sample_gdc Usage Instructions
Function Overview
The sample_gdc directory contains example programs demonstrating how to use GDC. The main functionalities are as follows:
generate_custom_config.py: Generates calibration configuration parameters for GDC correction.generate_bin: Reads a local JSON configuration file and generates the correspondinggdc.binfile.gdc_static_valid: Reads a localgdc.binfile and an original YUV file, processes them through GDC, and saves the output as a YUV file.gdc_stress_test: Reads a localgdc.binfile and repeatedly feeds an original YUV file into GDC for performance stress testing.gdc_equisolid: Reads a local NV12 YUV image and performs panoramic correction using GDC.gdc_transformation: Reads a local JSON configuration file and applies 180-degree linear transformation, cylindrical transformation, equidistant transformation, and trapezoidal correction + distortion removal to the input image via GDC.
1-custom_config
Function Overview
This example demonstrates how to prepare input images using a custom transformation method and generate a calibration parameter file to guide GDC correction.
Code Location and Directory Structure
-
Code location:
/app/multimedia_samples/sample_gdc/1-custom_config -
Directory structure:
sample_gdc/
├── 1-custom_config
│ ├── Makefile
│ ├── chessboard
│ ├── chessboard.png
│ ├── custom_config.txt
│ └── generate_custom_config.py
Development and Usage Workflow
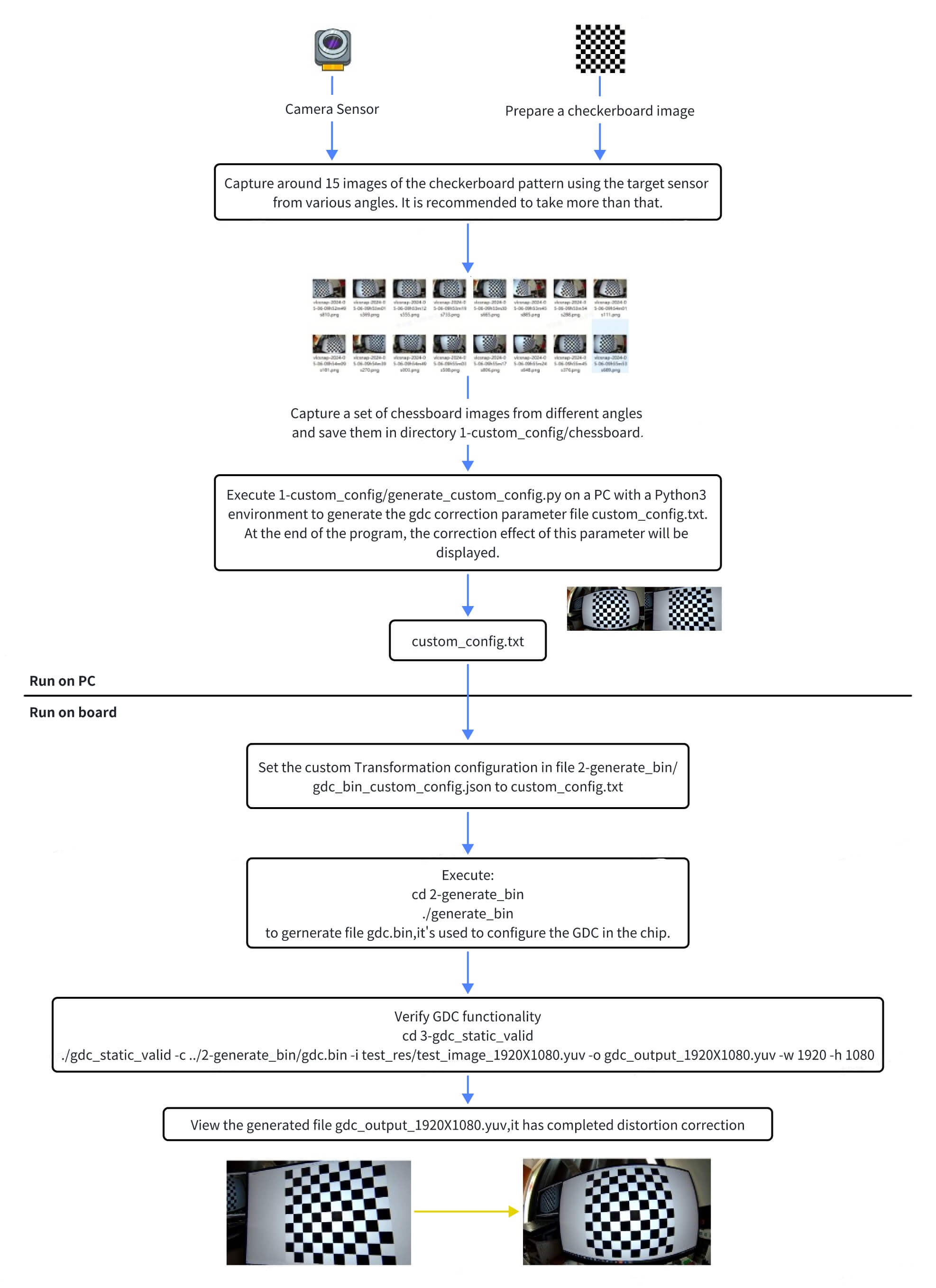
Use the generate_custom_config.py script on a PC to generate GDC calibration configuration parameters.
-
Prepare a chessboard image (
chessboard.png), either by printing it out or displaying it on a monitor. -
Capture approximately 15 chessboard images using the target camera sensor from various angles. It is recommended to capture more images for better results.
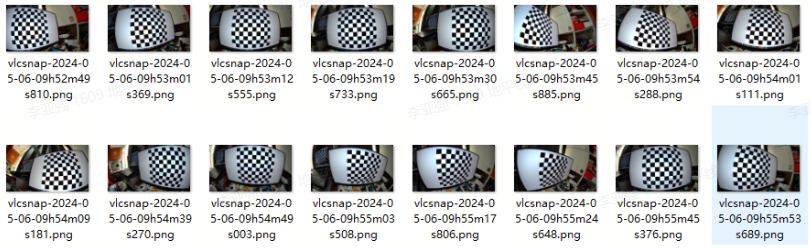
-
Use the captured chessboard images as input and run the following Python script (ensure Python 3 and the
opencv-pythonlibrary are installed) to generate the GDC calibration parameter file (custom_config.txt):# Enter /app/multimedia_samples/sample_gdc/1-custom_config directory
python3 ./generate_custom_config.pyNoteNote: When capturing chessboard images, maintain a greater distance from the board. If the chessboard occupies too large a portion of the image, the Python script may fail to recognize it.
Log output when running in a terminal:
No graphical environment detected. Skipping display of images.
Input images directory: ./chessboard
Test image file: ./chessboard/vlcsnap-2024-05-06-09h53m19s733.jpg
Output file: custom_config.txt
i: 0
i: 1
... omitted ...
i: 15
Intrinsic matrix (mtx):
[[784.57179685 0. 939.01168998]
[ 0. 784.35388599 554.71639175]
[ 0. 0. 1. ]]
Distortion coefficients (dist):
[[-3.16520533e-01 1.02422375e-01 -2.60692201e-04 7.23624256e-04
-1.44726239e-02]]
Rotation vectors (rvecs):
(array([[-0.07424795],
[ 0.17820099],
[-0.04684888]]), array([[0.44453246],
[0.01540531],
[0.03596364]]), array([[-0.38217217],
[-0.4097845 ],
[ 0.16419408]]), array([[-0.0713388 ],
[-0.04356189],
[ 0.00918689]]), array([[ 0.40326625],
[-0.65705694],
[ 0.07152059]]), array([[-0.28933582],
[ 0.07433653],
[ 0.09031559]]), array([[-0.1353966 ],
[-0.61689018],
[-0.06274773]]), array([[ 0.02193021],
[-0.52159079],
[ 0.08910704]]), array([[-0.10002557],
[-0.25580186],
[-0.08683701]]), array([[-0.37827059],
[-0.98115358],
[ 0.175653 ]]), array([[0.33652166],
[0.12869965],
[0.03961734]]), array([[ 0.40214666],
[-0.38128926],
[-0.0051477 ]]), array([[-0.04168182],
[ 0.0922567 ],
[-0.03109347]]))
Translation vectors (tvecs):
(array([[ -71.275847 ],
[-106.35748096],
[ 224.27593215]]), array([[ 3.80981104],
[-81.7694762 ],
[183.44645072]]), array([[ -81.59651772],
[-122.67796656],
[ 240.51602851]]), array([[ -86.84292041],
[-114.12437351],
[ 203.11264832]]), array([[-51.05204629],
[-57.97011932],
[168.23228488]]), array([[ -25.79903668],
[-139.06100345],
[ 248.06228137]]), array([[-193.45812779],
[-116.55450795],
[ 135.39187735]]), array([[ -91.12813213],
[-111.74470892],
[ 150.61397733]]), array([[ -89.4296275 ],
[-117.79736921],
[ 196.30732053]]), array([[-156.41212161],
[-146.02467216],
[ 191.13039641]]), array([[ -60.65720996],
[-111.66378957],
[ 191.3402483 ]]), array([[-56.56159122],
[-72.97166982],
[149.97470497]]), array([[ -60.28586566],
[-111.66429463],
[ 196.1187917 ]]))
New camera matrix (newcameramtx):
[[784.57179685 0. 939.01168998]
[ 0. 784.35388599 554.71639175]
[ 0. 0. 1. ]]
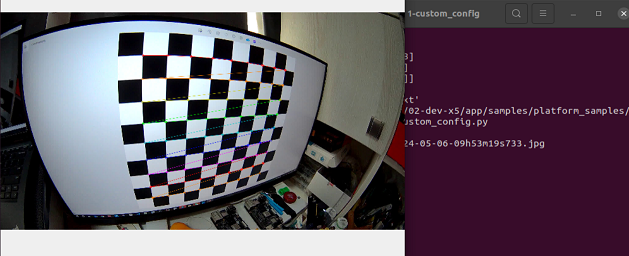
Validation of distortion correction
Saving mapx and mapy to 'custom_config.txt'
No graphical environment detected. The output image has been saved to 'custom_config.txt'.If run in a terminal within a graphical desktop environment, the calibration and correction effects will be displayed:

Command-line options for generate_custom_config.py:
usage: generate_custom_config.py [-h] [-i INPUT_IMAGES_DIR] [-t TEST_IMAGE]
[-o OUTPUT_FILE]
Gdc calibration and image undistortion.
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-i INPUT_IMAGES_DIR, --input_images_dir INPUT_IMAGES_DIR
Directory containing the chessboard images.
-t TEST_IMAGE, --test_image TEST_IMAGE
File path of the image to be undistorted.
-o OUTPUT_FILE, --output_file OUTPUT_FILE
File path for the output configuration.
2-generate_bin
Function Overview
This program reads a local gdc_bin_custom_config.json configuration file and generates the corresponding gdc.bin file.
Code Location and Directory Structure
-
Code location:
/app/multimedia_samples/sample_gdc/2-generate_bin -
Directory structure:
sample_gdc/
├── 2-generate_bin
│ ├── Makefile
│ ├── gdc_bin_custom_config.json
│ └── generate_bin.c
Compilation and Deployment
Compilation
- Enter the
sample_gdc/2-generate_bindirectory and runmaketo compile. - The compiled executable is
generate_bin, located in thesample_gdc/2-generate_bindirectory.
Program Deployment
After installing the hobot-multimedia-samples package and compiling, the executable for this sample is located on the board at: /app/multimedia_samples/sample_gdc/2-generate_bin.
Execution
How to Run the Program
Run ./generate_bin -h directly to display help information:
./generate_bin -h
genereate_bin [-c json_config_file] [-o output_file]
Program Argument Options Description
Options:
-
[-c json_config_file]: Specifies the JSON configuration file for GDC module (optional). Default:./gdc_bin_custom_config.json. -
[-o output_file]: Specifies the output path for the GDC bin file (optional). Default:./gdc.bin.
Execution Result
Run command:
# Enter /app/multimedia_samples/sample_gdc/2-generate_bin directory
./generate_bin
Execution log:
Gdc bin custom config: ./gdc_bin_custom_config.json
Generate gdc bin file: ./gdc.bin
gdc gen cfg_buf 0xffff82090010, size 10972
Generate bin file size:10972
3-gdc_static_valid
Function Overview
The gdc_static_valid program reads a local NV12 YUV image, sends both the gdc.bin configuration and the image to the GDC module for transformation processing, and finally saves the result as a local NV12-formatted YUV image.
Code Location and Directory Structure
-
Code location:
/app/multimedia_samples/sample_gdc/3-gdc_static_valid -
Directory structure:
sample_gdc/
├── 3-gdc_static_valid
│ ├── Makefile
│ ├── gdc_static_valid.c
│ └── test_res
│ ├── test_image_1920x1080.jpg
│ └── test_image_1920x1080.yuv
Compilation and Deployment
Compilation
- Enter the
sample_gdc/3-gdc_static_validdirectory and runmaketo compile. - The compiled output is
gdc_static_validlocated in thesample_gdc/3-gdc_static_validdirectory.
Program Deployment
After installing the hobot-multimedia-samples package and compiling, the executable for this sample resides on the board at: /app/multimedia_samples/sample_gdc/3-gdc_static_valid.
Execution
How to Run the Program
Running ./gdc_static_valid directly displays the help message:
Usage: gdc_static_valid [OPTIONS]
Options:
c, --config <gdc_bin_file> Specify the gdc configuration bin file.
i, --input <input_file> Specify the input image file.
o, --output <output_file> Specify the output image file.
w, --iw <input_width> Specify the width of the input image.
h, --ih <input_height> Specify the height of the input image.
x, --ow [output_width] Specify the width of the output image (optional).
y, --oh [output_height] Specify the height of the output image (optional).
f, --feedback Specify feedback mode
If --ow and --oh are not specified, they will default to the input width and height, respectively.
Program Argument Options Description
Option descriptions for gdc_static_valid:
c, --config: Specifies thegdc.binconfiguration file.i, --input: Specifies the input NV12 image.o, --output: Specifies the output NV12 image.w, --iw: Specifies the input image width (horizontal resolution).h, --ih: Specifies the input image height (vertical resolution).x, --ow: Specifies the output image width (horizontal resolution) (optional). Defaults to the same value as--iw.y, --oh: Specifies the output image height (vertical resolution) (optional). Defaults to the same value as--ih.
Execution Result
Run the following command to perform static image correction validation:
# Enter /app/multimedia_samples/sample_gdc/3-gdc_static_valid directory
./gdc_static_valid -c ../../vp_sensors/gdc_bin/imx219_gdc.bin -i test_res/test_image_1920x1080.yuv -o gdc_output_1920x1080.yuv -w 1920 -h 1080
Execution log:
GDC vnode work mode: vflow
config file: ../../vp_sensors/gdc_bin/imx219_gdc.bin
input image: test_res/test_image_1920x1080.yuv
output image: gdc_output_1920x1080.yuv
input:1920x1080
output:1920x1080
(read_yuvv_nv12_file):file read(test_res/test_image_1920x1080.yuv), y-size(2073600)
handle 34661 GDC dump yuv 1920x1080(stride:1920), buffer size: 2073600 + 1036800 frame id: 0, timestamp: 0
4-gdc_stress_test
Function Overview
The gdc_stress_test program reads a local NV12 YUV image, sends both the gdc.bin configuration and the image to the GDC module for transformation processing, and saves the result as a local NV12-formatted YUV image. It allows specifying the number of GDC processing iterations, records execution time, and calculates frames per second (FPS) and total processing time.
Code Location and Directory Structure
-
Code location:
/app/multimedia_samples/sample_gdc/4-gdc_stress_test -
Directory structure:
sample_gdc/
├── 4-gdc_stress_test
│ ├── Makefile
│ ��├── gdc_1920x1080.bin
│ ├── gdc_stress_test.c
│ ├── test.sh
│ └── test_res
│ ├── test_image_1920x1080.jpg
│ └── test_image_1920x1080.yuv
Compilation and Deployment
Compilation
- Enter the
sample_gdc/4-gdc_stress_testdirectory and runmaketo compile. - The compiled output is
gdc_stress_testlocated in thesample_gdc/4-gdc_stress_testdirectory.
Program Deployment
After installing the hobot-multimedia-samples package and compiling, the executable for this sample resides on the board at: /app/multimedia_samples/sample_gdc/4-gdc_stress_test.
Execution
How to Run the Program
Running ./gdc_stress_test directly displays the help message:
Usage: gdc_stress_test [OPTIONS]
Options:
c, --config <gdc_bin_file> Specify the gdc configuration bin file.
i, --input <input_file> Specify the input image file.
o, --output <output_file> Specify the output image file.
w, --iw <input_width> Specify the width of the input image.
h, --ih <input_height> Specify the height of the input image.
x, --ow [output_width] Specify the width of the output image (optional).
y, --oh [output_height] Specify the height of the output image (optional).
C, --Count [run count] Specify gdc sendframe and getframe count.
p, --p [process id] Specify id of process.
f, --feedback Specify feedback mode
If --ow and --oh are not specified, they will default to the input width and height, respectively.
Program Argument Options Description
Option descriptions for gdc_stress_test:
c, --config: Specifies thegdc.binconfiguration file.i, --input: Specifies the input NV12 image.o, --output: Specifies the output NV12 image.w, --iw: Specifies the input image width (horizontal resolution).h, --ih: Specifies the input image height (vertical resolution).x, --ow: Specifies the output image width (horizontal resolution) (optional). Defaults to the same value as--iw.y, --oh: Specifies the output image height (vertical resolution) (optional). Defaults to the same value as--ih.C, --Count: Specifies the number of times the image is sent to the GDC module for processing.p, --p: Specifies the process ID.f, --feedback: Enables feedback mode.
Execution Result
Run command:
# Enter /app/multimedia_samples/sample_gdc/4-gdc_stress_test directory
sh test.sh
Running log:
root@ubuntu:/app/multimedia_samples/sample_gdc/4-gdc_stress_test# GDC vnode work mode: vflow
GDC vnode work mode: vflow
GDC vnode work mode: vflow
config file: ./gdc_1920x1080.bin
config file: ./gdc_1920x1080.bin
config file: ./gdc_1920x1080.bin
input image: ./test_res/test_image_1920x1080.yuv
input image: ./test_res/test_image_1920x1080.yuv
input image: ./test_res/test_image_1920x1080.yuv
output image: ./gdc_output_1920x1080.yuv
output image: ./gdc_output_1920x1080.yuv
output image: ./gdc_output_1920x1080.yuv
input:1920x1080
input:1920x1080
input:1920x1080
output:1920x1080
output:1920x1080
output:1920x1080
(read_yuvv_nv12_file):file read(./test_res/test_image_1920x1080.yuv), y-size(2073600)
(read_yuvv_nv12_file):file read(./test_res/test_image_1920x1080.yuv), y-size(2073600)
(read_yuvv_nv12_file):file read(./test_res/test_image_1920x1080.yuv), y-size(2073600)
gdc temp fps [process3] = 150
gdc temp fps [process2] = 125
gdc temp fps [process1] = 125
gdc temp fps [process3] = 125
gdc temp fps [process2] = 116
gdc temp fps [process1] = 116
gdc temp fps [process3] = 116
gdc temp fps [process2] = 150
gdc temp fps [process1] = 150
gdc temp fps [process3] = 150
gdc temp fps [process2] = 137
.......
Gdc time consuming [process2]: 70
fps average gdc [process2] = 142
Gdc time consuming [process1]: 70
fps average gdc [process1] = 142
Gdc time consuming [process3]: 70
fps average gdc [process3] = 142
- The above printout is for illustration only; actual output depends on execution on the board.
- The stress-test script runs the stress-test program in the background continuously and will automatically stop after a period of time. To stop it earlier, use the command:
sudo killall gdc_stress_test
5-gdc_equisolid
Function Overview
The gdc_equisolid program reads a local NV12 YUV image, feeds it into the GDC module for panoramic correction processing, and finally saves the corrected result as a local NV12-formatted YUV image.
Code Location and Directory Structure
-
Code location:
/app/multimedia_samples/sample_gdc/5-gdc_equisolid -
Directory structure:
sample_gdc/
├── 5-gdc_equisolid
│ ├── Makefile
│ └── gdc_equisolid.c
Compilation and Deployment
Compilation
- Enter the
sample_gdc/5-gdc_equisoliddirectory and runmaketo compile. - The output binary is
gdc_equisolid, located in thesample_gdc/5-gdc_equisoliddirectory.
Program Deployment
After installing the hobot-multimedia-samples package and compiling, the executable for this sample resides on the board at: /app/multimedia_samples/sample_gdc/5-gdc_equisolid.
Execution
How to Run the Program
Running the program directly with ./gdc_equisolid -h displays the help information:
Usage: gdc_equisolid [OPTIONS]
Options:
i, --input <input_file> Specify the input image file.
o, --output <output_file> Specify the output image file.
w, --iw <input_width> Specify the width of the input image.
h, --ih <input_height> Specify the height of the input image.
f, --feedback Specify feedback mode
Program Parameter Description
Parameter options for gdc_equisolid:
i, --input: Specify the input NV12 image.o, --output: Specify the output NV12 image (optional).w, --iw: Specify the input image width (horizontal resolution).h, --ih: Specify the input image height (vertical resolution).f, --feedback: Enable feedback mode.
Execution Result
Run the following command to perform panoramic correction validation on a static image:
# Enter /app/multimedia_samples/sample_gdc/5-gdc_equisolid directory
./gdc_equisolid -i ../3-gdc_static_valid/test_res/test_image_1920x1080.yuv --iw 1920 --ih 1080
Running log:
GDC vnode work mode: vflow
input file: ../3-gdc_static_valid/test_res/test_image_1920x1080.yuv
output file: gdc_output_1920x1080.yuv
input:1920x1080
(read_yuvv_nv12_file):file read(../3-gdc_static_valid/test_res/test_image_1920x1080.yuv), y-size(2073600)
handle 34661 GDC dump yuv 1920x1080(stride:1920), buffer size: 2073600 + 1036800 frame id: 0, timestamp: 0
6-gdc_transformation
Function Overview
This gdc_transformation sample implements the GDC module to perform 180-degree linear transformation, cylindrical transformation, equidistant transformation, and keystone correction + dewarping on feedback-fed input images.
Software Architecture Description
The gdc_transformation program uses a feedback workflow: it reads the original YUV file and a JSON file generated by the GDC Tool from system storage as inputs to the GDC module. It relies on libgdcbin.so to compute GDC coordinate points and saves the transformed image as a local NV12-formatted YUV file.
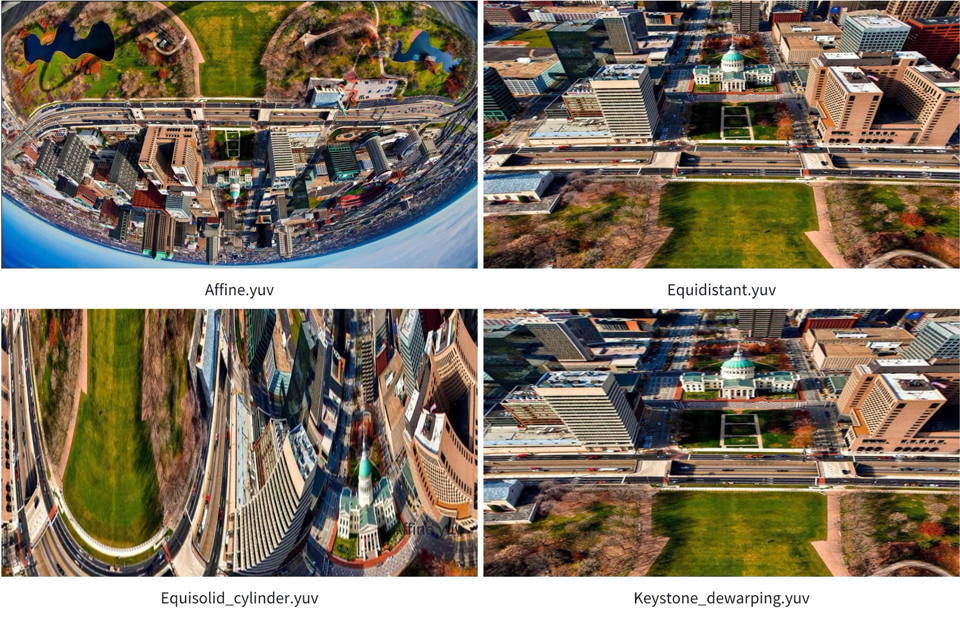
All JSON files generated by the GDC Tool are stored in the gdc_res directory. Currently, this directory contains four JSON files corresponding to the following transformation effects: Affine, Equisolid (cylinder), Equidistant, and Keystone + dewarping. gdc_transformation will generate four YUV output images based on these four JSON files.
Note: The number of JSON files in the gdc_res directory determines how many YUV images will be dumped.
Code Location and Directory Structure
-
Code location:
/app/multimedia_samples/sample_gdc/6-gdc_transformation -
Directory structure:
sample_gdc/
└── 6-gdc_transformation
├── Makefile
├── gdc_res
│ ├── Affine.json
│ ├── Equidistant.json
│ ├── Equisolid_cylinder.json
│ ├── Keystone_dewarping.json
│ └── test_building_1920x1080.yuv
└── gdc_transformation.c
The root directory contains the Makefile. The gdc_res directory holds resource files such as JSON files generated by the GDC Tool and YUV images. gdc_transformation.c is the main entry-point source file.
Compilation and Deployment
Compilation
- Enter the
sample_gdc/6-gdc_transformationdirectory and runmaketo compile. - The output binary is
gdc_transformation, located in thesample_gdc/6-gdc_transformationdirectory.
Program Deployment
After installing the hobot-multimedia-samples package and compiling, the executable for this sample resides on the board at: /app/multimedia_samples/sample_gdc/6-gdc_transformation.
Execution
How to Run the Program
Running the program directly with ./gdc_transformation displays the help information:
Usage: gdc_transformation [OPTIONS]
Options:
i, --input <input_file> Specify the input image file.
x, --ix <input_width> Specify the width of the input image.
y, --iy <input_height> Specify the height of the input image.
Program Parameter Description
Parameter options for gdc_transformation:
i, --input: Specify the input NV12 image.x, --ix: Specify the input image width (horizontal resolution).y, --iy: Specify the input image height (vertical resolution).
Execution Result
Run the following command to perform transformation validation on a static image:
# Enter /app/multimedia_samples/sample_gdc/6-gdc_transformation directory
./gdc_transformation -i gdc_res/test_building_1920x1080.yuv --ix 1920 --iy 1080
Running log:
# ./gdc_transformation -i gdc_res/test_building_1920x1080.yuv --ix 1920 --iy 1080
input file: gdc_res/test_building_1920x1080.yuv
input:1920x1080
(read_yuvv_nv12_file):file read(gdc_res/test_building_1920x1080.yuv), y-size(2073600)
gdc gen cfg_buf 0xaaab00d46460, size 5956
Dump image to file(Equidistant.yuv), size(2073600) + size1(1036800) succeeded
gdc gen cfg_buf 0xaaab00d868b0, size 7756
Dump image to file(Affine.yuv), size(2073600) + size1(1036800) succeeded
gdc gen cfg_buf 0xaaab00d868b0, size 5884
Dump image to file(Keystone_dewarping.yuv), size(2073600) + size1(1036800) succeeded
gdc gen cfg_buf 0xaaab00d868b0, size 8548
Dump image to file(Equisolid_cylinder.yuv), size(2073600) + size1(1036800) succeeded
Option parameter description for gdc_transformation:
#./gdc_transformation -h
Usage: gdc_transformation [OPTIONS]
Options:
i, --input <input_file> Specify the input image file.
x, --ix <input_width> Specify the width of the input image.
y, --iy <input_height> Specify the height of the input image.
Description of Running Results
The original image is shown below:
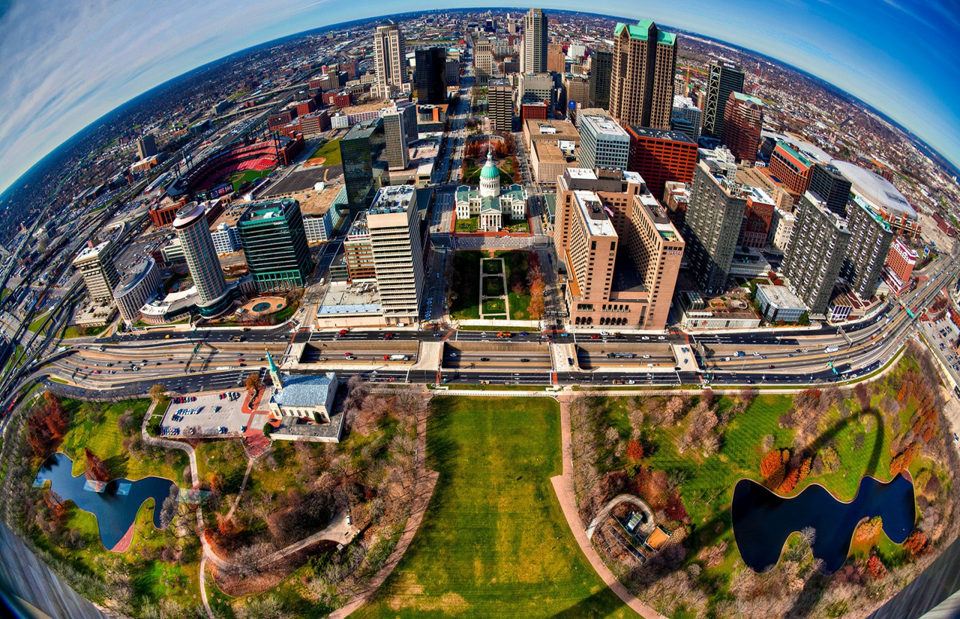

After applying transformations parsed from each JSON file, four processed YUV images in NV12 format are generated. The results are shown below:
