4.1.1 Model Zoo Overview
Product Introduction
This product is the model sample repository (Model Zoo) for the RDK series development boards, designed to provide developers with a rich variety of models that can be directly deployed on the boards.
The Model Zoo GitHub repository is here: https://github.com/D-Robotics/rdk_model_zoo
Through this repository, developers can access the following resources:
- Diverse D-Robotics Heterogeneous Models: The repository contains a variety of D-Robotics heterogeneous models that can be directly deployed on the boards and are suitable for various scenarios. These general-purpose models cover fields such as image classification, object detection, semantic segmentation, and natural language processing, provided as .bin files. All models are carefully selected and optimized for high performance.
- Detailed Usage Guides: Each model comes with a Jupyter Notebook, which includes a detailed model introduction, usage instructions, sample code, and comments to help developers get started quickly. For some models, we also provide performance evaluation reports and tuning suggestions to facilitate customization and optimization according to specific needs.
- Integrated Development Tools: We provide a set of Python interfaces,
bpu_infer_lib, for developers to quickly deploy models on RDK series development boards. By studying the Jupyter Notebooks provided with each model, including data preprocessing scripts and inference methods, developers can quickly master the use of this interface, greatly simplifying the model development and deployment process.
Environment Setup
First, prepare the corresponding RDK development board according to your branch, and visit the D-Robotics official website to complete hardware preparation, driver installation, software download, and image flashing. For X3 and X5 images, please select version 3.0.0 or above.
After completing hardware connection and network configuration, use MobaXTerm to remotely log in to the development board. Configure the network connection for the board.
Install the required Python libraries using pip:
- bpu_infer_lib
For RDK X5:
pip install bpu_infer_lib_x5 -i http://sdk.d-robotics.cc:8080/simple/ --trusted-host sdk.d-robotics.cc
For RDK X3:
pip install bpu_infer_lib_x3 -i http://sdk.d-robotics.cc:8080/simple/ --trusted-host sdk.d-robotics.cc
- jupyterlab
pip install jupyterlab
Then, use the following command to clone the Model Zoo repository:
git clone https://github.com/D-Robotics/rdk_model_zoo
Note: The default branch after cloning is the RDK X5 branch. If you are using another RDK series development board, please use the git checkout command to switch branches. For example, to switch to the RDK X3 branch, run:
git checkout rdk_x3
After cloning, enter the Model Zoo directory:
cd rdk_model_zoo
Then start Jupyter Lab with the following command (replace the IP address with the actual IP used to log in to the board):
jupyter lab --allow-root --ip 10.112.148.68
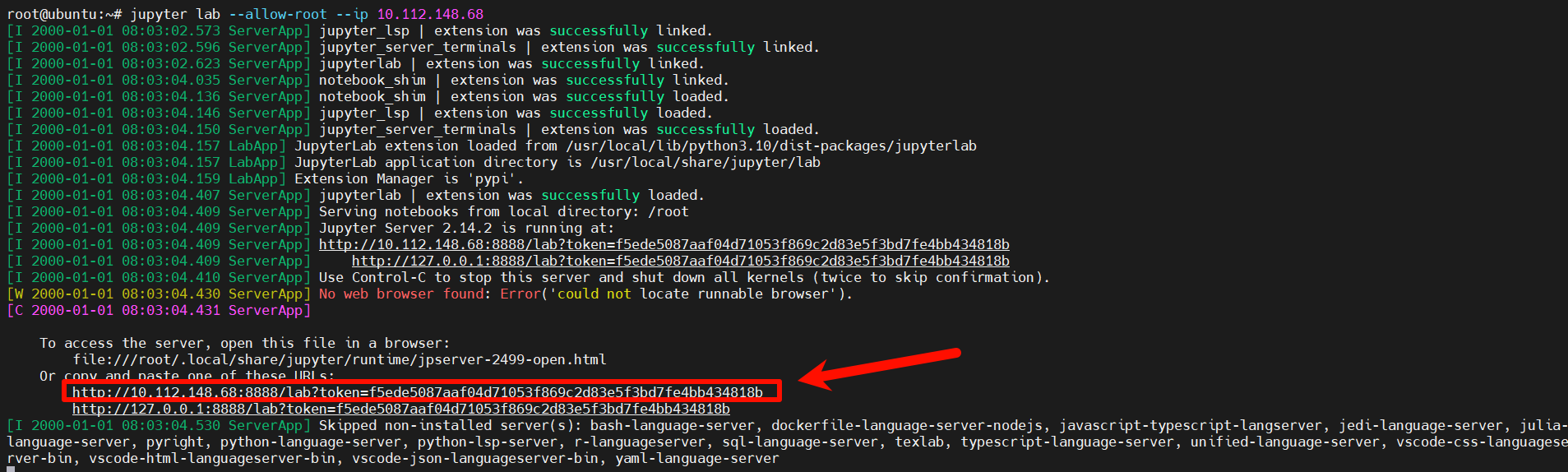
After running the command, you will see the above log. Hold Ctrl and left-click the link shown in the image to enter Jupyter Lab (as shown below). Double-click demos to select and experience models in the RDK Model Zoo.
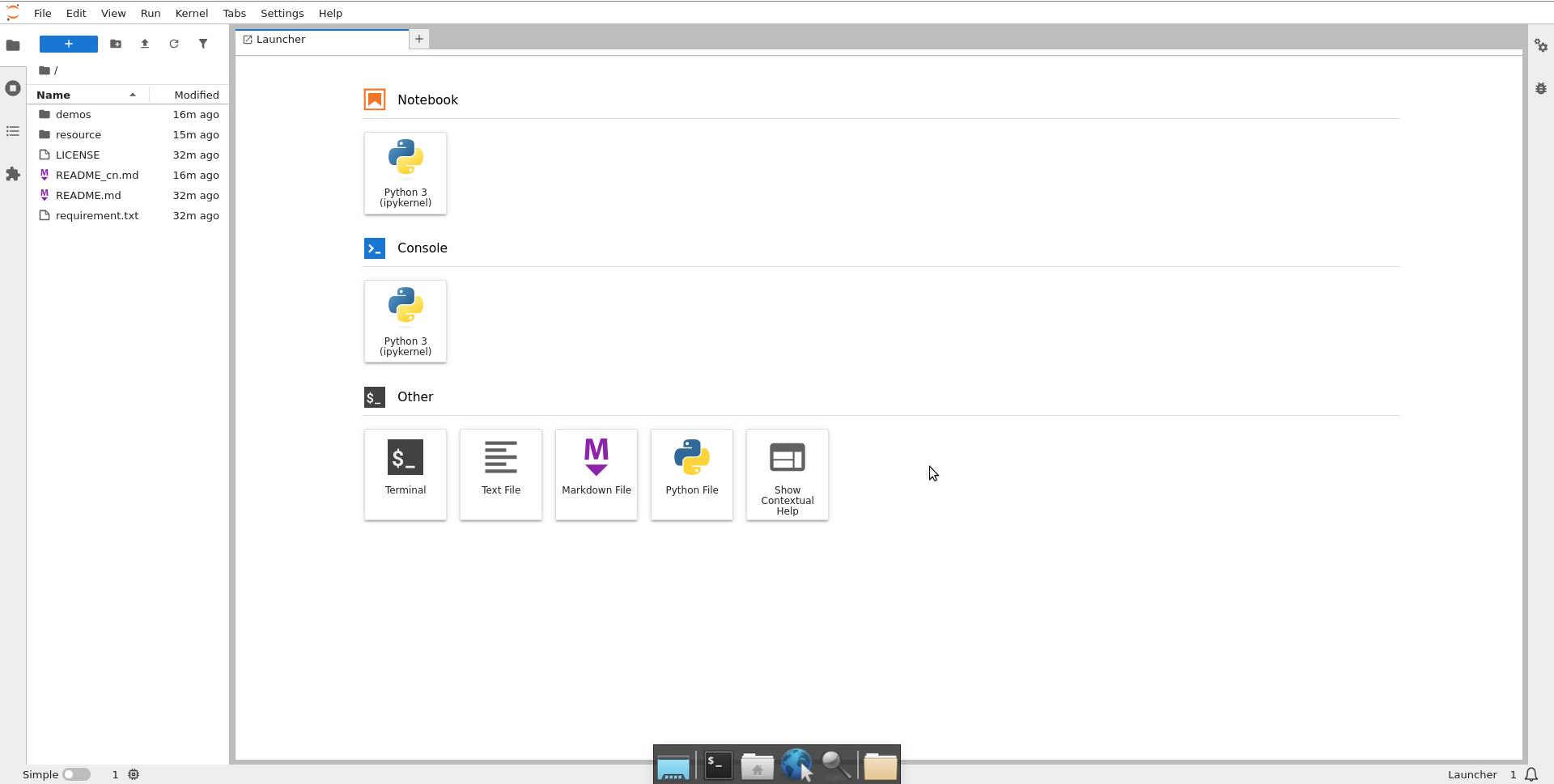
User Guide
After selecting a model's notebook in Jupyter Lab, you will see an interface similar to the following:
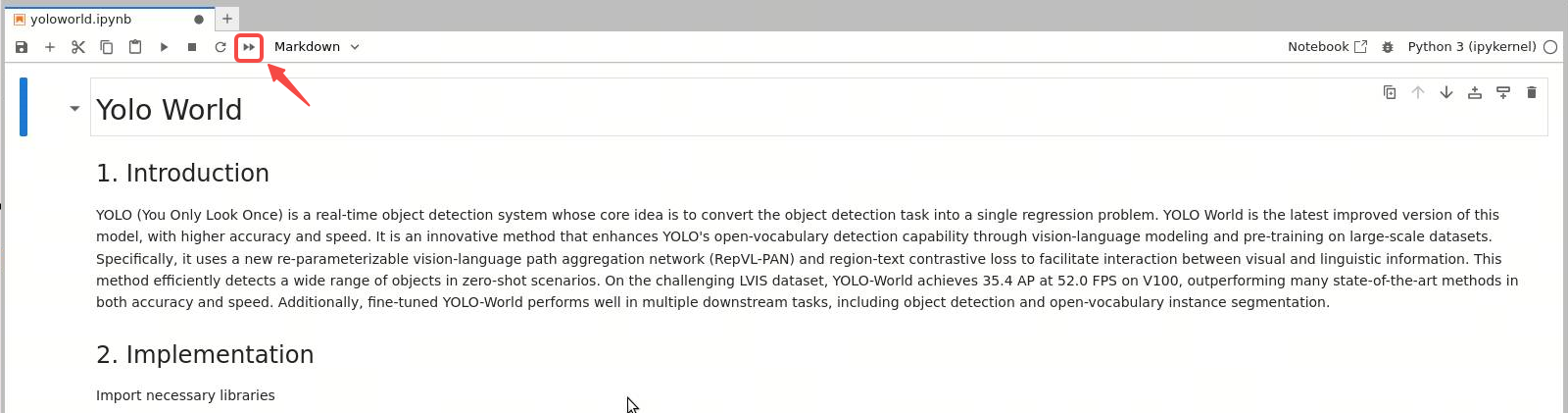
Taking the YOLO World model as an example, simply click the double triangle button shown above to run all cells. Scroll down to see the results:
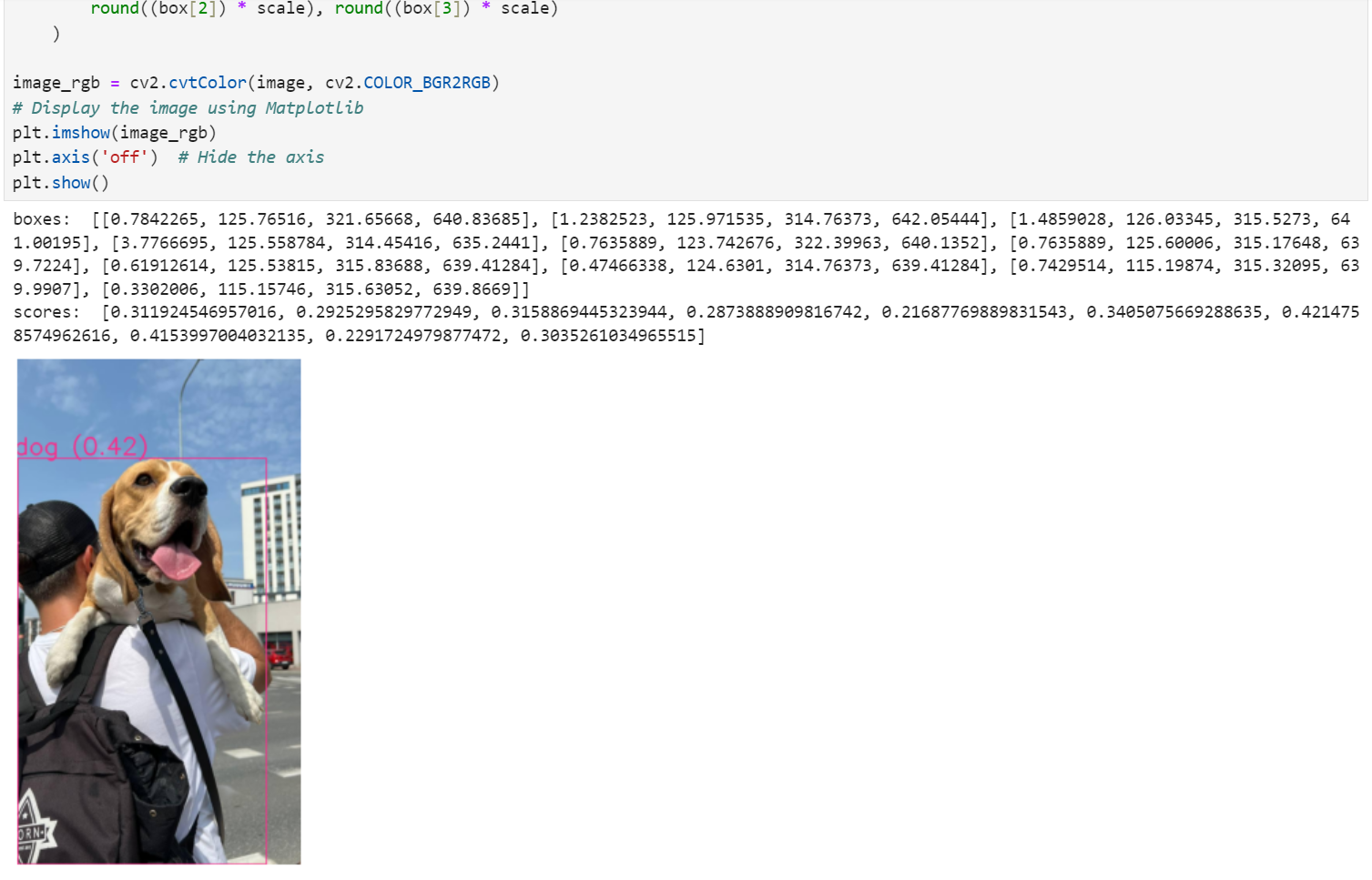
You can also run cells one by one by pressing Shift + Enter to execute the current cell and move to the next.