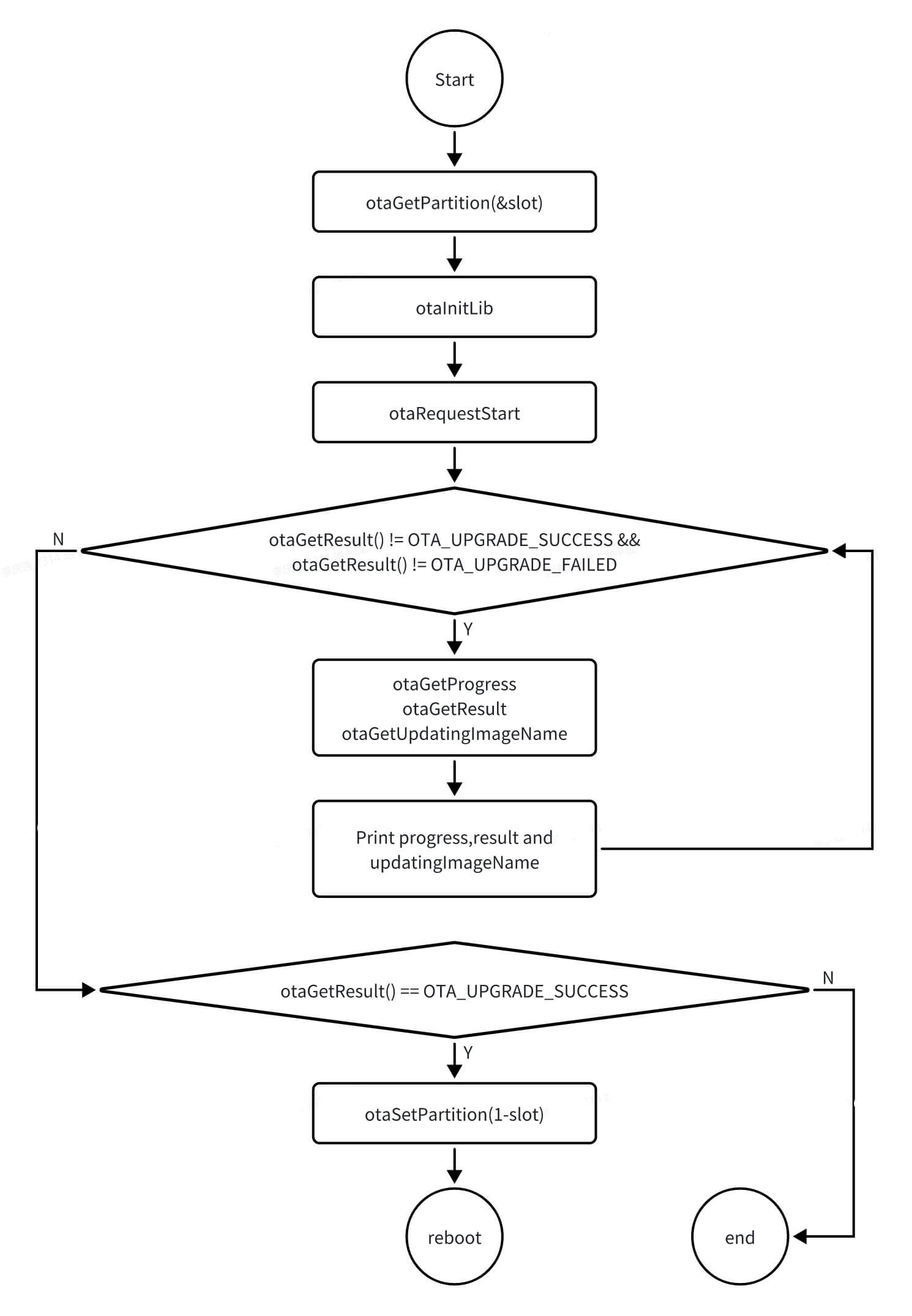
After the system reboots following the OTA upgrade process, run ota_tool -b to verify the upgrade result and perform subsequent operations.
ota_boot_check
After the S100 boots up, it starts the hobot-otatool.service, which invokes ota_tool -b. This option checks whether the file /ota/ota_tool_force_upgrade exists. If it exists, the system enters the upgrade process (the process will re-invoke the upgrade command). If the file does not exist, the system proceeds to the upgrade verification process ota_boot_check.
int32_t ota_boot_check(void)
{
int32_t ret = 0;
enum ota_update_owner owner = 0;
if ((ret = otaInitLib()) != 0) {
printf("error: init failed!\n");
goto exit;
}
if ((ret = otaGetOwnerFlag(&owner)) != 0) {
printf("error: Get owner flag failed!\n");
goto exit;
}
if (owner == NORMAL_BOOT) {
printf("Normal boot\n");
if ((ret = otaMarkOTASuccessful()) != 0) {
printf("error: mark boot success failed\n");
}
return ret;
}
if (owner != OTA_TOOL) {
printf("ota_tool is not owner, owner is [%d]\n", owner);
return 0;
}
if ((ret = otaCheckUpdate()) != 0) {
printf("error: boot check failed\n");
goto exit;
}
if ((ret = otaMarkOTASuccessful()) != 0) {
printf("error: mark boot success failed\n");
goto exit;
}
if ((ret = otaPartitionSync()) != 0) {
printf("error: partition sync failed\n");
goto exit;
}
ret = otaDeinitLib();
exit:
otaClearFlags();
return ret;
}
-
Call
otaInitLib. -
Call
otaGetOwnerFlagto obtain the OTA owner. -
If the owner is
NORMAL_BOOT, callotaMarkOTASuccessfulto mark the boot as successful, then exit. -
If the owner is not
OTA_TOOL, exit normally. -
Call
otaCheckUpdateto verify the upgrade result. If the result indicates an abnormal upgrade, callotaClearFlagsto clear OTA flags and terminate the OTA process. -
Call
otaMarkOTASuccessfulto mark the boot as successful. -
Call
otaPartitionSyncto synchronize the AB partitions and BAK partitions.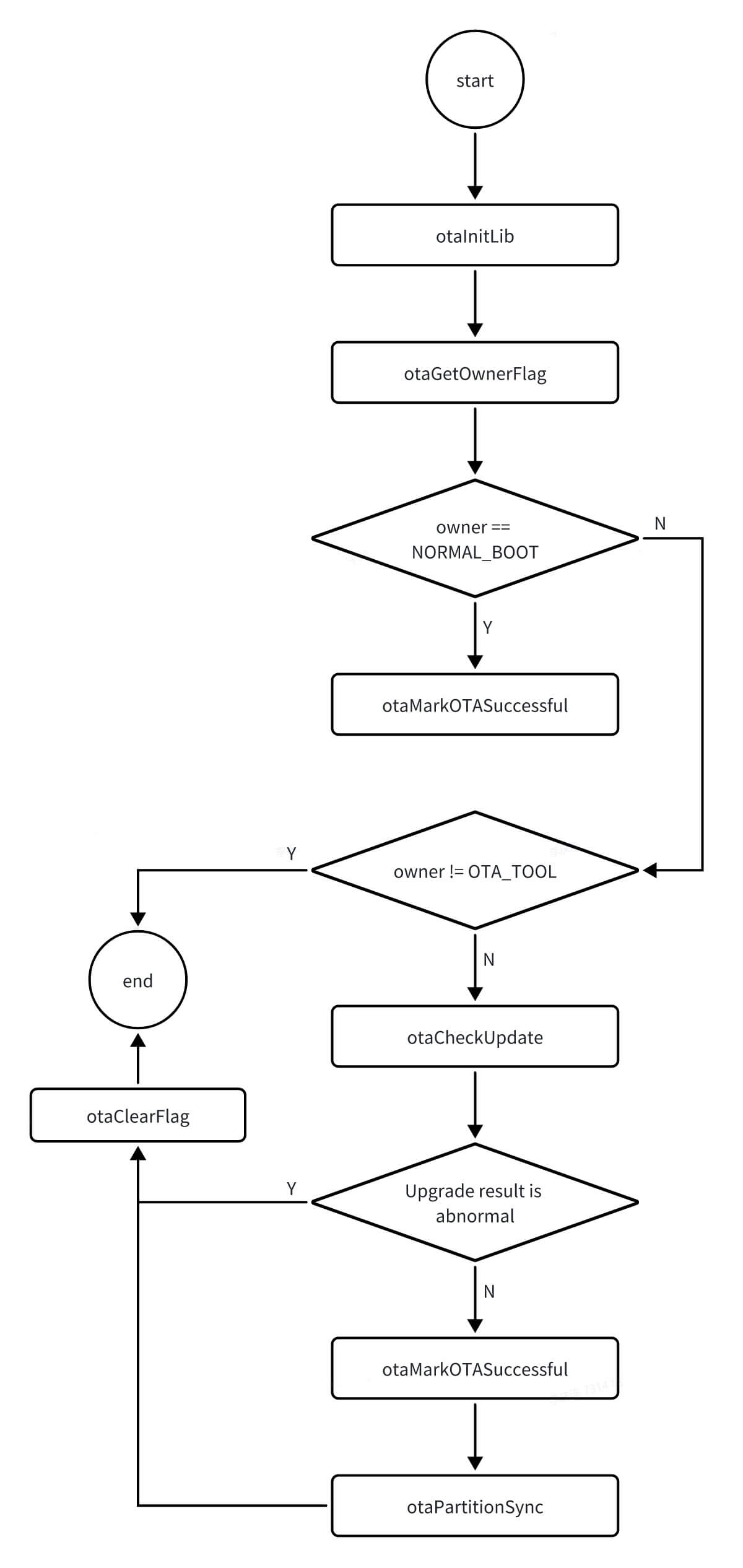
OTA API Introduction
The S100 provides a low-level flashing library, libupdate.so, which implements a set of cross-platform APIs for flashing OTA packages.
Based on the OTA High-Level APIs, the underlying software has developed the ota_tool utility.
Header file: hobot_ota_hl.h
Link library: libupdate.so
Dynamic Library Interface Error Code List
enum ota_err_e {
OTA_SUCCESS = 0,
OTAERR_IO,
OTAERR_PLAT_UNSUPPORT,
OTAERR_REPEAT,
OTAERR_MUTEX_INIT_LOCK_ERR,
OTAERR_NOTINIT,
OTAERR_NULLPOINTER,
OTAERR_SHORTBUF,
OTAERR_THREAD_CREATE,
OTAERR_RANGE,
OTAERR_STAGE,
OTAERR_IMAGE_WRITE,
OTAERR_BOOT_FAILED,
OTAERR_VEEPROM,
OTAERR_FILE_TYPE,
OTAERR_UNZIP,
OTAERR_NO_EXISTS,
OTAERR_MALLOC,
OTAERR_VERIFY,
OTAERR_IMG_SIZE,
OTAERR_UPDATE_STATUS,
};
Interface List
| Interface Prototype | Description |
|---|---|
int32_t otaInitLib(void); | Initialize the dynamic library |
int32_t otaDeinitLib(void); | Deinitialize the dynamic library |
int32_t otaGetLibVersion(char *version, int32_t len); | Get the dynamic library version |
int32_t otaRequestStart(const char *image_name, enum ota_update_owner owner); | Start the upgrade thread |
int32_t otaGetResult(void); | Get the upgrade status and result |
int32_t otaGetProgress(void); | Get the upgrade progress |
int32_t otaGetUpdatingImageName(char *image_name, int32_t len); | Get the package currently being upgraded |
int32_t otaGetPartition(uint8_t *partition); | Get the currently booted AB partition |
int32_t otaSetPartition(uint8_t partition); | Set the AB partition to boot from next time |
int32_t otaGetOwnerFlag(enum ota_update_owner *owner); | Get the OTA owner (after reboot) |
int32_t otaMarkOTASuccessful(); | Mark the OTA upgrade as successful (after reboot) |
int32_t otaCheckUpdate(); | Check whether the upgrade succeeded (after reboot) |
int32_t otaPartitionSync(void); | Synchronize AB partitions and BAK partitions |
void otaClearFlags(void); | Finalize the upgrade and clear OTA flags |
Interface: otaInitLib
| Interface Name | int32_t otaInitLib(void); |
|---|---|
| Interface Type | C function |
| Input Parameters | N/A |
| Output Parameters | N/A |
| Return Value | 0: Success;-OTAERR_REPEAT: Repeated initialization |
| Description | Initializes the on-device flashing interface dynamic library, primarily initializing the global structure g_upgrade_info. |
Example Code
#include <stdio.h>
#include <hobot_ota_hl.h>
int main(void) {
int32_t ret;
ret = otaInitLib();
if (ret != 0) {
printf("otaInitLib return: %d\n", ret);
return ret;
}
ret = otaDeinitLib();
if (ret != 0) {
printf("otaDeinitLib return: %d\n", ret);
return ret;
}
return 0;
}
Interface: otaDeinitLib
| Interface Name | int32_t otaDeinitLib(void); |
|---|---|
| Interface Type | C function |
| Input Parameters | N/A |
| Output Parameters | N/A |
| Return Value | 0: Success;-OTAERR_NOTINIT: Not initialized; deinitialization cannot be called |
| Description | Deinitializes the library |
Example Code
Refer to otaInitLib.
Interface: otaGetLibVersion
| Interface Name | int32_t otaGetLibVersion(char *version, int32_t len); |
|---|---|
| Interface Type | C function interface |
| Input Parameters | len: Length of the input buffer |
| Output Parameters | version: Buffer for storing version information. The version is returned as a three-part string (e.g., "1.0.0"). |
| Return Value | 0: Success; -OTAERR_NULLPOINTER: version is a null pointer; -OTAERR_SHORTBUF: The provided buffer is too small. |
| Function Description | Retrieve the version of this dynamic library |
Example Code
#include <stdio.h>
#include <hobot_ota_hl.h>
int main(void) {
int32_t ret;
char version[128];
if (ret = otaGetLibVersion(version, sizeof(version))) {
return ret;
}
printf("version: %s\n", version);
}
Interface: otaRequestStart
| Interface Name | int32_t otaRequestStart(const char *image_name, enum ota_update_owner owner); |
|---|---|
| Interface Type | C function interface |
| Input Parameters | image_name: Absolute path(s) to the OTA package(s). Multiple package types can be specified simultaneously, separated by semicolons. owner: The process initiating this OTA update. The owner is defined by the enum ota_update_owner. |
| Output Parameters | N/A |
| Return Value | 0: Success; -OTAERR_NULLPOINTER: image_name is a null pointer; -OTAERR_RANGE: Invalid owner value, outside the defined range; -OTAERR_NOTINIT: This dynamic library has not been initialized; -OTAERR_REPEAT: Another process is already performing an OTA update; -OTAERR_IO: I/O failure; -OTAERR_THREAD_CREATE: Failed to create thread. |
| Function Description | Start the OTA update process for the specified image_name and set the current update owner. |
Example Code
#include <stdio.h>
#include <hobot_ota_hl.h>
int main(void) {
int32_t ret;
int32_t result;
int32_t progress;
char imgname[256];
ret = otaInitLib();
if (ret != 0) {
printf("otaInitLib return: %d\n", ret);
return ret;
}
if (ret = otaRequestStart("/ota/all_in_one-secure_signed.zip;/ota/middleware.zip;/ota/param.zip", OTA_TOOL)) {
printf("otaRequestStart return: %d\n", ret);
return ret;
}
do {
result = otaGetResult();
if (ret = otaGetUpdatingImageName(imgname, sizeof(imgname))) {
printf("otaGetUpdatingImageName return: %d\n", imgname);
}
progress = otaGetProgress();
printf("current image: %s, progress: %d\n", imgname, progress);
sleep(1);
} while(result != OTA_UPGRADE_SUCCESS && result != OTA_UPGRADE_FAILED);
ret = otaGetPartition(&cur_part);
if (ret != 0) {
printf("otaGetPartition returned with %d\n", ret);
}
ret = otaSetPartition(1 - cur_part);
if (ret != 0) {
printf("otaSetPartition returned with %d\n", ret);
}
/* Then reboot system */
return 0;
}
Interface: otaGetResult
| Interface Name | int32_t otaGetResult(void); |
|---|---|
| Interface Type | C function interface |
| Input Parameters | N/A |
| Output Parameters | N/A |
| Return Value | -OTAERR_NOTINIT: This dynamic library has not been initialized; OTA_UPGRADE_NOT_START: OTA update has not started; OTA_UPGRADE_IN_PROGRESS: OTA update is in progress; OTA_UPGRADE_SUCCESS: OTA update completed successfully; OTA_UPGRADE_FAILED: OTA update completed but failed. |
| Function Description | Retrieve the OTA update result |
Example Code
See otaRequestStart
Interface: otaGetProgress
| Interface Name | int32_t otaGetProgress(void); |
|---|---|
| Interface Type | C function interface |
| Input Parameters | N/A |
| Output Parameters | N/A |
| Return Value | 0 ~ 100: Current OTA progress (%) -OTAERR_NOTINIT: This dynamic library has not been initialized |
| Description | Retrieve the current OTA progress |
Example Code
See otaRequestStart
Interface: otaGetUpdatingImageName
| Interface Name | int32_t otaGetUpdatingImageName(char *image_name, int32_t len); |
|---|---|
| Interface Type | C function interface |
| Input Parameters | len: Buffer length |
| Output Parameters | image_name: Buffer to store the result. Possible values for image_name include: "idle_state" – OTA not started, "all_img_finish" – OTA completed, "app_param" – application parameters, or other package names ending with ".img". |
| Return Value | 0: Success -OTAERR_NULLPOINTER: image_name is a null pointer -OTAERR_NOTINIT: This dynamic library has not been initialized -OTAERR_SHORTBUF: Buffer length is too short |
| Description | Retrieve the name of the image currently being updated |
Example Code
See otaRequestStart
Interface: otaGetPartition
| Interface Name | int32_t otaGetPartition(uint8_t *partition); |
|---|---|
| Interface Type | C function interface |
| Input Parameters | N/A |
| Output Parameters | partition: Pointer to a variable that receives the current partition. *partition=0: Currently on partition A; *partition=1: Currently on partition B |
| Return Value | 0: Success -OTAERR_NULLPOINTER: partition is a null pointer -OTAERR_IO: I/O error, please retry |
| Description | Retrieve the currently active A/B boot partition |
Example Code
See otaRequestStart
Interface: otaSetPartition
| Interface Name | int32_t otaSetPartition(uint8_t partition); |
|---|---|
| Interface Type | C function interface |
| Input Parameters | partition: Partition to boot from next time. 0: Partition A, 1: Partition B |
| Output Parameters | N/A |
| Return Value | 0: Success -OTAERR_NOTINIT: This dynamic library has not been initialized -OTAERR_RANGE: Invalid partition value; valid values are 0 and 1 -OTAERR_IO: I/O error, please retry -OTAERR_STAGE: Operation not supported at current OTA stage. Not allowed during or after a failed OTA update. |
| Description | Set the next boot A/B partition |
Example Code
See otaRequestStart
Interface: otaGetOwnerFlag
| Interface Name | int32_t otaGetOwnerFlag(enum ota_update_owner *owner); |
|---|---|
| Interface Type | C function interface |
| Input Parameters | N/A |
| Output Parameters | owner: Pointer to a variable that receives the current OTA update owner. See enum ota_update_owner for details. |
| Return Value | OTA_SUCCESS: Success -OTAERR_NOTINIT: Not initialized -OTAERR_NULLPOINTER: partition is a null pointer -OTAERR_IO: I/O error, please retry |
| Description | Retrieve the current OTA update owner |
Example Code
static int check_and_mark(void) {
enum ota_update_owner owner;
int32_t ret;
ret = otaGetOwnerFlag(&owner);
if (ret != 0) {
printf("otaGetOwnerFlag returned with %d\n", ret);
return -1;
}
if (owner != OTA_TOOL) {
printf("The OTA update is not launched by ota_tool, owner: %d\n", owner);
return -1;
}
ret = otaCheckUpdate();
if (ret == -OTAERR_IMAGE_WRITE) {
printf("ota_tool: OTA image write failed, is there a reboot during update?\n");
goto clearFlags;
}
if (ret == -OTAERR_BOOT_FAILED) {
printf("ota_tool: The new package boot failed. Please check the packages\n");
goto clearFlags;
}
if (ret != 0) {
printf("otaCheckUpdate returned with %d\n", ret);
goto clearFlags;
}
ret = otaMarkOTASuccessful();
if (ret != 0) {
printf("otaMarkOTASuccessful returned with %d\n", ret);
goto clearFlags;
}
ret = otaPartitionSync();
if (ret != 0) {
printf("otaPartitionSync returned with %d\n", ret);
goto clearFlags;
}
clearFlags:
otaClearFlags();
return ret;
}
Interface: otaMarkOTASuccessful
| Interface Name | int32_t otaMarkOTASuccessful(); |
|---|---|
| Interface Type | C function interface |
| Input Parameters | N/A |
| Output Parameters | N/A |
| Return Value | 0: Success -OTAERR_NOTINIT: Not initialized -OTAERR_IO: I/O error, please retry |
| Description | Mark the current OTA update as successful |
Example Code
Refer to otaGetOwnerFlag
Interface: otaCheckUpdate
| Interface Name | int32_t otaCheckUpdate(); |
|---|---|
| Interface Type | C function interface |
| Input Parameters | N/A |
| Output Parameters | N/A |
| Return Value | 0: Success -OTAERR_IO: I/O error, please retry -OTAERR_STAGE: Upgrade not performed -OTAERR_IMAGE_WRITE: Image write failed -OTAERR_BOOT_FAILED: New image failed to boot or partition switch did not occur |
| Description | Checks whether the current upgrade was successful |
Example Code
Refer to otaGetOwnerFlag
Interface: otaClearFlags
| Interface Name | void otaClearFlags(void); |
|---|---|
| Interface Type | C function interface |
| Input Parameters | N/A |
| Output Parameters | N/A |
| Return Value | N/A |
| Description | Clears OTA flags |
Example Code
Refer to otaGetOwnerFlag
Interface: otaPartitionSync
| Interface Name | int32_t otaPartitionSync(void); |
|---|---|
| Interface Type | C function interface |
| Input Parameters | N/A |
| Output Parameters | N/A |
| Return Value | 0: Success -OTAERR_NOTINIT: Not initialized -OTAERR_IO: I/O error -OTAERR_REPEAT: Conflict with another upgrade process |
| Description | Synchronizes AB partitions and BAK partitions |
Example Code
Refer to otaGetOwnerFlag