3.3.4 UART Application
The RDK S100 supports UART2 on the 40-pin header, which is disabled by default. The physical pin numbers are 8 and 10, with an I/O voltage of 3.3V.
The 40-pin header requires a DIP switch to select between UART2 and I2C5. For specific details, please refer to the image below:
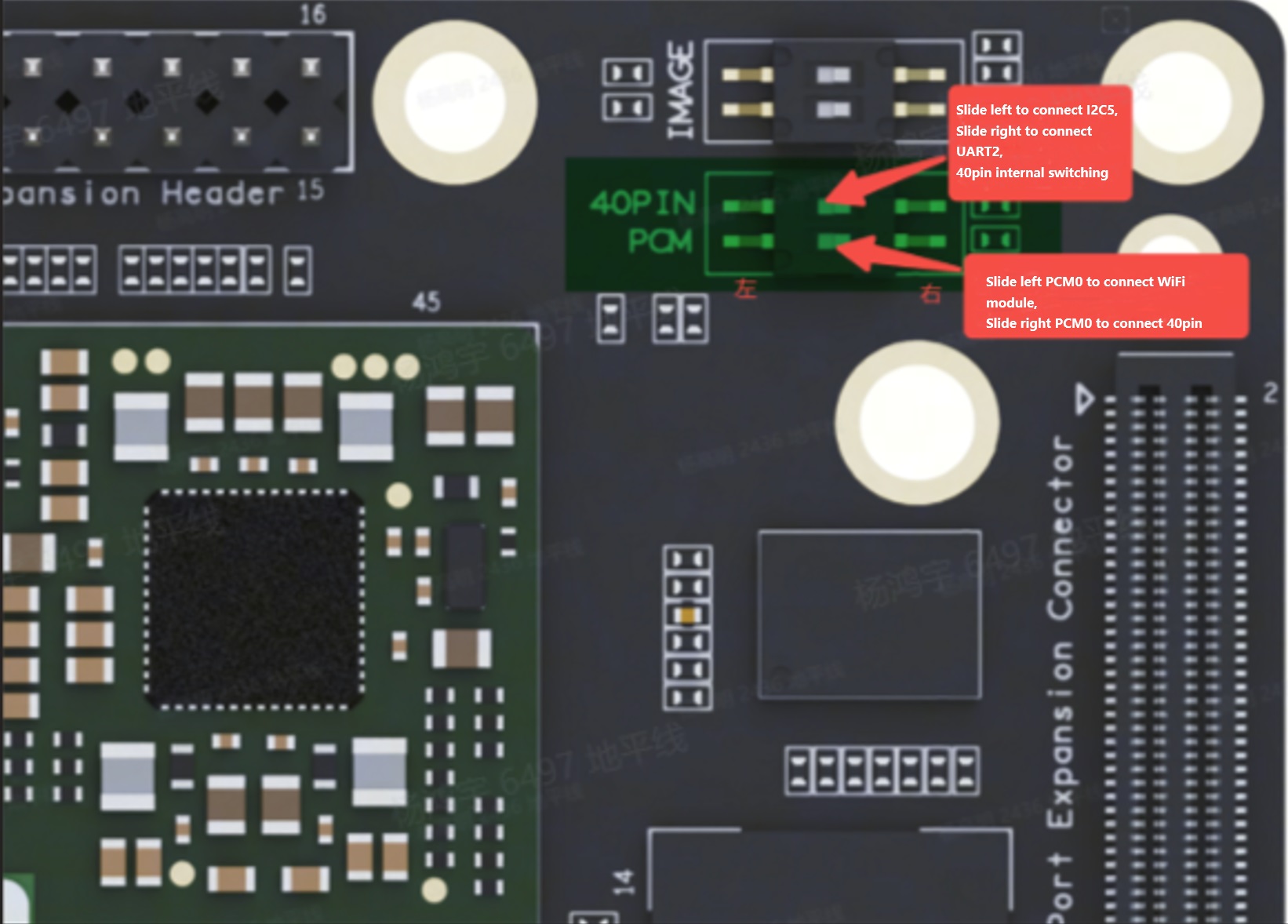
After toggling the DIP switch, you also need to modify the device tree file. The modification path and method are as follows:
/*kernel/arch/arm64/boot/dts/hobot/drobot-s100-soc.dtsi*/
uart2: uart@394C0000 {
power-domains = <&scmi_smc_pd PD_IDX_LSPERI_TOP>;
compatible = "snps,dw-apb-uart";
reg = <0x0 0x394C0000 0x0 0x10000>;
reg-shift = <2>;
reg-io-width = <4>;
interrupts = <GIC_SPI PERISYS_UART2_INTR PERISYS_UART2_INTR_TRIG_TYPE>;
clock-frequency = <200000000>;
pinctrl-names = "default";
pinctrl-0 = <&peri_uart2>;
status = "okay";
};
For pin definitions, please refer to Pin Configuration and Definitions.
Please refer to /app/40pin_samples/test_serial.py for detailed instructions on how to use the UART interface.
The pins mentioned below are provided for illustrative purposes only. Port values may differ across platforms; always verify against your actual hardware setup. Alternatively, you can directly use the code under the /app/40pin_samples/ directory, which has already been verified on the board.
Loopback Test
Connect TXD and RXD together physically, then run the test program to perform write and read operations. The expected result is that the received data should be identical to the transmitted data.
Hardware Connection
Directly connect TXD and RXD together using a jumper wire:

Test Procedure
- Run
python3 /app/40pin_samples/test_serial.py. - From the printed list of UART devices (note:
/dev/ttyS0is the system debug console; testing it is not recommended unless you fully understand its function), select the appropriate bus and chip select number as input options. For example:- On RDK X3, test
/dev/ttyS3 - On RDK X5, test
/dev/ttyS1 - On RDK Ultra, test
/dev/ttyS2 - On RDK S100, test
/dev/ttyS2
- On RDK X3, test
Press Enter to confirm your selection, then input the baud rate:
root@ubuntu:/app/40pin_samples# ./test_serial.py
List of enabled UART:
/dev/ttyS0 /dev/ttyS1 /dev/ttyS2 /dev/ttyS3
Please enter the UART device name to test: /dev/ttyS2
Please enter the baud rate (9600,19200,38400,57600,115200,921600): 921600
Serial<id=0x7f819dcac0, open=True>(port='/dev/ttyS3', baudrate=921600, bytesize=8, parity='N', stopbits=1, timeout=1, xonxoff=False, rtscts=False, dsrdtr=False)
- Once the program runs correctly, it will continuously print
Send: AA55andRecv: AA55:
Starting demo now! Press CTRL+C to exit
Send: AA55
Recv: AA55
Test Code
#!/usr/bin/env python3
import sys
import signal
import os
import time
# Import Python serial library
import serial
import serial.tools.list_ports
def signal_handler(signal, frame):
sys.exit(0)
def serialTest():
print("List of enabled UART:")
os.system('ls /dev/tty[a-zA-Z]*')
uart_dev = input("Please enter the UART device name to test: ")
baudrate = input("Please enter the baud rate (9600,19200,38400,57600,115200,921600): ")
try:
ser = serial.Serial(uart_dev, int(baudrate), timeout=1) # 1s timeout
except Exception as e:
print("Failed to open serial port!\n")
print(ser)
print("Starting demo now! Press CTRL+C to exit")
while True:
test_data = "AA55"
write_num = ser.write(test_data.encode('UTF-8'))
print("Send: ", test_data)
received_data = ser.read(write_num).decode('UTF-8')
print("Recv: ", received_data)
time.sleep(1)
ser.close()
return 0
if __name__ == '__main__':
signal.signal(signal.SIGINT, signal_handler)
if serialTest() != 0:
print("Serial test failed!")
else:
print("Serial test success!")