DDR Bandwidth Test
Test Principle
DDR (Double Data Rate) memory bandwidth is a key performance metric that measures the data transfer capability of a memory system. It reflects the amount of data the memory can transfer per unit time, typically expressed in MB/s or GB/s. By performing specific memory operations and measuring their execution time, the memory bandwidth performance can be estimated. The primary test operations include: Copy, Scale, Add, and Triad.
1. Copy Operation:
for (j=0; j<STREAM_ARRAY_SIZE; j++)
c[j] = a[j];
- This operation copies data from array
a[]to arrayc[]. It involves only memory reads and writes, thus measuring pure memory bandwidth.
2. Scale Operation:
for (j=0; j<STREAM_ARRAY_SIZE; j++)
b[j] = scalar * c[j];
- This operation multiplies each element of array
c[]by a constantscalarand stores the result in arrayb[]. Bandwidth is measured through readingc[]and writing tob[].
3. Add Operation:
for (j=0; j<STREAM_ARRAY_SIZE; j++)
c[j] = a[j] + b[j];
- This operation adds corresponding elements from arrays
a[]andb[], storing the result in arrayc[]. It reads two arrays and writes to a third.
4. Triad Operation:
for (j=0; j<STREAM_ARRAY_SIZE; j++)
a[j] = b[j] + scalar * c[j];
- This is a more complex operation that performs a fused multiply-add on elements from arrays
b[]andc[]using the constantscalar, storing the result in arraya[].
Preparation
1. Confirm DDR type and frequency: Different DDR memory types (e.g., LPDDR4) and their frequencies affect bandwidth test results. Use the command cat /sys/class/boardinfo/ddr_type to check DDR status information.
sunrise@ubuntu:/# cat /sys/class/boardinfo/ddr_type
LPDDR5
Currently, the RDKS100 DDR frequency is 6400 MHz.
2. Ensure the stream test file exists under /app/chip_base_test/08_ddr_bandwidth/. If not present, recompile it in this directory:
sunrise@ubuntu:/# cd /app/chip_base_test/08_ddr_bandwidth
sunrise@ubuntu:/# gcc -O3 -fopenmp -DNTIMES=100 stream.c -lgomp -o stream
Test Procedure
After completing the preparation steps, run the test command:
sunrise@ubuntu:/# ./stream
After approximately 10 seconds, you will obtain the following results:
-------------------------------------------------------------
STREAM version $Revision: 5.10 $
-------------------------------------------------------------
This system uses 8 bytes per array element.
-------------------------------------------------------------
Array size = 10000000 (elements), Offset = 0 (elements)
Memory per array = 76.3 MiB (= 0.1 GiB).
Total memory required = 228.9 MiB (= 0.2 GiB).
Each kernel will be executed 100 times.
The *best* time for each kernel (excluding the first iteration)
will be used to compute the reported bandwidth.
-------------------------------------------------------------
Number of Threads requested = 6
Number of Threads counted = 6
-------------------------------------------------------------
Your clock granularity/precision appears to be 1 microseconds.
Each test below will take on the order of 3674 microseconds.
(= 3674 clock ticks)
Increase the size of the arrays if this shows that
you are not getting at least 20 clock ticks per test.
-------------------------------------------------------------
WARNING -- The above is only a rough guideline.
For best results, please be sure you know the
precision of your system timer.
-------------------------------------------------------------
-------------------------------------------------------------
Function Best Rate MB/s Avg time Min time Max time
Copy: 47239.8 0.003658 0.003387 0.004648
Scale: 48721.4 0.003657 0.003284 0.005366
Add: 46592.6 0.006095 0.005151 0.008138
Triad: 46431.4 0.006107 0.005169 0.008374
-------------------------------------------------------------
Solution Validates: avg error less than 1.000000e-13 on all three arrays
-------------------------------------------------------------
Explanation of Key Information:
The four metrics in the test results—Copy, Scale, Add, and Triad—represent bandwidth measurements. The test principles for these four operations are illustrated in the figure below:
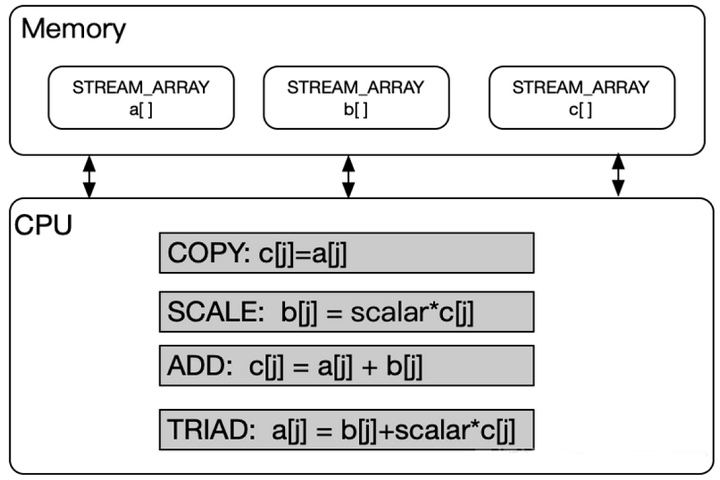
-
Copy: Reads a value from one memory location and writes it to another.
- Test Description: In the Copy test, the system copies the contents of one array to another. This is the most basic memory bandwidth test, primarily evaluating performance during simple memory-to-memory data copying.
- Bandwidth Result: 47578.1 MB/s
-
Scale: Reads a value from memory, performs a multiplication, and writes the result to another memory location.
- Test Description: Scale involves not only memory bandwidth but also CPU computation, thus better reflecting the collaboration between processor and memory.
- Bandwidth Result: 47904.1 MB/s
-
Add: Reads two values from memory, adds them, and writes the result to another memory location.
- Test Description: The Add test simulates adding two arrays and storing the result in a third array, testing bandwidth requirements during parallel CPU and memory operations.
- Bandwidth Result: 44642.0 MB/s
-
Triad (Combined Operation): Combines Copy, Scale, and Add operations. Specifically, it reads two values
aandbfrom memory, performs a fused multiply-add operation (a + scalar * b), and writes the result to another memory location.- Test Description: Triad not only adds two arrays but also scales the result with another array, representing a composite operation involving computation, addition, and memory access simultaneously.
- Bandwidth Result: 42987.3 MB/s
-
Meaning of Values in Output Results:
-
Best Rate MB/s: The highest memory transfer rate achieved during the operation, measured in megabytes per second (MB/s). Represents peak performance.
-
Avg time: Average time per operation in seconds, indicating average latency.
-
Min time: Shortest operation time in seconds, representing best-case performance in a single run.
-
Max time: Longest operation time in seconds, representing worst-case performance in a single run.
-
Test Metrics
DDR bandwidth is typically calculated based on memory clock frequency and bus width, using the following formula:
Bandwidth (MB/s) = Memory Clock Frequency (MHz) × 2 × Bus Width (bit) / 8
On the S100 platform, the DDR memory frequency is 4266 MHz (2133 × 2), and the memory bus width is 96 bits (i.e., 12 bytes). Thus, the theoretical bandwidth is:
Bandwidth (MB/s) = 6400 MHz × 12 Byte = 76800 MB/s
Pass Criteria
Actual DDR bandwidth test results are usually lower than theoretical bandwidth. A typical standard is 60%–70% of the theoretical bandwidth. For the S100 platform, with a theoretical bandwidth of 76800 MB/s, the pass threshold is:
Pass Criterion = ddr_score(76800) × 0.6 = 46080
Test Result
Taking the Triad operation—which closely mimics real-world DDR usage—as an example, its measured bandwidth exceeds the pass criterion of 46080 MB/s. Therefore, the test result meets the DDR bandwidth standard and satisfies expected performance requirements.