UART Driver Debugging Guide
The X5 chip has a total of 8 UART ports: UART0, UART1, UART2, UART3, UART4, UART5, UART6, UART7.
- UART0 is used as the debugging UART port, and only UART1 and UART7 support hardware flow control.
- It supports bitrates of 115.2Kbps, 230.4Kbps, 460.8Kbps, 921.6Kbps, 1.5Mbps, 2Mbps, and 4Mbps.
- It supports interrupt-based or DMA-based modes.
Driver Code
Code Path
drivers/tty/serial/8250/8250_dw.c
drivers/tty/serial/8250/8250_dwlib.c
drivers/tty/serial/8250/8250_dwlib.h
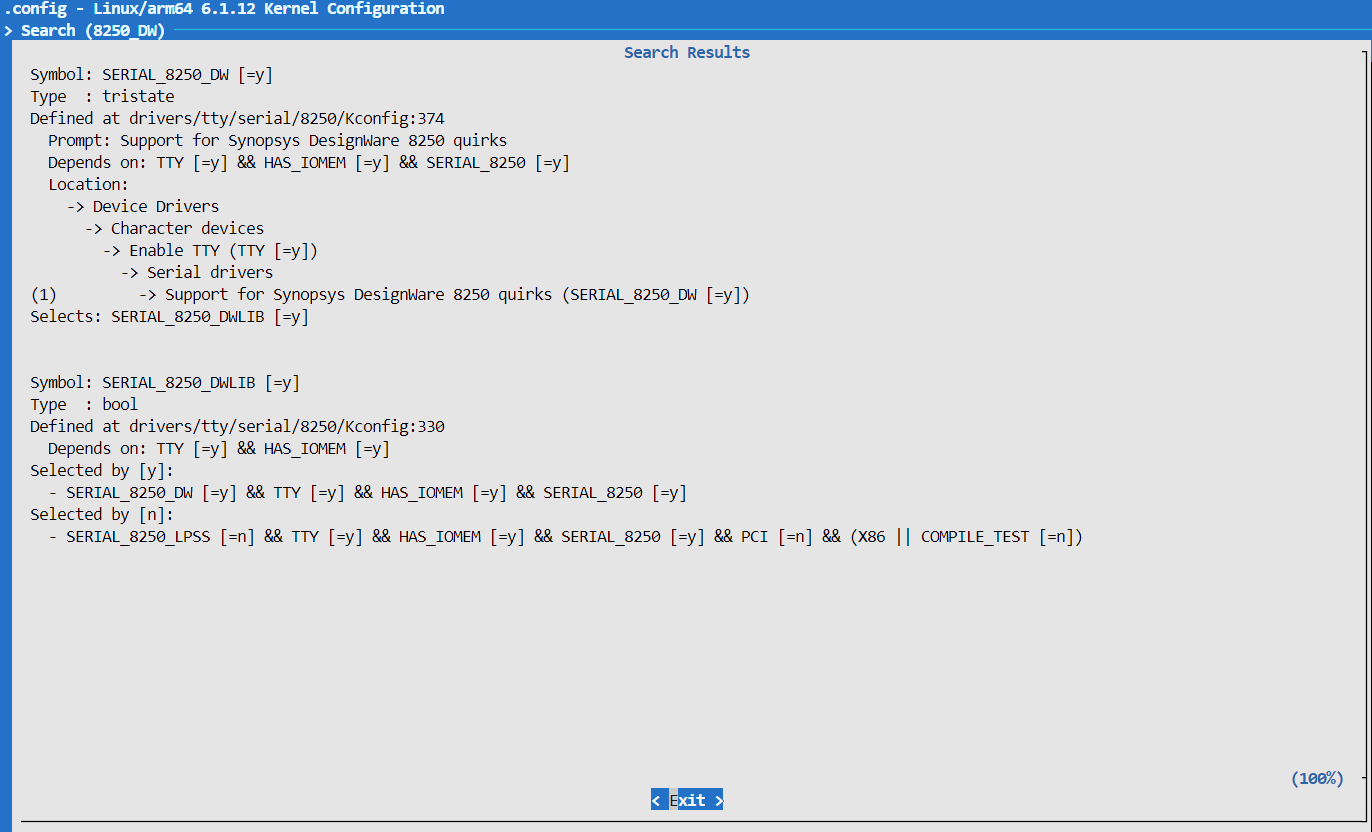
Kernel Configuration
SERIAL_8250_DW
SERIAL_8250_DWLIB
DTS Device Node Configuration
The device tree definition for the X5 UART controller is located in the <font color="red">arch/arm64/boot/dts/hobot/x5.dtsi</font> file under the SDK package's kernel folder.
Note: The nodes in x5.dtsi mainly declare SoC-level features and are not specific to any particular circuit board, so they generally do not need to be modified.
By default, the X5 UART controller is disabled. When you need to enable the corresponding UART ports, you can modify or add custom configurations in the device tree specific to your board.
For example, to enable UART0, UART2, and UART5 in the x5-rdk-v1p0.dts file:
/* arch/arm64/boot/dts/hobotx5-rdk-v1p0.dts */
...
&uart0 {
status = "okay";
};
&uart2 {
status = "okay";
pinctrl-names = "default";
pinctrl-0 = <&pinctrl_uart2>;
...
};
&uart5 {
status = "okay";
pinctrl-names = "default";
pinctrl-0 = <&pinctrl_uart5>;
};
...
DTS Configuration for DMA Binding
All UARTs on the X5 support DMA transfer.
Note:- UART0 (dsp_uart), as the default UART for the kernel, does not allow DMA transfer in Linux.
- When configuring UART to use DMA transfer, the transfer must be 16-byte aligned.
For example, to configure UART7:
/* arch/arm64/boot/dts/hobotx5-rdk-v1p0.dts */
...
&uart7 {
status = "okay";
pinctrl-names = "default";
pinctrl-0 = <&pinctrl_uart7>;
dma-names = "tx", "rx";
dmas = <&axi_dmac 1>, <&axi_dmac 0>;
}
Note: UART7 on the EVB board is configured by default as GPIO. If you need to use UART7, you must first remove the corresponding PINs for UART7 (lsio_gpio0_0~lsio_gpio0_3) from the “ls_gpio0_porta” configuration.
The UART DMA handshake list is as follows:
| UART | RX | TX |
|---|---|---|
| UART1 | 2 | 3 |
| UART2 | 4 | 5 |
| UART3 | 6 | 7 |
| UART4 | 8 | 9 |
| UART5 | 35 | 36 |
| UART6 | 37 | 38 |
| UART7 | 0 | 1 |
UART Testing
On the hardware side, connect the TX and RX pins of UART1. These correspond to pins 8 and 10 of the 40-pin header.
Compile the uart_duplex.c code (see Appendix A for the code).
Please make sure to modify the cross-compilation toolchain path in the following commands.
/opt/arm-gnu-toolchain-11.3.rel1-x86_64-aarch64-none-linux-gnu -o uart_duplex uart_duplex.c -lpthread
Loopback Test Command: Open /dev/ttyS1 with the default baud rate of 4Mbps. The test sends and receives 1MB of data per round by default, running for 100 rounds. Reading and writing occur simultaneously, with data verification performed every 512 bytes sent or received. At the end of a complete test round, if no errors occur, the program prints a "verification correct" message.
# ./uart_duplex -c 100 -d /dev/ttyS1
test size:1024 Kbytes, baud:4000000
Start receive thread
Start send thread
Start recv_check thread
This is receive test 1 times
This is uart send 1 times
receive sum:102416 bytes
receive sum:205312 bytes
...
receive sum:924164 bytes
receive sum:1027076 bytes
send 1024Kbytes,time:2700.000000ms, BPS:379259.250000
This is receive test 2 times
### Check the received data is correct ###
uart_duplex命令是测试uart的,可以阅读它的帮助信息获取更多使用方法。
Appendix (Test Code)
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdint.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <termios.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <getopt.h>
#include <sys/time.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <semaphore.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define BUFF_SIZE (20 * 1024 * 1024)
pthread_t recv_thread_id;
pthread_t recv_check_thread_id;
pthread_t send_thread_id;
char send_buffer[BUFF_SIZE] = {0};
char recv_buffer[BUFF_SIZE] = {0};
static uint32_t test_size = 1024;
static uint32_t baud = 4000000;
static uint32_t test_count = 0;
int g_fd;
uint64_t recv_total = 0;
sem_t sem_check;
#define FRAME_LEN 512
#if 1
static void dump_recv_data(uint32_t sum, uint32_t len)
{
int ii = 0;
printf("dump receive data:\n");
for (ii = 0; ii < len; ii += 4) {
printf("0x%x: 0x%x, 0x%x, 0x%x, 0x%x\n", sum + ii,
recv_buffer[sum + ii],
recv_buffer[sum + ii + 1],
recv_buffer[sum + ii + 2],
recv_buffer[sum + ii + 3]);
}
}
static void dump_send_data(uint32_t sum, uint32_t len)
{
int ii = 0;
printf("dump send data:\n");
for (ii = 0; ii < len; ii += 4) {
printf("0x%x: 0x%x, 0x%x, 0x%x, 0x%x\n", sum + ii,
send_buffer[sum + ii],
send_buffer[sum + ii + 1],
send_buffer[sum + ii + 2],
send_buffer[sum + ii + 3]);
}
}
#endif
static void set_baudrate(int fd, int nSpeed)
{
struct termios newtio;
tcgetattr(fd, &newtio);
switch (nSpeed) {
case 2400:
cfsetispeed(&newtio, B2400);
cfsetospeed(&newtio, B2400);
break;
case 4800:
cfsetispeed(&newtio, B4800);
cfsetospeed(&newtio, B4800);
break;
case 9600:
cfsetispeed(&newtio, B9600);
cfsetospeed(&newtio, B9600);
break;
case 19200:
cfsetispeed(&newtio, B19200);
cfsetospeed(&newtio, B19200);
break;
case 38400:
cfsetispeed(&newtio, B38400);
cfsetospeed(&newtio, B38400);
break;
case 57600:
cfsetispeed(&newtio, B57600);
cfsetospeed(&newtio, B57600);
break;
case 115200:
cfsetispeed(&newtio, B115200);
cfsetospeed(&newtio, B115200);
break;
case 230400:
cfsetispeed(&newtio, B230400);
cfsetospeed(&newtio, B230400);
break;
case 921600:
cfsetispeed(&newtio, B921600);
cfsetospeed(&newtio, B921600);
break;
case 1000000:
cfsetispeed(&newtio, B1000000);
cfsetospeed(&newtio, B1000000);
break;
case 1152000:
cfsetispeed(&newtio, B1152000);
cfsetospeed(&newtio, B1152000);
break;
case 1500000:
cfsetispeed(&newtio, B1500000);
cfsetospeed(&newtio, B1500000);
break;
case 2000000:
cfsetispeed(&newtio, B2000000);
cfsetospeed(&newtio, B2000000);
break;
case 2500000:
cfsetispeed(&newtio, B2500000);
cfsetospeed(&newtio, B2500000);
break;
case 3000000:
cfsetispeed(&newtio, B3000000);
cfsetospeed(&newtio, B3000000);
break;
case 3500000:
cfsetispeed(&newtio, B3500000);
cfsetospeed(&newtio, B3500000);
break;
case 4000000:
cfsetispeed(&newtio, B4000000);
cfsetospeed(&newtio, B4000000);
break;
default:
printf("\tSorry, Unsupported baud rate, use previous baudrate!\n\n");
break;
}
tcsetattr(fd,TCSANOW,&newtio);
}
static void set_termios(int fd)
{
struct termios term;
tcgetattr(fd, &term);
term.c_cflag &= ~(CSIZE | CSTOPB | PARENB | INPCK);
term.c_cflag |= (CS8 | CLOCAL | CREAD);
term.c_lflag &= ~(ICANON | ECHO | ECHOE | ISIG);
term.c_oflag &= ~(OPOST | ONLCR | OCRNL);
term.c_iflag &= ~(ICRNL |INLCR | IXON | IXOFF | IXANY);
term.c_cc[VTIME] = 0;
term.c_cc[VMIN] = 1;
tcsetattr(fd, TCSAFLUSH, &term);
}
static void *send_test(void *times)
{
/*send thread*/
struct timeval start, end;
int32_t i = 0;
uint32_t j = 0;
uint32_t tmp = 0;
uint32_t exe_count = 0;
int32_t ret = 0;
float ts = 0;
printf("Start send thread\n");
sleep(1);
if (test_count == 0) {
tmp = 10;
} else
tmp = test_count;
for (j = 0; j < tmp; j++) {
if (test_count == 0)
j = 0;
sleep(1);
printf("This is uart send %d times\n", ++exe_count);
gettimeofday(&start, NULL);
for (i = 0; i < test_size * 1024; i = i + FRAME_LEN) {
ret = write(g_fd, &send_buffer[i], FRAME_LEN);
if (ret < FRAME_LEN) {
printf("write ttyS2 error\n");
return NULL;
}
}
#if 1
gettimeofday(&end, NULL);
// printf("start %ld sec, %ld usec, end %ld sec, %ld usec\n", start.tv_sec, start.tv_usec, end.tv_sec, end.tv_usec);
ts = ((end.tv_sec * 1000000 + end.tv_usec) - (start.tv_sec * 1000000 + start.tv_usec)) / 1000;
printf("send %dKbytes,time:%fms, BPS:%f\n", test_size, ts, test_size * 1000 / (ts / 1000));
#endif
}
close(g_fd);
return NULL;
}
static void *recv_test(void *times)
{
int32_t j = 0;
uint32_t exe_count = 0;
int tmp = 0;
int size = 0;
int sum = 0;
int last_count = 0;
int len = 0;
int len_frame = 0; /*use to get correct frame len*/
printf("Start receive thread\n");
memset(recv_buffer, 0, sizeof(recv_buffer));
if (test_count == 0) {
tmp = 10;
} else
tmp = test_count;
for (j = 0; j < tmp; j++) {
sum = 0;
last_count = 0;
if (test_count == 0)
j = 0;
printf("This is receive test %d times\n", ++exe_count);
//gettimeofday(&start, NULL);
size = test_size * 1024;
while (size > 0) {
len = read(g_fd, &recv_buffer[sum], FRAME_LEN);
if (len < 0) {
printf("read error\n");
return NULL;
}
recv_total += len;
len_frame += len;
if (len_frame >= FRAME_LEN) {
len_frame -= FRAME_LEN;
sem_post(&sem_check);
}
#if 0
ret = memcmp(&recv_buffer[sum], &send_buffer[sum], len);
if (ret != 0) {
printf("data compare error\n");
return NULL;
}
#endif
sum +=len;
size -= len;
if ((sum - last_count) > 100 * 1024) {
printf("receive sum:%d bytes\n", sum);
last_count = sum;
}
}
#if 0
gettimeofday(&end, NULL);
printf("start %ld sec, %ld usec, end %ld sec, %ld usec\n", start.tv_sec, start.tv_usec, end.tv_sec, end.tv_usec);
ts = ((end.tv_sec * 1000000 + end.tv_usec) - (start.tv_sec * 1000000 + start.tv_usec)) / 1000;
printf("receive %dKbytes,time:%fms, BPS:%f\n", test_size, ts, test_size * 1000 / (ts / 1000));
#endif
}
close(g_fd);
return NULL;
}
int32_t error_bit(uint64_t *data1, uint64_t *data2, int32_t len)
{
uint64_t c=0;
int32_t sum = 0;
int i = 0;
for(i = 0; i < len / 8; i++) {
c = data1[i] ^ data2[i];
while(c!=0) {
c &= (c - 1);
sum++;
}
}
return sum;
}
static void *recv_check_test(void *times)
{
int32_t check_pos = 0;
uint32_t *cur_frame = NULL;
int32_t error_bit_cnt = 0;
printf("Start recv_check thread\n");
while (1) {
sem_wait(&sem_check);
/*check data*/
cur_frame = (uint32_t *)&recv_buffer[check_pos];
if (*cur_frame != check_pos / FRAME_LEN) {
printf("error: may lost frame, curruent frame is %d, expected frame is %d position: 0x%x\n",
*cur_frame, check_pos / FRAME_LEN, check_pos);
//dump_recv_data(check_pos, FRAME_LEN);
//dump_send_data(check_pos, FRAME_LEN);
error_bit_cnt = 0;
error_bit_cnt = error_bit((uint64_t *)&recv_buffer[check_pos],
(uint64_t *)&send_buffer[check_pos],
FRAME_LEN / 8);
check_pos += FRAME_LEN;
printf("test total data: 0x%lx, error bit count:%d\n", recv_total, error_bit_cnt);
if (check_pos == test_size * 1024) {
//exit(1);
printf("uart: frame head error\n");
}
continue;
}
error_bit_cnt = 0;
error_bit_cnt = error_bit((uint64_t *)&recv_buffer[check_pos],
(uint64_t *)&send_buffer[check_pos],
FRAME_LEN / 8);
if (error_bit_cnt) {
printf("test total data: 0x%lx!!!!!!!, error bit count:%d\n", recv_total, error_bit_cnt);
//dump_recv_data(check_pos, FRAME_LEN);
//dump_send_data(check_pos, FRAME_LEN);
check_pos += FRAME_LEN;
if (check_pos == test_size * 1024) {
//exit(1);
printf("uart: frame data error\n");
}
continue;
}
memset(&recv_buffer[check_pos], 0, FRAME_LEN);
check_pos += FRAME_LEN;
if (check_pos == test_size * 1024) {
check_pos = 0;
printf("### Check the received data is correct ###\n");
}
}
return NULL;
}
static const char short_options[] = "s:u:c:b:d:h";
static const struct option long_options[] = {
{"size", required_argument, NULL, 's'},
{"baudrate", required_argument, NULL, 'b'},
{"count", required_argument, NULL, 'c'},
{"device", required_argument, NULL, 'd'},
{"help", no_argument, NULL, 'h'},
{0, 0, 0, 0}};
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
int ret = 0;
char *pDevice = NULL;
int i = 0;
int32_t cmd_parser_ret = 0;
uint32_t *frame_num = NULL;
uint32_t *frame_value = NULL;
while ((cmd_parser_ret = getopt_long(argc, argv, short_options, long_options, NULL)) != -1) {
switch (cmd_parser_ret) {
case 's':
test_size = atoi(optarg);
break;
case 'b':
baud = atoi(optarg);
break;
case 'c':
test_count = atoi(optarg);
break;
case 'd':
pDevice = optarg;
break;
case 'h':
printf("**********UART STRESS TEST HELP INFORMATION*********\n");
printf(">>> -s/--size [test size,unit--Kbytes,default is 1M, MAX is 20M]\n");
printf(">>> -b/--baudrate [baud,default is 4M]\n");
printf(">>> -c/--count [test count,default is forever]\n");
printf(">>> -d/--uart [uart device, user must set this]\n");
return 0;
}
}
if (baud > 4000000) {
printf("baud is larger than max baud\n");
return -1;
}
g_fd = open(pDevice, O_RDWR | O_NOCTTY);
if (0 > g_fd) {
printf("open fail\n");
return -1;
}
set_baudrate(g_fd, baud);
set_termios(g_fd);
printf("test size:%d Kbytes, baud:%d\n", test_size, baud);
for (i = 0; i < test_size * 1024; i+=4) {
if (i % FRAME_LEN) {
frame_value = (uint32_t *)&send_buffer[i];
*frame_value = rand();
}
}
for (i = 0; i < test_size * 1024 / FRAME_LEN; i++) {
frame_num = (uint32_t *)&send_buffer[i * FRAME_LEN];
*frame_num = i;
// printf("pos:0x%x, value:0x%x\n", i * FRAME_LEN, *frame_num);
}
sem_init(&sem_check, 0, 0);
ret = pthread_create(&recv_thread_id,
NULL,
recv_test,
NULL);
if (ret < 0) {
printf("create uart1 test thread failed\n");
return -1;
}
ret = pthread_create(&send_thread_id,
NULL,
send_test,
NULL);
if (ret < 0) {
printf("create uart2 test thread failed\n");
return -1;
}
ret = pthread_create(&recv_check_thread_id,
NULL,
recv_check_test,
NULL);
if (ret < 0) {
printf("create receive check thread failed\n");
return -1;
}
pthread_join(recv_thread_id, NULL);
pthread_join(recv_check_thread_id, NULL);
pthread_join(send_thread_id, NULL);
return 0;
}